Final ID: Su3121
Impact of Percutaneous Mitral Valve Repair on Atrial Fibrillation Burden in Patients with Mitral Regurgitation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Transcatheter Edge to Edge Repair (TEER) of the mitral valve is offered to severely symptomatic patients with mitral regurgitation (MR) and high or prohibitive surgical risk. Chronic MR promotes atrial dilation and electrical remodelling, raising the risk of atrial fibrillation (AF). However, it remains unclear whether correcting MR via TEER reduces AF burden in patients who already have AF.
Research Question: What is the effect of percutaneous repair of MR on AF burden and characteristics one year after the procedure in patients with AF undergoing TEER?
Methods: We performed a retrospective single-center study where 73 patients were identified who had a diagnosis of AF and underwent TEER for MR between January 2021 and December 2023. The AF characteristics and burden are identified from chart review and reviewing EKG, Holter monitors, loop recorders, or already implanted device interrogations. A descriptive and comparative analysis of AF characteristics pre- and 1 year post-procedure is then performed.
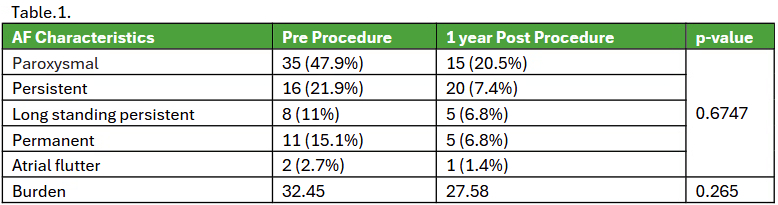
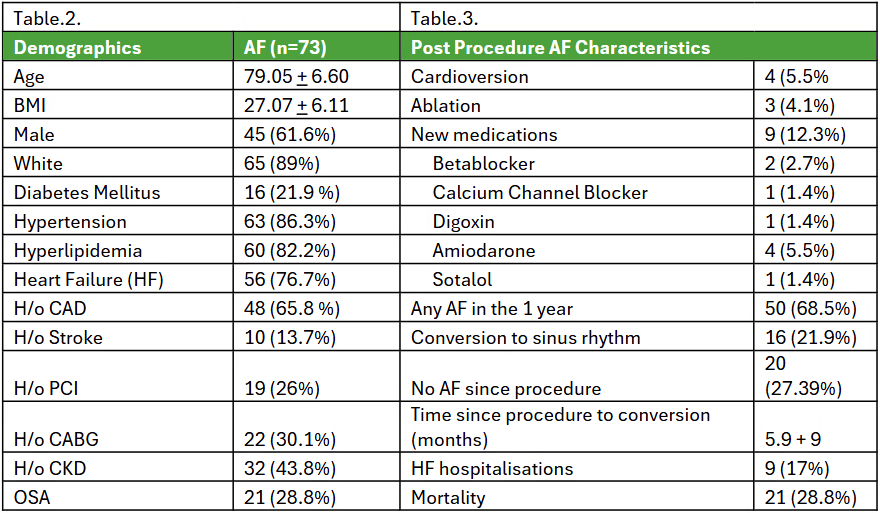
Result: The Mean age of this cohort was 79 + 6.6 years, with a 61% male and 89% white population. About 28.8% and 15% of patients had a pre-TEER history of cardioversion and ablation. Post procedure 68% (n=50) still had AF at least once during follow-up. A total of 20 patients had no AF noted since the procedure, corresponding to a 27.4 % relative risk reduction in AF persistence and an NNT of 4. About 22% of patients were noted to convert to sinus rhythm in 5.9 + 9 months and maintain it through the first year. During the follow-up, 5.5% and 4.1% underwent repeat cardioversion and ablation, respectively. New rhythm control agents were started in 6.8% of the total population. A total of 21 patients had quantified AF burden documented before and after the procedure. The burden numerically dropped from 32.45% to 27.58%, with a p=0.265.
Conclusion: Our study indicates a possible numerical decrease in burden and shift in AF subtype distribution, which is comparable to the results of a prior study. This was not statistically significant given small sample size, retrospective nature. Although TEER alone would not reliably eliminate AF, it achieved a 27.4 % relative reduction in AF persistence (NNT = 4), suggesting a clinically meaningful benefit in reducing AF burden and promoting sinus rhythm. Prospective studies with larger cohorts and systematic rhythm monitoring are needed to clarify the true impact of MR correction on AF dynamics.
Research Question: What is the effect of percutaneous repair of MR on AF burden and characteristics one year after the procedure in patients with AF undergoing TEER?
Methods: We performed a retrospective single-center study where 73 patients were identified who had a diagnosis of AF and underwent TEER for MR between January 2021 and December 2023. The AF characteristics and burden are identified from chart review and reviewing EKG, Holter monitors, loop recorders, or already implanted device interrogations. A descriptive and comparative analysis of AF characteristics pre- and 1 year post-procedure is then performed.
Result: The Mean age of this cohort was 79 + 6.6 years, with a 61% male and 89% white population. About 28.8% and 15% of patients had a pre-TEER history of cardioversion and ablation. Post procedure 68% (n=50) still had AF at least once during follow-up. A total of 20 patients had no AF noted since the procedure, corresponding to a 27.4 % relative risk reduction in AF persistence and an NNT of 4. About 22% of patients were noted to convert to sinus rhythm in 5.9 + 9 months and maintain it through the first year. During the follow-up, 5.5% and 4.1% underwent repeat cardioversion and ablation, respectively. New rhythm control agents were started in 6.8% of the total population. A total of 21 patients had quantified AF burden documented before and after the procedure. The burden numerically dropped from 32.45% to 27.58%, with a p=0.265.
Conclusion: Our study indicates a possible numerical decrease in burden and shift in AF subtype distribution, which is comparable to the results of a prior study. This was not statistically significant given small sample size, retrospective nature. Although TEER alone would not reliably eliminate AF, it achieved a 27.4 % relative reduction in AF persistence (NNT = 4), suggesting a clinically meaningful benefit in reducing AF burden and promoting sinus rhythm. Prospective studies with larger cohorts and systematic rhythm monitoring are needed to clarify the true impact of MR correction on AF dynamics.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Fat Chance: Paradoxical Embolic Stroke from Lipomatous Hypertrophy of the Interatrial Septum
Kalathoor Abraham
Association of renal function with mortality and heart failure hospitalization rates after Transcatheter Mitral Valve Edge to Edge RepairAbuzeid Wael, Shuvy Mony, Cantor Warren, Mehta Shamir, Fam Neil, Abdel-qadir Husam, Sacoransky Ethan, Czarnecki Andrew, Ke Danny Yu Jia, Teng Carolyn, Dave Prasham, Osten Mark, Zile Brigita, Wang Xuesong