Final ID: Sa2049
Cardiovascular and Rhythm Benefits of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Obese Patients: A Real-World Multicenter Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Obesity is a well-established risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including atrial fibrillation (AF) and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) may reduce AF burden and adverse cardiac outcomes through weight loss and metabolic improvements.
Objective:
To assess whether GLP-1 RA use is associated with reduced incidence of atrial fibrillation and other adverse outcomes among obese patients (BMI ≥35 kg/m2).
Methods:
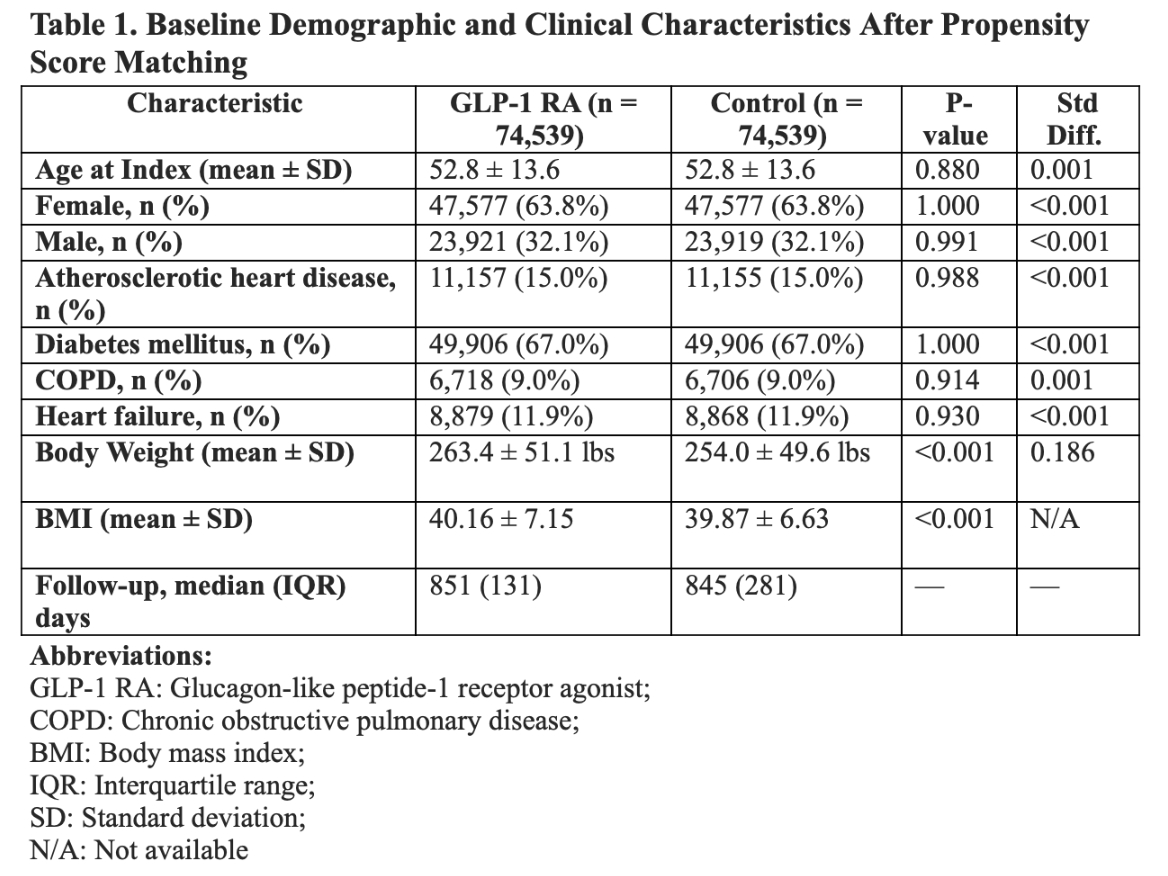
A retrospective cohort study was conducted using the TriNetX global federated health research network, encompassing 103 healthcare organizations. Adults with BMI ≥35 kg/m2 between October 1, 2022 and December 31, 2022 were identified. Patients prescribed GLP-1 RAs (n = 74,539) were compared to propensity score-matched controls not using GLP-1 RAs (n = 74,539). Outcomes included atrial fibrillation (ICD-10 I48), all-cause mortality, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), and changes in BMI. Analyses included risk ratios, risk differences, odds ratios, and Kaplan-Meier survival statistics.
Results:
GLP-1 RA use was associated with lower incidence of AF (8.4% vs 8.9%; risk difference -0.4%, 95% CI [-0.7%, -0.1%]; risk ratio 0.95, 95% CI [0.92–0.98]; p=0.003) and reduced all-cause mortality (1.7% vs 2.6%; risk difference -0.9%, 95% CI [-1.0%, -0.7%]; risk ratio 0.67, 95% CI [0.62–0.72]; p<0.001). MACE risk was also lower in the GLP-1 RA group (6.8% vs 7.8%; risk difference -1.1%, 95% CI [-1.3%, -0.8%]; risk ratio 0.87, 95% CI [0.84–0.90]; p<0.001). Mean BMI at follow-up was slightly higher in the GLP-1 RA group (40.16 vs 39.87 kg/m2; p<0.001). Kaplan-Meier analysis confirmed significant reductions in AF and mortality risk (log-rank p<0.001 for both).
Conclusions:
Among obese patients, GLP-1 RA use was associated with a modest reduction in atrial fibrillation incidence, lower rates of major adverse cardiovascular events, and reduced all-cause mortality compared to matched controls. These findings support the potential cardioprotective effects of GLP-1 RAs in high-risk obese populations.
Obesity is a well-established risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including atrial fibrillation (AF) and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) may reduce AF burden and adverse cardiac outcomes through weight loss and metabolic improvements.
Objective:
To assess whether GLP-1 RA use is associated with reduced incidence of atrial fibrillation and other adverse outcomes among obese patients (BMI ≥35 kg/m2).
Methods:
A retrospective cohort study was conducted using the TriNetX global federated health research network, encompassing 103 healthcare organizations. Adults with BMI ≥35 kg/m2 between October 1, 2022 and December 31, 2022 were identified. Patients prescribed GLP-1 RAs (n = 74,539) were compared to propensity score-matched controls not using GLP-1 RAs (n = 74,539). Outcomes included atrial fibrillation (ICD-10 I48), all-cause mortality, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), and changes in BMI. Analyses included risk ratios, risk differences, odds ratios, and Kaplan-Meier survival statistics.
Results:
GLP-1 RA use was associated with lower incidence of AF (8.4% vs 8.9%; risk difference -0.4%, 95% CI [-0.7%, -0.1%]; risk ratio 0.95, 95% CI [0.92–0.98]; p=0.003) and reduced all-cause mortality (1.7% vs 2.6%; risk difference -0.9%, 95% CI [-1.0%, -0.7%]; risk ratio 0.67, 95% CI [0.62–0.72]; p<0.001). MACE risk was also lower in the GLP-1 RA group (6.8% vs 7.8%; risk difference -1.1%, 95% CI [-1.3%, -0.8%]; risk ratio 0.87, 95% CI [0.84–0.90]; p<0.001). Mean BMI at follow-up was slightly higher in the GLP-1 RA group (40.16 vs 39.87 kg/m2; p<0.001). Kaplan-Meier analysis confirmed significant reductions in AF and mortality risk (log-rank p<0.001 for both).
Conclusions:
Among obese patients, GLP-1 RA use was associated with a modest reduction in atrial fibrillation incidence, lower rates of major adverse cardiovascular events, and reduced all-cause mortality compared to matched controls. These findings support the potential cardioprotective effects of GLP-1 RAs in high-risk obese populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acculturation and Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome: a Study of Immigrant Adults From the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Chakrabarti Amit, Le Austin, Elfassy Tali, Yang Eugene
Effect of Caloric Restriction on Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Health in Young Adults: Insights from the CALERIE TrialChang Ryan, Claggett Brian, Redman Leanne, Ravussin Eric, Apovian Caroline, Ostrominski John