Final ID: MP1868
Two-Hit Model of JAK1–STAT1 Immune Amplification by Clonal Hematopoiesis in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated Myocarditis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) affects over 10% of older adults and is enriched in cancer patients, where it independently predicts cardiovascular mortality. Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy, though life-extending, can trigger fulminant myocarditis—a complication with up to 50% mortality. We have shown that CHIP more than doubles ICI-myocarditis risk, yet the mechanisms remain unresolved.
Hypothesis:
We propose a novel two-hit model in which ICI therapy initiates inflammatory priming (Hit 1), while CHIP acts as a second hit, amplifying JAK1–STAT1-mediated immune activation that culminates in myocardial infiltration, cytokine storm, and fibrosis.
Methods:
We performed single-cell RNA sequencing on PBMCs from six ICI-myocarditis patients—three CHIP-positive (TET2/DNMT3A mutations) and three CHIP-negative. Data were processed using Seurat (Louvain clustering, CCA integration), annotated via ScType, and subjected to pathway enrichment with AUCell and VISION. Pathways evaluated included JAK–STAT, interferon, TNF, and NF-κB signaling axes.
Results:
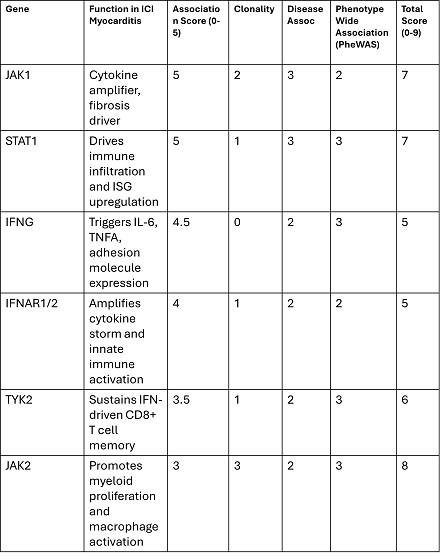
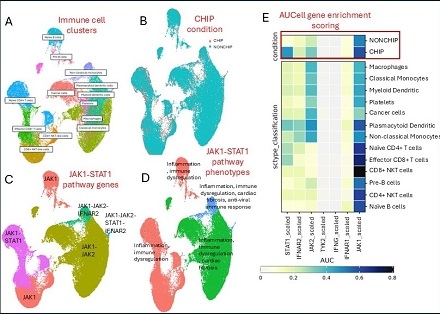
CHIP+ patients showed significant upregulation of pro-inflammatory and fibrotic gene programs across myeloid and lymphoid cells, including JAK1, STAT1, IFNG, TYK2, and JAK2 (Figure 1). AUCell enrichment (AUC > 0.75, p < 0.01) highlighted activation of JAK1–STAT1 and chemokine pathways in monocytes and dendritic cells, accompanied by elevated expression of fibrosis-linked genes (e.g., COL1A1, FN1). CHIP+ immune clusters also exhibited NF-κB, IL17, and MAPK pathway amplification (Figure 2). A gene-level association matrix incorporating clonality, disease relevance, and PheWAS links (Table 1) prioritized JAK1, STAT1, and JAK2 (scores ≥7/9) as key transcriptional amplifiers of immune injury, with STAT1 acting as the central effector and JAK2 contributing CHIP-specific clonal expansion and IL-6–driven myeloid skewing.
Conclusion:
Our findings support a two-hit immune model in ICI myocarditis, in which CHIP amplifies ICI-induced immune signaling through a JAK1–STAT1–centered axis. This synergistic mechanism promotes pro-inflammatory gene expression and fibrotic remodeling, particularly within monocytes and dendritic cells. Our CHIP-enhanced gene scoring framework may enable risk stratification and therapeutic targeting in cardio-oncology. Future directions include pseudotime modeling of CHIP clone trajectories, integration with cardiac MRI phenotypes, and multi-center validation.
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) affects over 10% of older adults and is enriched in cancer patients, where it independently predicts cardiovascular mortality. Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy, though life-extending, can trigger fulminant myocarditis—a complication with up to 50% mortality. We have shown that CHIP more than doubles ICI-myocarditis risk, yet the mechanisms remain unresolved.
Hypothesis:
We propose a novel two-hit model in which ICI therapy initiates inflammatory priming (Hit 1), while CHIP acts as a second hit, amplifying JAK1–STAT1-mediated immune activation that culminates in myocardial infiltration, cytokine storm, and fibrosis.
Methods:
We performed single-cell RNA sequencing on PBMCs from six ICI-myocarditis patients—three CHIP-positive (TET2/DNMT3A mutations) and three CHIP-negative. Data were processed using Seurat (Louvain clustering, CCA integration), annotated via ScType, and subjected to pathway enrichment with AUCell and VISION. Pathways evaluated included JAK–STAT, interferon, TNF, and NF-κB signaling axes.
Results:
CHIP+ patients showed significant upregulation of pro-inflammatory and fibrotic gene programs across myeloid and lymphoid cells, including JAK1, STAT1, IFNG, TYK2, and JAK2 (Figure 1). AUCell enrichment (AUC > 0.75, p < 0.01) highlighted activation of JAK1–STAT1 and chemokine pathways in monocytes and dendritic cells, accompanied by elevated expression of fibrosis-linked genes (e.g., COL1A1, FN1). CHIP+ immune clusters also exhibited NF-κB, IL17, and MAPK pathway amplification (Figure 2). A gene-level association matrix incorporating clonality, disease relevance, and PheWAS links (Table 1) prioritized JAK1, STAT1, and JAK2 (scores ≥7/9) as key transcriptional amplifiers of immune injury, with STAT1 acting as the central effector and JAK2 contributing CHIP-specific clonal expansion and IL-6–driven myeloid skewing.
Conclusion:
Our findings support a two-hit immune model in ICI myocarditis, in which CHIP amplifies ICI-induced immune signaling through a JAK1–STAT1–centered axis. This synergistic mechanism promotes pro-inflammatory gene expression and fibrotic remodeling, particularly within monocytes and dendritic cells. Our CHIP-enhanced gene scoring framework may enable risk stratification and therapeutic targeting in cardio-oncology. Future directions include pseudotime modeling of CHIP clone trajectories, integration with cardiac MRI phenotypes, and multi-center validation.
More abstracts on this topic:
Analysis of First Morning Urine Transcriptomes in Normotensive and Hypertensive Patients Identify Upregulated Inflammatory and Signaling Pathways Associated with Hypertension
Umanath Kausik, Ortiz Pablo, Sohaney Ryann, Atchison Douglas, Abraham Emmy, Meng Ze, She Ruicong, Adrianto Indra, Levin Albert, Wu Andrew
Aging Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction is Mediated by Noncoding RNAsChakraborty Sankalpa, Dickerson Bryce, Bounds Curren, Lemus Sophia, Hickman Caleb, Rajagopalan Viswanathan