Final ID: MP701
SGLT-2 inhibitors in pediatric heart failure, congenital heart disease and adults with congenital heart disease – a systematic review
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
SGLT-2 inhibitors, initially intended to treat diabetes, have had efficacy in adult trials to reduce mortality and morbidity with heart failure (HF). This mediations were recently added to GDMT guidelines for adults with HF in 2022. FDA has approved SGLT 2 inhibitors in children aged 10 years and older with type 2 diabetes. In pediatric congenital heart disease (CHD) patients with HF, there is a scarcity of data for the safety and efficacy of SGLT-2 inhibitors, as well as adults with CHD (ACHD) who have developed HF. The purpose of this systematic review is to understand if SGLT-2 inhibitors have the appropriate safety, tolerability, and efficacy in these specific patient populations.
Methods:
The articles selected for this review were case series, case-control studies, prospective & retrospective cohort reviews, and randomized controlled trials. Articles that were selected had study populations of either pediatric patients (ages 0-18) in heart failure and/or congenital heart disease, or adult patients, older than 18 years with congenital heart disease (ACHD). The articles were searched in all the major search engines, PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and the Cochrane Library using designated key words.
Results:
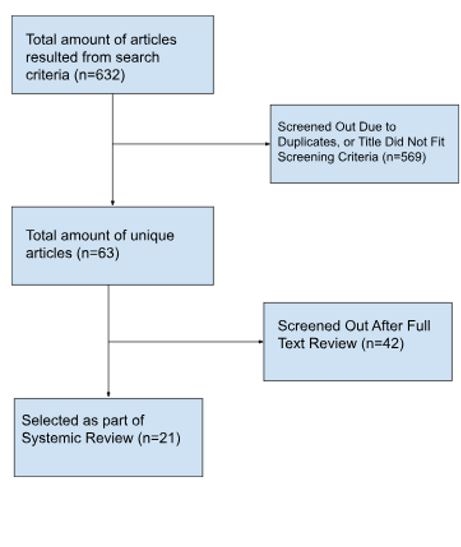
A total of 632 articles were found from databases. From this initial number, 21 specific articles fit the eligibility criteria and were included in the systematic review from 2022-2024. In total, SGLT2 inhibitors was used in 157 pediatric and 433 adult patients with CHD based on published literature.
30% (n=47) of pediatric patients had side effects (SE) related to SGLT-2i, whereas 6% (n=26) of adults in studies had the side effects. The most common documented side effects were glycosuria, UTI’s, and abdominal pain. None of the patient developed DKA or hypoglycemia. No deaths were reported and no significant changes were seen in renal funtion and GFR.
Efficacy data is available in only 48 patients so far and 29 patients had significant symptomatic improvement, 3 patients had significant improvement in systemic ventricular ejection fraction, and 18 had significant drop in BNP levels.
Conclusion:
This is the first systematic review of SGLT2 inhibitors in pediatric patients with heart failure and adults with congenital heart disease. SGLT-2 inhibitors appear to be safe, and efficacious so far with no significant side effect profile in pediatric patients with CHD associated heart failure and adult patients with ACHD.
SGLT-2 inhibitors, initially intended to treat diabetes, have had efficacy in adult trials to reduce mortality and morbidity with heart failure (HF). This mediations were recently added to GDMT guidelines for adults with HF in 2022. FDA has approved SGLT 2 inhibitors in children aged 10 years and older with type 2 diabetes. In pediatric congenital heart disease (CHD) patients with HF, there is a scarcity of data for the safety and efficacy of SGLT-2 inhibitors, as well as adults with CHD (ACHD) who have developed HF. The purpose of this systematic review is to understand if SGLT-2 inhibitors have the appropriate safety, tolerability, and efficacy in these specific patient populations.
Methods:
The articles selected for this review were case series, case-control studies, prospective & retrospective cohort reviews, and randomized controlled trials. Articles that were selected had study populations of either pediatric patients (ages 0-18) in heart failure and/or congenital heart disease, or adult patients, older than 18 years with congenital heart disease (ACHD). The articles were searched in all the major search engines, PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and the Cochrane Library using designated key words.
Results:
A total of 632 articles were found from databases. From this initial number, 21 specific articles fit the eligibility criteria and were included in the systematic review from 2022-2024. In total, SGLT2 inhibitors was used in 157 pediatric and 433 adult patients with CHD based on published literature.
30% (n=47) of pediatric patients had side effects (SE) related to SGLT-2i, whereas 6% (n=26) of adults in studies had the side effects. The most common documented side effects were glycosuria, UTI’s, and abdominal pain. None of the patient developed DKA or hypoglycemia. No deaths were reported and no significant changes were seen in renal funtion and GFR.
Efficacy data is available in only 48 patients so far and 29 patients had significant symptomatic improvement, 3 patients had significant improvement in systemic ventricular ejection fraction, and 18 had significant drop in BNP levels.
Conclusion:
This is the first systematic review of SGLT2 inhibitors in pediatric patients with heart failure and adults with congenital heart disease. SGLT-2 inhibitors appear to be safe, and efficacious so far with no significant side effect profile in pediatric patients with CHD associated heart failure and adult patients with ACHD.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acceptability and Gain of Knowledge of Community Educational Tools About Rheumatic Heart Disease Integrated With Screening In Low-Income Settings
Abrams Jessica, Nunes Maria, Diniz Marina, Fraga Lucas, Paula Luiza, Coelho Cecilia, Tacuri Chavez Luz Marina, Lemos Larissa, Correia Julliane, Ribeiro Antonio, Nascimento Bruno, Sable Craig, Spaziani Alison, Zuhlke Liesl, Cardoso Clareci, Vinhal Wanessa, Ribeiro Isabely, Oliveira Kaciane, Amaral Ingred Beatriz
A Case Presentation of Severe Left Ventricular Dysfunction from Focal Myocarditis due to Immune Checkpoint InhibitorPatel Romil, Hussain Kifah, Gordon Robert