Final ID: 4368865
Ly6C-Targeted LNP Delivery of CAR-ABCA1 mRNA Reprograms Macrophages for Enhanced Efferocytosis and Cholesterol Efflux in Atherosclerosis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Atherosclerosis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by lipid accumulation and defective clearance of apoptotic cells in plaques. Traditional LDL-C-lowering therapies such as statins show limited efficacy, as they fail to correct underlying metabolic imbalances. These imbalances cause anti-inflammatory macrophages to become lipid-laden foam cells following efferocytosis, ultimately exacerbating plaque progression.
Research Questions:
1. How can monocyte/macrophage targeting be optimized to improve therapeutic efficacy?
2. Can macrophages engineered to enhance both efferocytosis and cholesterol homeostasis stabilize atherosclerotic plaques?
3. What technologies enable in vivo delivery of mRNA to generate dual-functional macrophages?
Methods:
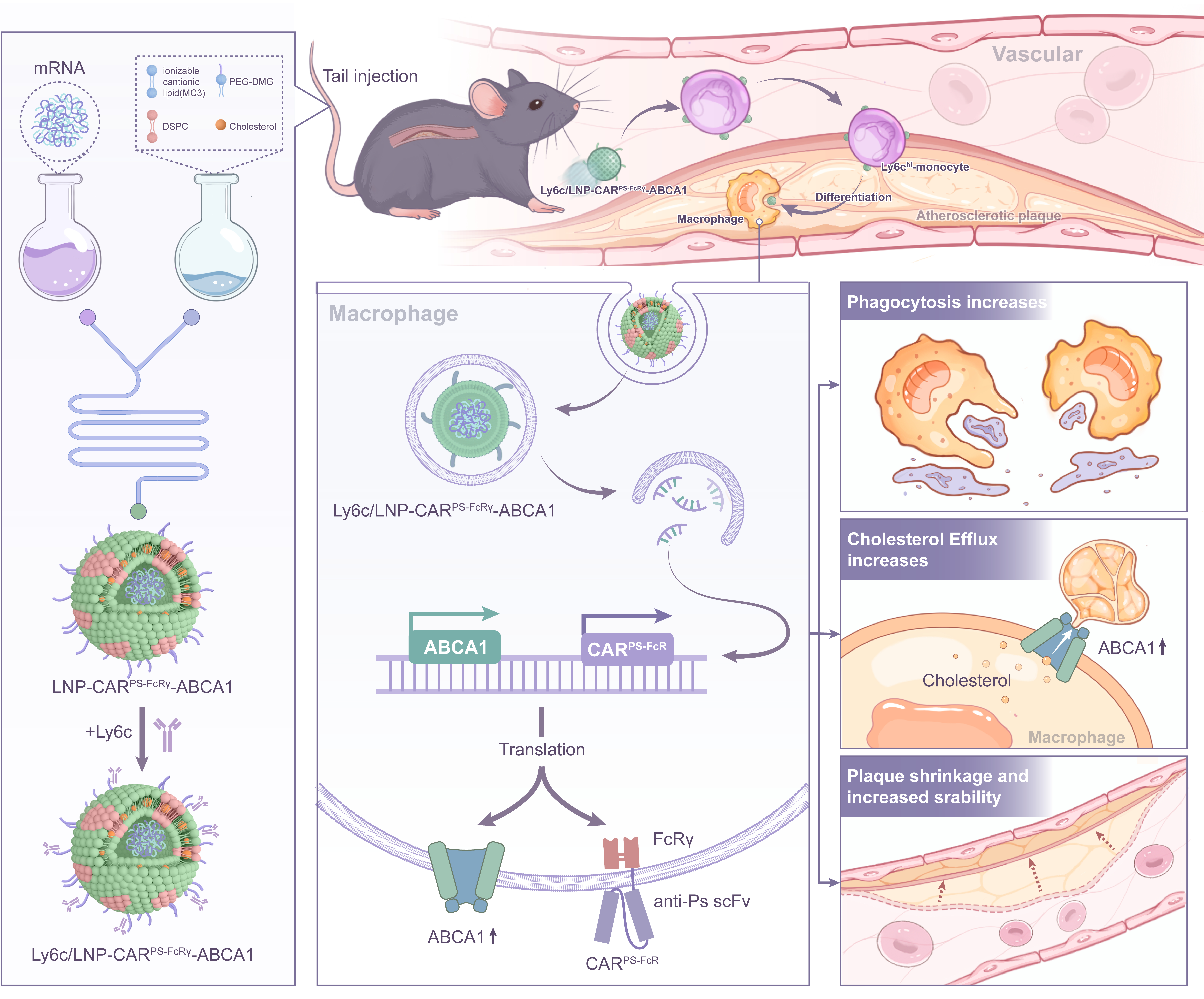
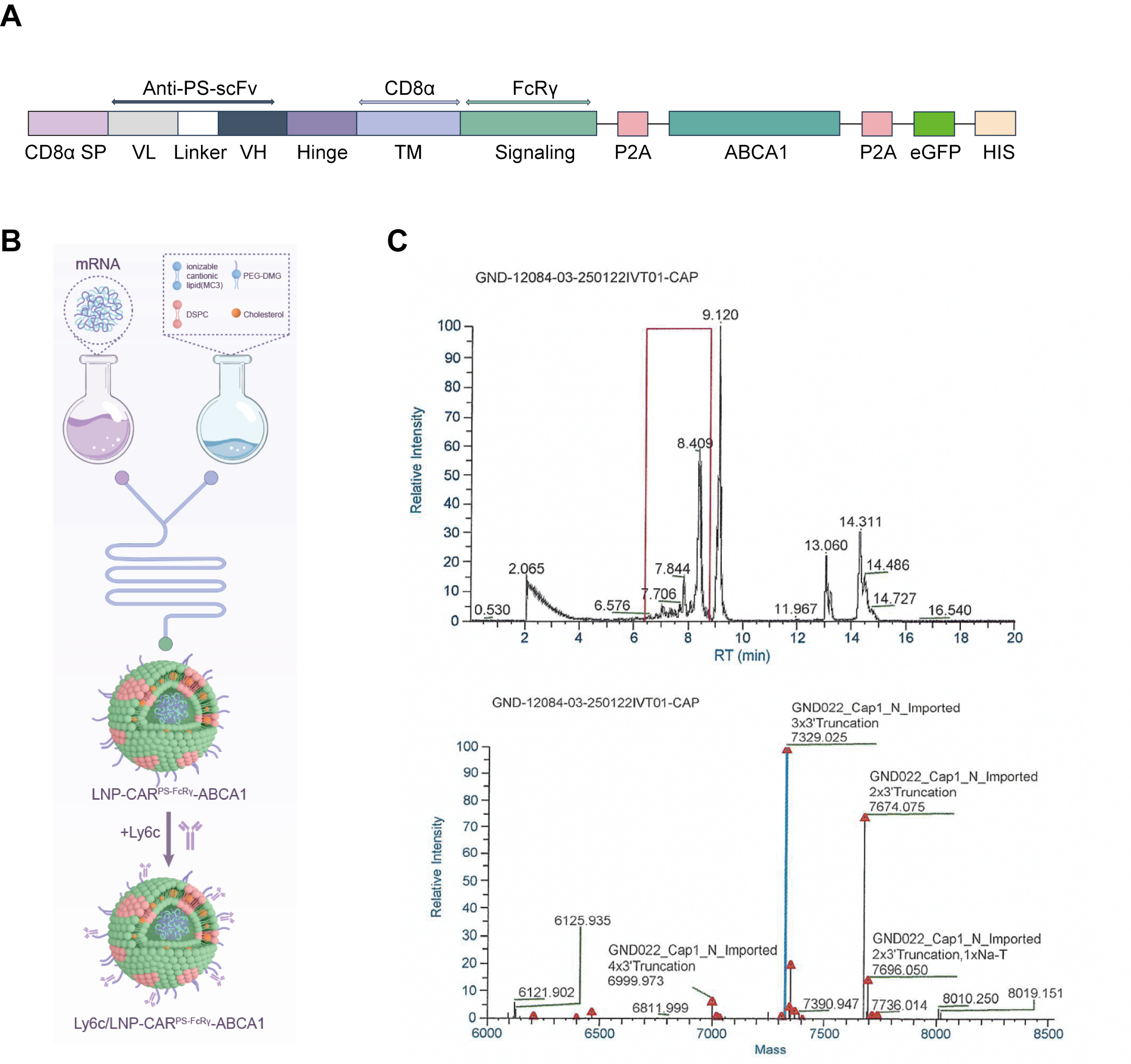
We developed Ly6C-targeted lipid nanoparticles (Ly6C/LNPs) to co-deliver mRNA encoding a fusion construct comprising a chimeric antigen receptor (CARPS-FcRγ), which enhances efferocytosis, and the cholesterol efflux transporter ABCA1. Microfluidics was used to optimize mRNA encapsulation. Targeting efficiency, transgene expression, biosafety, and therapeutic outcomes—such as plaque area reduction, fibrous cap thickening, and decreased inflammation—were evaluated in established AS mouse models.
Results:
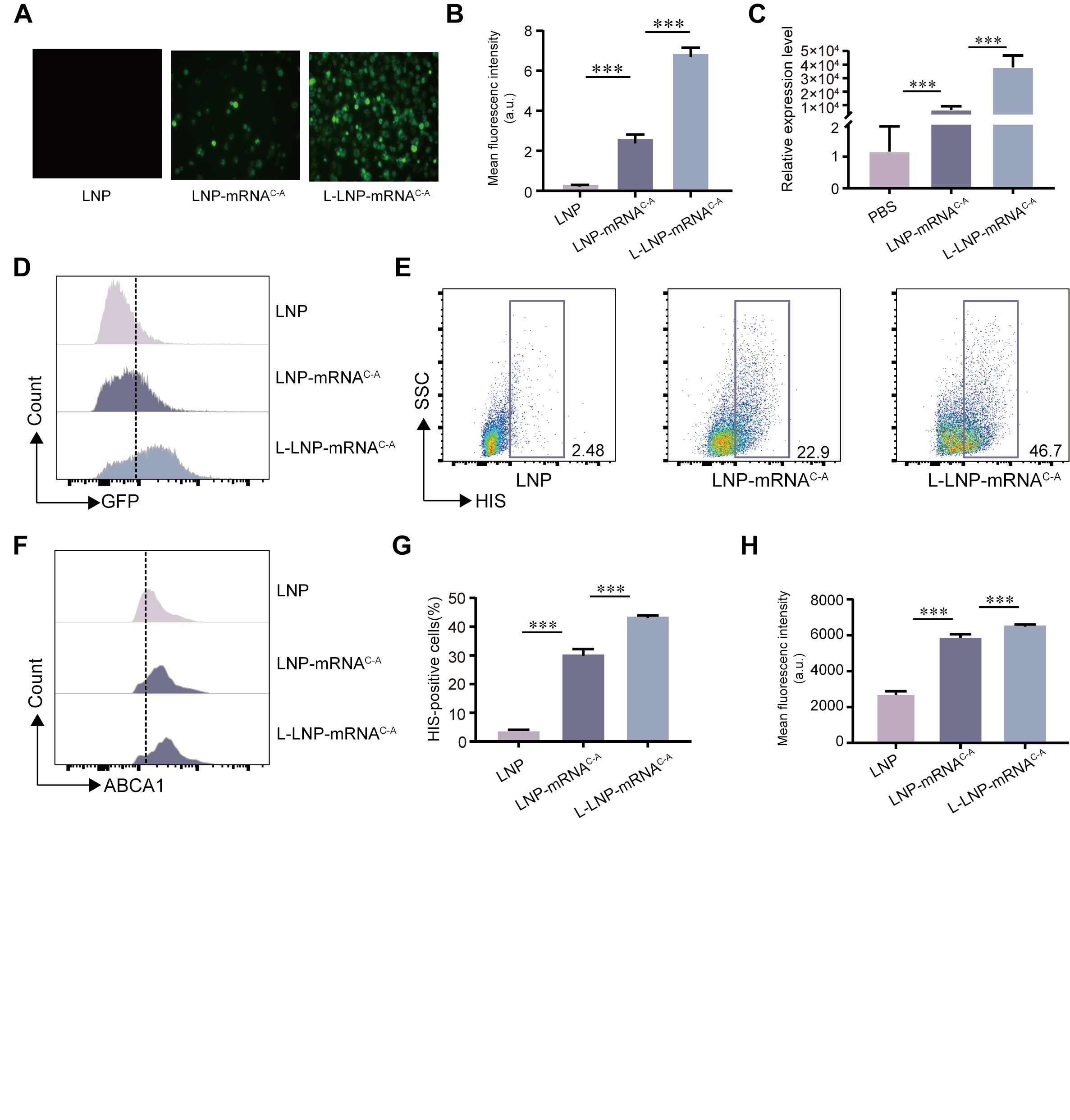
Ly6C/LNPs markedly improved monocyte-specific delivery and co-expression of CAR and ABCA1 in macrophages. This led to restored efferocytosis and enhanced cholesterol efflux, thereby reducing foam cell formation. In vivo treatment significantly decreased plaque size, increased cap thickness, and reduced inflammatory cell infiltration. The approach also demonstrated excellent safety and feasibility, avoiding risks associated with ex vivo manipulation.
Conclusion:
This study introduces a novel in vivo mRNA-based strategy to generate dual-functional CAR-macrophages (CAR-M) for AS therapy. By simultaneously promoting efferocytosis and cholesterol clearance, CAR-M address both inflammation and metabolic dysfunction within plaques. This platform offers a promising, clinically translatable approach to stabilize atherosclerotic lesions and overcome the limitations of conventional therapies.
Atherosclerosis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by lipid accumulation and defective clearance of apoptotic cells in plaques. Traditional LDL-C-lowering therapies such as statins show limited efficacy, as they fail to correct underlying metabolic imbalances. These imbalances cause anti-inflammatory macrophages to become lipid-laden foam cells following efferocytosis, ultimately exacerbating plaque progression.
Research Questions:
1. How can monocyte/macrophage targeting be optimized to improve therapeutic efficacy?
2. Can macrophages engineered to enhance both efferocytosis and cholesterol homeostasis stabilize atherosclerotic plaques?
3. What technologies enable in vivo delivery of mRNA to generate dual-functional macrophages?
Methods:
We developed Ly6C-targeted lipid nanoparticles (Ly6C/LNPs) to co-deliver mRNA encoding a fusion construct comprising a chimeric antigen receptor (CARPS-FcRγ), which enhances efferocytosis, and the cholesterol efflux transporter ABCA1. Microfluidics was used to optimize mRNA encapsulation. Targeting efficiency, transgene expression, biosafety, and therapeutic outcomes—such as plaque area reduction, fibrous cap thickening, and decreased inflammation—were evaluated in established AS mouse models.
Results:
Ly6C/LNPs markedly improved monocyte-specific delivery and co-expression of CAR and ABCA1 in macrophages. This led to restored efferocytosis and enhanced cholesterol efflux, thereby reducing foam cell formation. In vivo treatment significantly decreased plaque size, increased cap thickness, and reduced inflammatory cell infiltration. The approach also demonstrated excellent safety and feasibility, avoiding risks associated with ex vivo manipulation.
Conclusion:
This study introduces a novel in vivo mRNA-based strategy to generate dual-functional CAR-macrophages (CAR-M) for AS therapy. By simultaneously promoting efferocytosis and cholesterol clearance, CAR-M address both inflammation and metabolic dysfunction within plaques. This platform offers a promising, clinically translatable approach to stabilize atherosclerotic lesions and overcome the limitations of conventional therapies.
More abstracts on this topic:
Combinatorial Transcription Factor Gene Transfer Accelerates Direct Reprogramming of Ventricular Myocytes to Pacemaker Phenotype
Fan Jinqi, Leng Jing, Cho Hee Cheol
Abdominal Aortic Perivascular Adipose Tissue Lipolysis Is Activated In Hypertensive Dahl SS Rats Fed a High-Fat DietChirivi Miguel, Rendon Javier, Lauver Adam, Fink Gregory, Watts Stephanie, Contreras Andres