Final ID: MP741
Core lab versus computer: Pediatric echocardiogram measurement agreement between expert human and AI readers
Methods: We analyzed a retrospective dataset of pediatric echocardiogram DICOM files from 5 pediatric centers and corresponding core lab measurements collected from childhood cancer survivors under 21 years of age. The automated software processed the DICOM files, and agreement with core lab measurements for 17 2D and Doppler measurements was assessed using mean difference and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC; two-way random effects, absolute agreement, single measures).
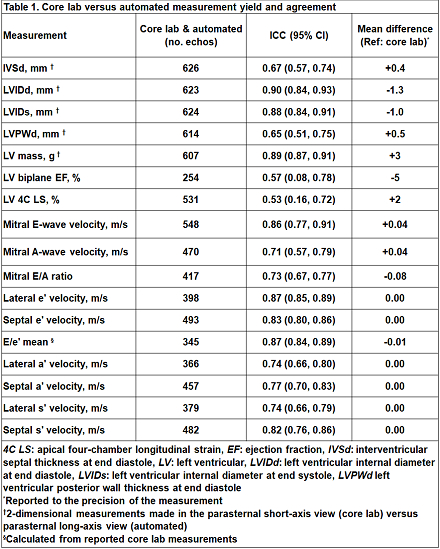
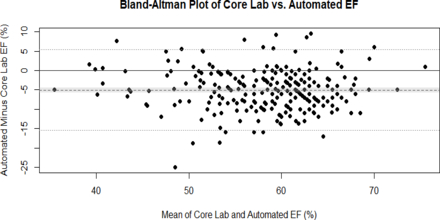
Results: A total of 652 echocardiograms from 153 childhood cancer survivors were included. Median age at time of study was 13.4 (Q1 - Q3: 9.5 - 16.3) years, and 16% of studies showed depressed LV systolic function by core lab measurements (LV shortening fraction ≤28% or ejection fraction [EF] ≤50%). Table 1 summarizes the mean difference and ICC between the automated and core lab reader. Agreement was at least moderate (ICC > 0.5) across all variables. On average, the automated software underestimated biplane EF by 5 percentage points compared to the core lab reader with greater mean differences observed at higher EFs (-1 for core lab EF ≤ 50% and -5 for EF >50%; Figure 1).
Conclusions: Independent validation of an automated echocardiographic measurement software in a pediatric dataset demonstrated at least moderate agreement of all measurements with gold-standard core lab measurements. The software exhibited a bias toward lower ejection fraction values; however, ICC for ejection fraction was comparable to previously reported interobserver variability among human pediatric readers.
- Edwards, Lindsay ( Duke University School of Medicine , Durham , North Carolina , United States )
- Meacham, Lillian ( Emory University School of Medicine , Atlanta , Georgia , United States )
- Nathan, Paul ( The Hospital for Sick Children , Toronto , Ontario , Canada )
- Narasimhan, Shanti ( University of Minnesota , Minneapolis , Minnesota , United States )
- Sachdeva, Ritu ( Emory University School of Medicine , Atlanta , Georgia , United States )
- Sadak, Karim ( University of Minnesota , Minneapolis , Minnesota , United States )
- Stratton, Kayla ( Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center , Seattle , Washington , United States )
- Vemulapalli, Sreekanth ( Duke University School of Medicine , Durham , North Carolina , United States )
- Chow, Eric ( Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center , Seattle , Washington , United States )
- Sharma, Surbhi ( University of Washington , Seattle , Washington , United States )
- Armenian, Saro ( City of Hope , Duarte , California , United States )
- Bhat, Aarti ( University of Washington , Seattle , Washington , United States )
- Blythe, Nancy ( Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center , Seattle , Washington , United States )
- Border, William ( Emory University School of Medicine , Atlanta , Georgia , United States )
- Boyle, Patrick ( University of Washington , Seattle , Washington , United States )
- Leger, Kasey ( University of Washington , Seattle , Washington , United States )
- Leisenring, Wendy ( Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center , Seattle , Washington , United States )
Meeting Info:
Session Info:
Smarter Systems, Better Outcomes: AI and Data-Driven Strategies in Pediatric Cardiac Care
Saturday, 11/08/2025 , 03:15PM - 04:15PM
Moderated Digital Poster Session
More abstracts on this topic:
Liang Kaizhi, Pang Yusheng, Su Danyan
A machine learning approach to classifying ischemic stroke etiology using variables available in the Get-with-the-Guidelines Stroke RegistryLee Ho-joon, Schwamm Lee, Turner Ashby, De Havenon Adam, Kamel Hooman, Brandt Cynthia, Zhao Hongyu, Krumholz Harlan, Sharma Richa
More abstracts from these authors:
Ittleman Benjamin, Pinto Nelangi, Studer Matthew, Young Luciana, Arya Bhawna, Howard Waylon, Virk Kathryn, Brown Nicholas, Bhat Aarti, Caris Elizabeth, Conwell Jeff, Edwards Lindsay, Lewin Mark
Leveraging the Target: Aortic Stenosis Program for Active Surveillance in ASVemulapalli Sreekanth