Final ID: Su1034
A blood test based on RNA-seq and machine learning for the detection of steatotic liver disease: A Pilot Study on Cardiometabolic Health
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Whole blood gene expression is modified in response to signals from various tissues, including the liver. Steatotic (fatty) liver disease (SLD) is a hallmark of cardiometabolic disorder strongly associated with vascular disease (50% of patients undergoing coronary angiography). The main goal of this study was to evaluate the classification performance of peripheral whole blood RNAseq analyzed by artificial intelligence (AI) in identifying or ruling out SLD.
Methods: The training set consisted of 118 men 40-70 years and women 50-70 years with no history of cardiovascular disease enrolled in a clinical study for assessing coronary artery calcification via a chest computed tomography scan. SLD was defined as <48 Hounsfield Units. Whole blood RNA was isolated and deep sequenced. Different AI models were trained using clinical and transcriptome variables as distinctive features for identifying the presence of SLD. The predictive performance of the combined model (which included transcriptome data, age, sex, BMI, diabetes, and dyslipidemia) was compared against models using only transcriptome data or relevant clinical variables for the presence of SLD. To ensure a robust evaluation of the model's performance, an external validation was conducted using two independent groups (Validation 1 (V1): 32 participants and Validation 2 (V2): 33 participants).
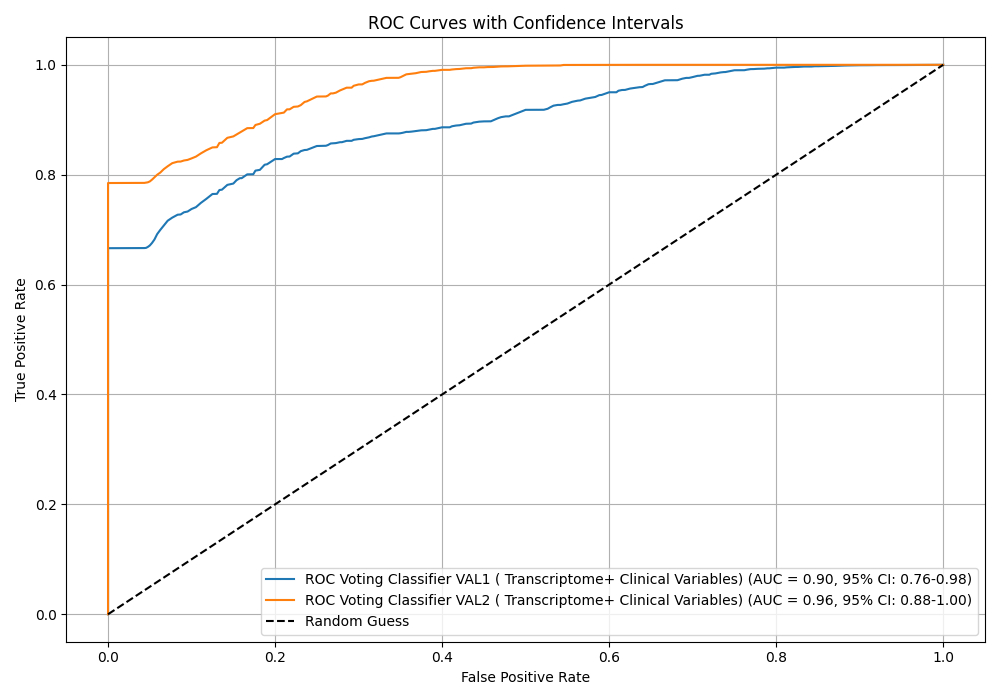
Results: The prevalence of SLD was 47.5% in the training set, 50% in V1 and 51% in V2 sets. The population variables were as follows (control versus cases): mean age 56 vs. 57 ys; females 26% vs. 29%; diabetes 16% vs. 25%; hypertension 42% vs. 55%; dyslipidemia 23 vs. 34%; obesity 34 vs.57% (p 0.02) and coronary calcium score (mean 96.1 vs. 131.12 Agatston Units, p 0.08). The combined AI model exhibited the highest accuracy for the presence of SLD in the validation set (V2), achieving an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.96 (95%CI 0.90-1.00), sensitivity of 76%, specificity of 94%, positive predictive value of 93%, negative predictive value of 79%, and overall accuracy of 85%. The combined AI model exhibited significant discrimination improvement over the clinical risk model (AUC=0.83; p<0.011).
Conclusions: In this pilot study, a blood test based on whole blood transcriptome, clinical variables, and AI analysis showed better discrimination ability than clinical risk factors for predicting the presence of steatotic liver disease.
Methods: The training set consisted of 118 men 40-70 years and women 50-70 years with no history of cardiovascular disease enrolled in a clinical study for assessing coronary artery calcification via a chest computed tomography scan. SLD was defined as <48 Hounsfield Units. Whole blood RNA was isolated and deep sequenced. Different AI models were trained using clinical and transcriptome variables as distinctive features for identifying the presence of SLD. The predictive performance of the combined model (which included transcriptome data, age, sex, BMI, diabetes, and dyslipidemia) was compared against models using only transcriptome data or relevant clinical variables for the presence of SLD. To ensure a robust evaluation of the model's performance, an external validation was conducted using two independent groups (Validation 1 (V1): 32 participants and Validation 2 (V2): 33 participants).
Results: The prevalence of SLD was 47.5% in the training set, 50% in V1 and 51% in V2 sets. The population variables were as follows (control versus cases): mean age 56 vs. 57 ys; females 26% vs. 29%; diabetes 16% vs. 25%; hypertension 42% vs. 55%; dyslipidemia 23 vs. 34%; obesity 34 vs.57% (p 0.02) and coronary calcium score (mean 96.1 vs. 131.12 Agatston Units, p 0.08). The combined AI model exhibited the highest accuracy for the presence of SLD in the validation set (V2), achieving an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.96 (95%CI 0.90-1.00), sensitivity of 76%, specificity of 94%, positive predictive value of 93%, negative predictive value of 79%, and overall accuracy of 85%. The combined AI model exhibited significant discrimination improvement over the clinical risk model (AUC=0.83; p<0.011).
Conclusions: In this pilot study, a blood test based on whole blood transcriptome, clinical variables, and AI analysis showed better discrimination ability than clinical risk factors for predicting the presence of steatotic liver disease.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Deep Learning Topic Analysis Approach for Enhancing Risk Assessment in Heart Failure Using Unstructured Clinical Notes
Adejumo Philip, Pedroso Aline, Khera Rohan
A Rare Case of Atypical Sarcoidosis Presenting as an Intra-Atrial Septal MassDod Rohan, Tushak Zackary