Final ID: Su2041
Longitudinal protein associations with impaired fasting glucose (IFG) and diabetes in MESA
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Intro: Circulating diabetes protein biomarkers have been studied in large human cohorts using measurements from a single timepoint. There are limited studies, however, on how protein changes over time may be associated with T2D, which could reveal novel, dynamic biomarkers of disease.
Hypothesis: The use of repeated plasma samples from the same individual will identify novel circulating proteins modified by IFG and associated with diabetes development over time.
Methods: We measured 2,943 proteins using Olink in 1,923 participants of the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA, mean age 57.7 years old, 52% women) without diabetes at baseline and with plasma samples from Exam 1 (2000-2002), 5 (2010-2012), and 6 (2016-2018). The effect of IFG on longitudinal protein time trends were modeled as an interaction between time×presence of IFG at Exam 1 (n=244 with IFG, n=1,676 without) using linear mixed effects models adjusted for sex, race/ethnicity, and time-varying values for age, BMI, and eGFR. Proteins with significant interactions were probed for causality using cis-Mendelian Randomization (cis-MR). Longitudinal protein associations with incident diabetes (mean follow-up=21.6 years) were modeled using time-varying Cox models (TV Cox, 447 cases, 1,476 non-cases) adjusted for sex, race/ethnicity, and time-varying age, BMI, eGFR, total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL-c, and hypertension. Associations were also compared with Cox models using single-timepoint protein values as the dependent variable in the UK Biobank (UKBB). A false discovery (q)<0.05 was used.
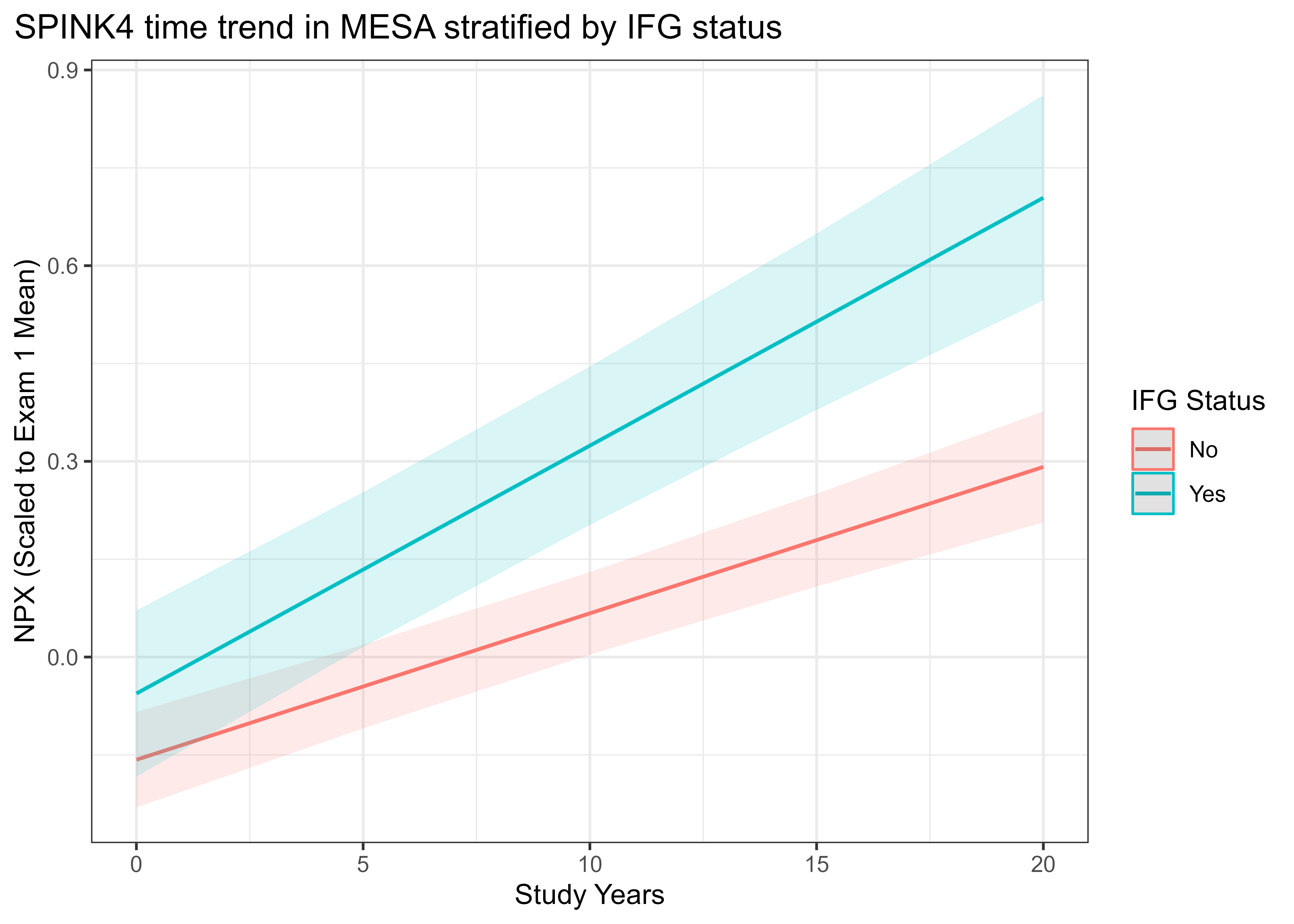
Results: We found 189 proteins with time trends that differed based on IFG status (time×IFG interaction term q<0.05). Of these, 54 (28.6%) were associated with incident diabetes in MESA (q<0.05 TV Cox) and the UKBB (q<0.05 Cox). These included SPINK4, a Kazal-type serine protease inhibitor in the intestinal mucosa that had a greater increase over time among individuals with IFG (Fig 1, q=6.5×10-4). Inverse weighted cis-MR supported SPINK4 having a possible causal role in fasting glucose levels (β=-0.002, q=5.51×10-10). Circulating SPINK4 was positively associated with incident diabetes in MESA (TV Cox HR 1.25 [1.14-1.37], q=7.12×10-5) and in UKBB (Cox HR 1.43 [1.36-1.52], q=1.74×10-34).
Conclusions: We found 189 protein trajectories modified by IFG, 54 of which were additionally associated with diabetes risk. These proteins can reveal dynamic associations that help further elucidate diabetes pathways.
Hypothesis: The use of repeated plasma samples from the same individual will identify novel circulating proteins modified by IFG and associated with diabetes development over time.
Methods: We measured 2,943 proteins using Olink in 1,923 participants of the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA, mean age 57.7 years old, 52% women) without diabetes at baseline and with plasma samples from Exam 1 (2000-2002), 5 (2010-2012), and 6 (2016-2018). The effect of IFG on longitudinal protein time trends were modeled as an interaction between time×presence of IFG at Exam 1 (n=244 with IFG, n=1,676 without) using linear mixed effects models adjusted for sex, race/ethnicity, and time-varying values for age, BMI, and eGFR. Proteins with significant interactions were probed for causality using cis-Mendelian Randomization (cis-MR). Longitudinal protein associations with incident diabetes (mean follow-up=21.6 years) were modeled using time-varying Cox models (TV Cox, 447 cases, 1,476 non-cases) adjusted for sex, race/ethnicity, and time-varying age, BMI, eGFR, total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL-c, and hypertension. Associations were also compared with Cox models using single-timepoint protein values as the dependent variable in the UK Biobank (UKBB). A false discovery (q)<0.05 was used.
Results: We found 189 proteins with time trends that differed based on IFG status (time×IFG interaction term q<0.05). Of these, 54 (28.6%) were associated with incident diabetes in MESA (q<0.05 TV Cox) and the UKBB (q<0.05 Cox). These included SPINK4, a Kazal-type serine protease inhibitor in the intestinal mucosa that had a greater increase over time among individuals with IFG (Fig 1, q=6.5×10-4). Inverse weighted cis-MR supported SPINK4 having a possible causal role in fasting glucose levels (β=-0.002, q=5.51×10-10). Circulating SPINK4 was positively associated with incident diabetes in MESA (TV Cox HR 1.25 [1.14-1.37], q=7.12×10-5) and in UKBB (Cox HR 1.43 [1.36-1.52], q=1.74×10-34).
Conclusions: We found 189 protein trajectories modified by IFG, 54 of which were additionally associated with diabetes risk. These proteins can reveal dynamic associations that help further elucidate diabetes pathways.
More abstracts on this topic:
An Integrative Strategy Combining Genetic, Proteomic, and Clinical Data Identifies Circulating WARS as a Candidate Target for Hypertension.
Chignon Arnaud, Lettre Guillaume
Circulating Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) Proteins Are Associated with Risk of Late Life Heart Failure: the ARIC StudyDehghan Arshama, Mosley Thomas, Palta Priya, Yu Bing, Shah Amil, Giugni Fernando, Lamberson Victoria, Yang Yimin, Boerwinkle Eric, Fornage Myriam, Giannarelli Chiara, Grams Morgan, Windham B Gwen