Final ID: 4131674
ADP-Ribosylation In a Mouse Model of Atherosclerosis: a Potential Novel Link Between Dyslipidemia and Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Inflammation and lipid accumulation are major features of atherosclerosis, a leading cause of death and morbidity worldwide. Our previous study recognized ADP-ribosylation, a post-translational modification, as a novel regulator of macrophage activation. We also have established mass spectrometry-based ADP-ribosylation proteomics. Using this technology, we evaluated the completely uncharacterized role of ADP-ribosylation in atherogenesis. We hypothesized that ADP-ribosylated proteins circulate from liver, accumulate in aorta and promote atherogenesis.
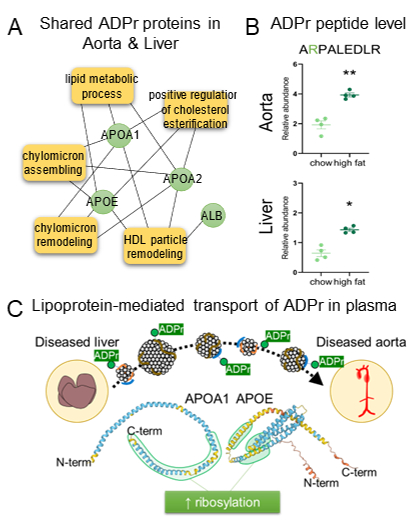
Methods and Results: We harvested the aorta, liver, and plasma of LDL receptor-deficient (Ldlr-/-) mice that were on a regular chow or high-fat diet for 3 or 6 months (n=40/condition). To increase ADP-ribosyl peptide signals in the aorta, we applied our novel recently optimized ion mobility mass spectrometry strategy to generate ADP-ribosylation proteomics data. We analyzed 160 mice aortas and identified 3 APOA1 and 3 APOE ADP-ribosylated peptides in both the aorta and the liver (Fig. A). In addition, these peptides were differentially abundant in the aorta of HFD-fed mice, compared to controls (i.e, APOA1 ARPALEDLR peptide relative abundance (Fig. B)).
Using the same mouse plasma, we then validated the presence of ADP-ribosylated APOA1 and ADP-ribosylated APOE in HDL and chylomicron/VLDL/LDL fractions (Western blot), respectively. This finding indicates that classical apolipoproteins circulate as ADP-ribosylated forms, representing a completely novel class of modified apolipoproteins. Immunohistochemistry confirmed the enrichment of aortic lesions in macrophages and ADP-ribosylation signal (5-fold increase, p=0.0006).
Conclusions: This work provides the first in vivo evidence that ADP-ribosylation occurs in atherosclerotic lesions, which may originate from the liver via circulating blood (Fig. C). Future studies will examine whether ADP-ribosylation of apolipoproteins, specifically APOA1, alters anti-atherogenic functions of HDL.
Methods and Results: We harvested the aorta, liver, and plasma of LDL receptor-deficient (Ldlr-/-) mice that were on a regular chow or high-fat diet for 3 or 6 months (n=40/condition). To increase ADP-ribosyl peptide signals in the aorta, we applied our novel recently optimized ion mobility mass spectrometry strategy to generate ADP-ribosylation proteomics data. We analyzed 160 mice aortas and identified 3 APOA1 and 3 APOE ADP-ribosylated peptides in both the aorta and the liver (Fig. A). In addition, these peptides were differentially abundant in the aorta of HFD-fed mice, compared to controls (i.e, APOA1 ARPALEDLR peptide relative abundance (Fig. B)).
Using the same mouse plasma, we then validated the presence of ADP-ribosylated APOA1 and ADP-ribosylated APOE in HDL and chylomicron/VLDL/LDL fractions (Western blot), respectively. This finding indicates that classical apolipoproteins circulate as ADP-ribosylated forms, representing a completely novel class of modified apolipoproteins. Immunohistochemistry confirmed the enrichment of aortic lesions in macrophages and ADP-ribosylation signal (5-fold increase, p=0.0006).
Conclusions: This work provides the first in vivo evidence that ADP-ribosylation occurs in atherosclerotic lesions, which may originate from the liver via circulating blood (Fig. C). Future studies will examine whether ADP-ribosylation of apolipoproteins, specifically APOA1, alters anti-atherogenic functions of HDL.
More abstracts on this topic:
Age-Related Impairment of Mitochondrial Protein Turnover Exacerbates Pathogenesis of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction in Old Mice
Kobak Kamil, Zarzycka Weronika, King Catherine, Borowik Agnieszka, Peelor Frederick, Kinter Michael, Miller Benjamin, Chiao Ying Ann
A major uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate impairs macrophage efferocytosis and accelerates atherogenesis: a potential mechanism for cardiovascular risk in chronic kidney diseaseJha Prabhash, Kasai Taku, Vromman Amelie, Holden Rachel, Libby Peter, Tabas Ira, Singh Sasha, Aikawa Elena, Aikawa Masanori, Lupieri Adrien, Sonawane Abhijeet, Le Thanh-dat, Becker-greene Dakota, Chelvanambi Sarvesh, Turner Mandy, Nakamura Yuto, Passos Livia