Final ID: MP1039
Mavacamten: Real-World Experience from 34 Months of the Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) Program
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Introduction
Mavacamten is a first-in-class cardiac myosin inhibitor approved by the FDA for the treatment of adults with symptomatic New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II–III obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), to improve functional capacity and symptoms. The REMS program is unique to the United States and is the largest database providing insight into the safety of mavacamten in the real-world.
Aim: To evaluate the largest real-world safety cohort (3-year) of mavacamten patients from the mavacamten REMS database, (28-Apr-2022 to 27-Feb-2025), including safety data for patients treated for ≥2 year.
Methods
This retrospective analysis uses patient-level data from the mavacamten REMS database, including routine monitoring before each dispense, patient status forms [PSFs], echocardiograms, and drug-drug interaction (DDI) screening.
Results
During the cumulative reporting period (28-Apr-2022 to 27-Feb-2025), a total of 11,982 patients received ≥1 dispenses of mavacamten. However, PSFs, which are required to continue treatment, were submitted for 11,007 unique patients; of these 740 (6.7%) experienced LVEF <50% and 188 (1.7%) had HF requiring hospitalization (HFH).
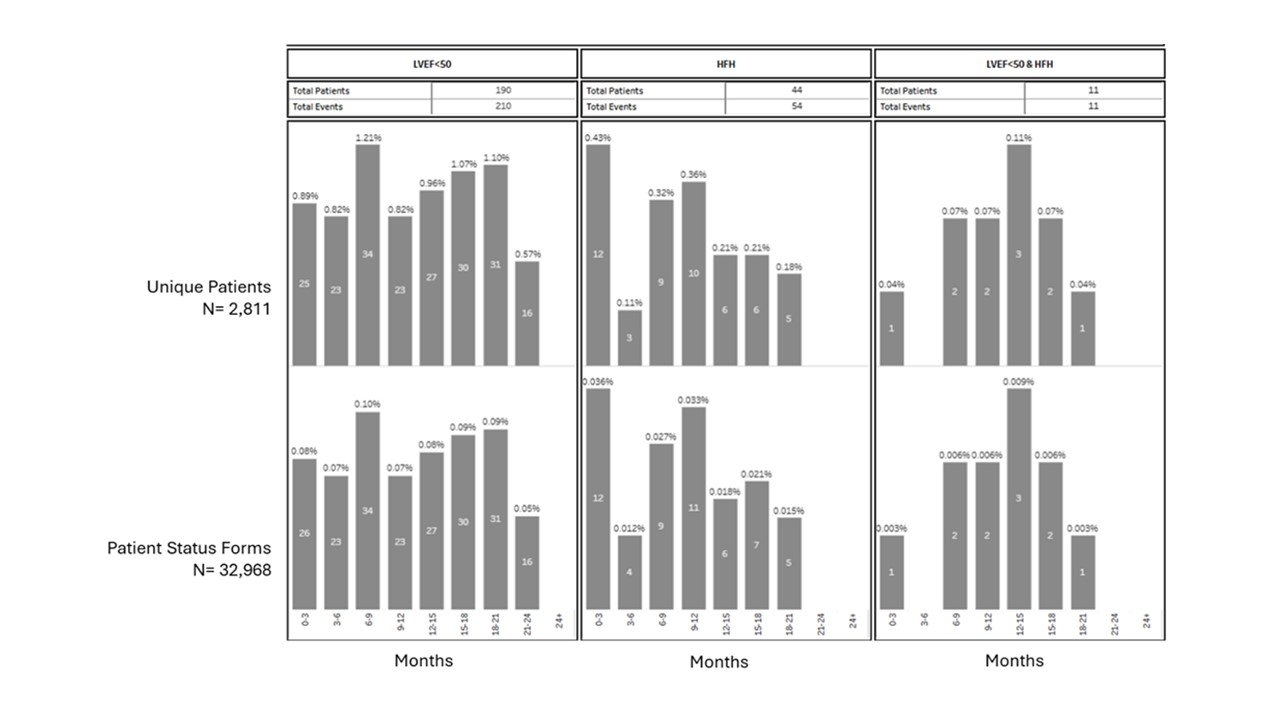
Altogether, 2,811 patients were treated ≥2 years: 190 (6.8%) experienced LVEF <50%, 44 (1.6%) had HFH and 11 (0.4%) had both reduction in LVEF<50% and HFH. (Figure 1). Further analysis on these long-term patients will be provided in the presentation.
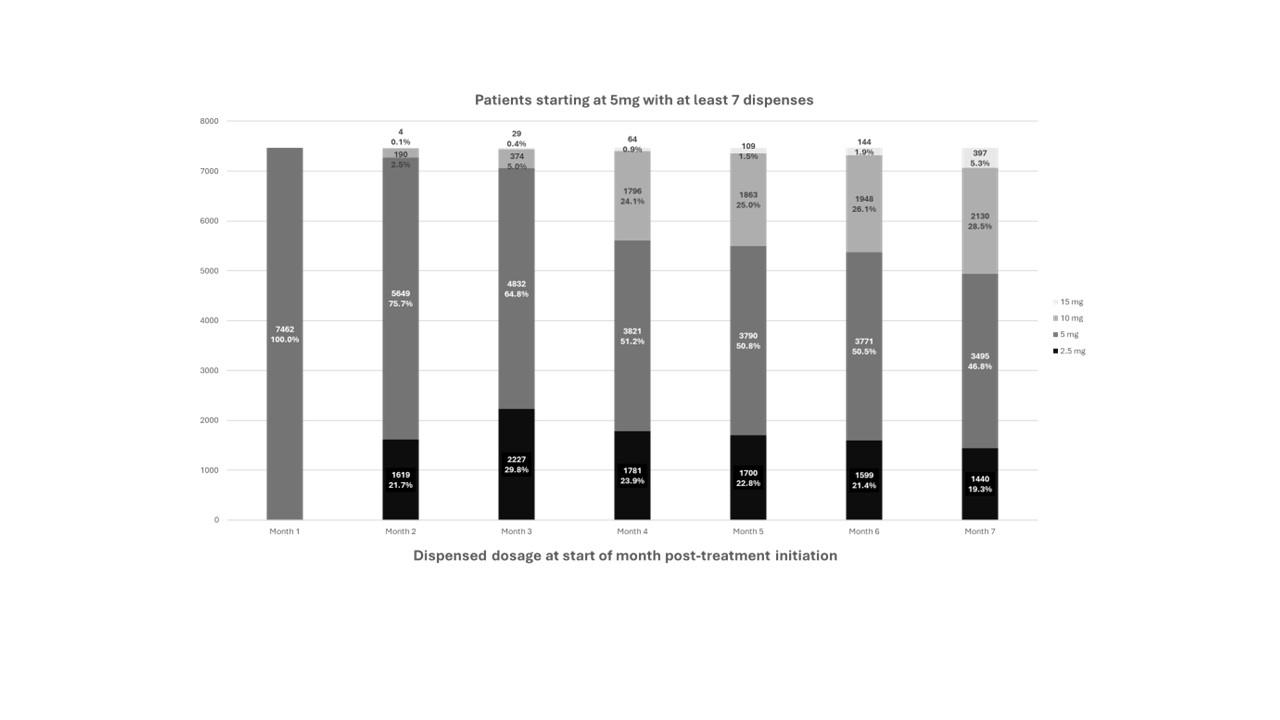
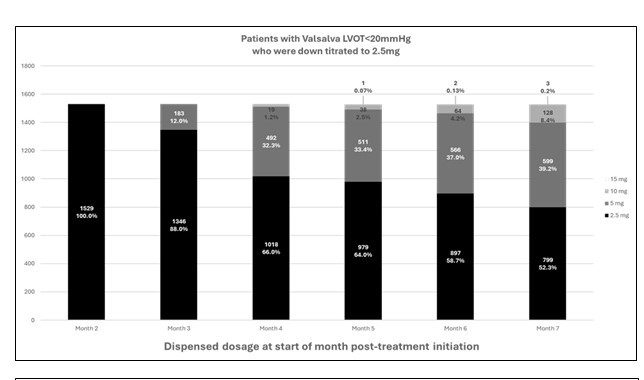
A total of 7,462 patients initiated mavacamten at 5 mg/day and were treated for at least 6 months, of which 5,649 (75.7%) remained on 5 mg/day at the second dispense (Figure 2). Down titration occurred in 1,619 (21.7%) patients to 2.5 mg at the second dispense. Of these, 94.4% (n=1,529) had VLVOT <20 mmHg (Figure 3). A planned analysis of the reported LVEF<50% and HFH for these patients will provide more insights.
Among 147,306 DDI checklists completed, 213 (0.14%) led to mavacamten dose reduction, 1 mavacamten discontinuation and 231 (0.16%) to discontinuation of a concurrent medication.
Conclusion
Mavacamten treatment continued to remain consistent with clinical trials and previous reported REMS data, demonstrating a favourable real-world safety profile amongst patients treated for ≥2 years with infrequent temporary interruptions, low rates of DDIs, LVEF<50%, and HFH.
Introduction
Mavacamten is a first-in-class cardiac myosin inhibitor approved by the FDA for the treatment of adults with symptomatic New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II–III obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), to improve functional capacity and symptoms. The REMS program is unique to the United States and is the largest database providing insight into the safety of mavacamten in the real-world.
Aim: To evaluate the largest real-world safety cohort (3-year) of mavacamten patients from the mavacamten REMS database, (28-Apr-2022 to 27-Feb-2025), including safety data for patients treated for ≥2 year.
Methods
This retrospective analysis uses patient-level data from the mavacamten REMS database, including routine monitoring before each dispense, patient status forms [PSFs], echocardiograms, and drug-drug interaction (DDI) screening.
Results
During the cumulative reporting period (28-Apr-2022 to 27-Feb-2025), a total of 11,982 patients received ≥1 dispenses of mavacamten. However, PSFs, which are required to continue treatment, were submitted for 11,007 unique patients; of these 740 (6.7%) experienced LVEF <50% and 188 (1.7%) had HF requiring hospitalization (HFH).
Altogether, 2,811 patients were treated ≥2 years: 190 (6.8%) experienced LVEF <50%, 44 (1.6%) had HFH and 11 (0.4%) had both reduction in LVEF<50% and HFH. (Figure 1). Further analysis on these long-term patients will be provided in the presentation.
A total of 7,462 patients initiated mavacamten at 5 mg/day and were treated for at least 6 months, of which 5,649 (75.7%) remained on 5 mg/day at the second dispense (Figure 2). Down titration occurred in 1,619 (21.7%) patients to 2.5 mg at the second dispense. Of these, 94.4% (n=1,529) had VLVOT <20 mmHg (Figure 3). A planned analysis of the reported LVEF<50% and HFH for these patients will provide more insights.
Among 147,306 DDI checklists completed, 213 (0.14%) led to mavacamten dose reduction, 1 mavacamten discontinuation and 231 (0.16%) to discontinuation of a concurrent medication.
Conclusion
Mavacamten treatment continued to remain consistent with clinical trials and previous reported REMS data, demonstrating a favourable real-world safety profile amongst patients treated for ≥2 years with infrequent temporary interruptions, low rates of DDIs, LVEF<50%, and HFH.
More abstracts on this topic:
Cellular and Subcellular Ventricular Localization of the Fast Transient Outward Potassium Channels in the Murine Heart
Gorman Renee, Backx Peter
Asiatic Acid, A Novel Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha Agonist, Ameliorates Cardiac Hypertrophy By Reducing Reactive Oxygen Species AccumulationGupta Soumyadeep, Sarkar Sagartirtha