Final ID: MP516
Natto Red Yeast Rice Dietary Supplement Regulates Lipids Profiles: a Multicenter, Double-Placebo, Double-Blinded, Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Natto Red Yeast Rice (NRYR) is a kind of dietary supplement, and its effectiveness to regulate lipid profiles, especially in combination with statins, is unknown.
Aims: We aimed to assess whether NRYR may lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels and regulate other lipid profiles alone or beyond the usage of Simvastatin.
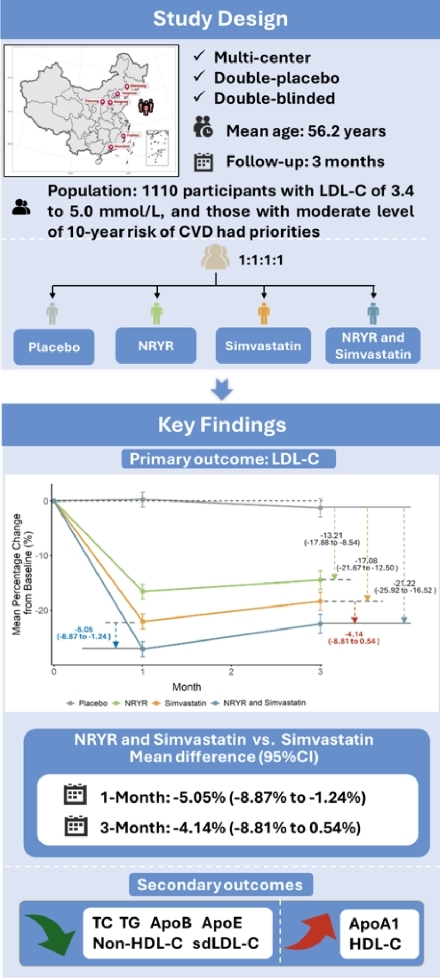
Methods: A multicenter, double-placebo, double-blinded, randomized controlled trial was conducted in 6 centers in China, eligible participants had LDL-C levels of 3.4 to 5.0 mmol/L and those having moderate predicted cardiovascular disease risk are preferential. Participants were enrolled and randomized into 4 groups by a combination of NRYR (or its placebo) and Simvastatin (or its placebo) at a ratio of 1:1:1:1. After baseline examinations, all participants underwent intervention for 3 months with two follow-up visits at 1-month and 3-month, respectively. The primary outcome was the change in LDL-C levels after 3-month’s intervention, and secondary outcomes included changes of other lipid profiles. Adverse events were also collected to assess safety.
Results: A total of 1,110 participants underwent intervention after randomization. Significant reductions in LDL-C levels were observed among participants from groups of NRYR, Simvastatin, and the combination of both, and the differences in the percent change of LDL-C levels at 3-month from baseline were -13.21% (95% CI, -17.88% to -8.54%), -17.08% (95% CI, -21.67% to -12.50%) and -21.22% (95% CI, -25.92% to -16.52%), as compared with placebo, respectively (all P<0.001). More importantly, compared with Simvastatin alone, a combination of NRYR and Simvastatin showed extra decreased LDL-C levels at 1-month with the net change of -5.05% (95% CI, -8.87% to -1.24%; P=0.009), and nominally significant net change of -4.14% (95% CI, -8.81% to 0.54%; P=0.0828) at 3-month, respectively. Similar reductions were also observed for total cholesterol, triglycerides, non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), small dense LDL-C, and apolipoprotein B, while increments on HDL-C and apolipoprotein A1 were observed in 3 intervention groups (Figure 1). Rates of adverse events were similar among the 4 groups.
Conclusion: For those with mild-to-moderate elevation of LDL-C or moderate risk of cardiovascular disease, NRYR effectively lowered LDL-C levels and its combination with Simvastatin yield potentially greater LDL-C reduction than Simvastatin alone.
Aims: We aimed to assess whether NRYR may lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels and regulate other lipid profiles alone or beyond the usage of Simvastatin.
Methods: A multicenter, double-placebo, double-blinded, randomized controlled trial was conducted in 6 centers in China, eligible participants had LDL-C levels of 3.4 to 5.0 mmol/L and those having moderate predicted cardiovascular disease risk are preferential. Participants were enrolled and randomized into 4 groups by a combination of NRYR (or its placebo) and Simvastatin (or its placebo) at a ratio of 1:1:1:1. After baseline examinations, all participants underwent intervention for 3 months with two follow-up visits at 1-month and 3-month, respectively. The primary outcome was the change in LDL-C levels after 3-month’s intervention, and secondary outcomes included changes of other lipid profiles. Adverse events were also collected to assess safety.
Results: A total of 1,110 participants underwent intervention after randomization. Significant reductions in LDL-C levels were observed among participants from groups of NRYR, Simvastatin, and the combination of both, and the differences in the percent change of LDL-C levels at 3-month from baseline were -13.21% (95% CI, -17.88% to -8.54%), -17.08% (95% CI, -21.67% to -12.50%) and -21.22% (95% CI, -25.92% to -16.52%), as compared with placebo, respectively (all P<0.001). More importantly, compared with Simvastatin alone, a combination of NRYR and Simvastatin showed extra decreased LDL-C levels at 1-month with the net change of -5.05% (95% CI, -8.87% to -1.24%; P=0.009), and nominally significant net change of -4.14% (95% CI, -8.81% to 0.54%; P=0.0828) at 3-month, respectively. Similar reductions were also observed for total cholesterol, triglycerides, non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), small dense LDL-C, and apolipoprotein B, while increments on HDL-C and apolipoprotein A1 were observed in 3 intervention groups (Figure 1). Rates of adverse events were similar among the 4 groups.
Conclusion: For those with mild-to-moderate elevation of LDL-C or moderate risk of cardiovascular disease, NRYR effectively lowered LDL-C levels and its combination with Simvastatin yield potentially greater LDL-C reduction than Simvastatin alone.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Framework for Developing Prehospital Intracerebral Hemorrhage Recognition Scales and Technologies
Taleb Shayandokht, Hsu Jamie, Saver Jeffrey
Aggressive LDL cholesterol lowering post ACS with triple combination therapy: Insights from the multicentric LAI-REACT studyPuri Raman, Mahajan Kunal, Agarwala Rajeev, Gupta Ashu, Batra Aditya, Khan Aziz, Vijan Vinod, Sharma Jai Bharat, Himral Surender