Final ID: MP1726
Immunogenicity of Recaticimab Does Not Impact Its Efficacy in Patients with Dyslipidemia: A Pooled Analysis of Three Phase III and One Phase Ib/II Studies
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Recaticimab, a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) with a novel YTE mutation, prolongs its half-life by enhancing neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) binding, making it the longest-acting anti-PCSK9 antibody. Approved for dyslipidemia management, its clinical performance concerning immunogenicity is still under study.
Aims:
To explore the impact of immunogenicity on the efficacy and safety of recaticimab in patients with dyslipidemia.
Methods:
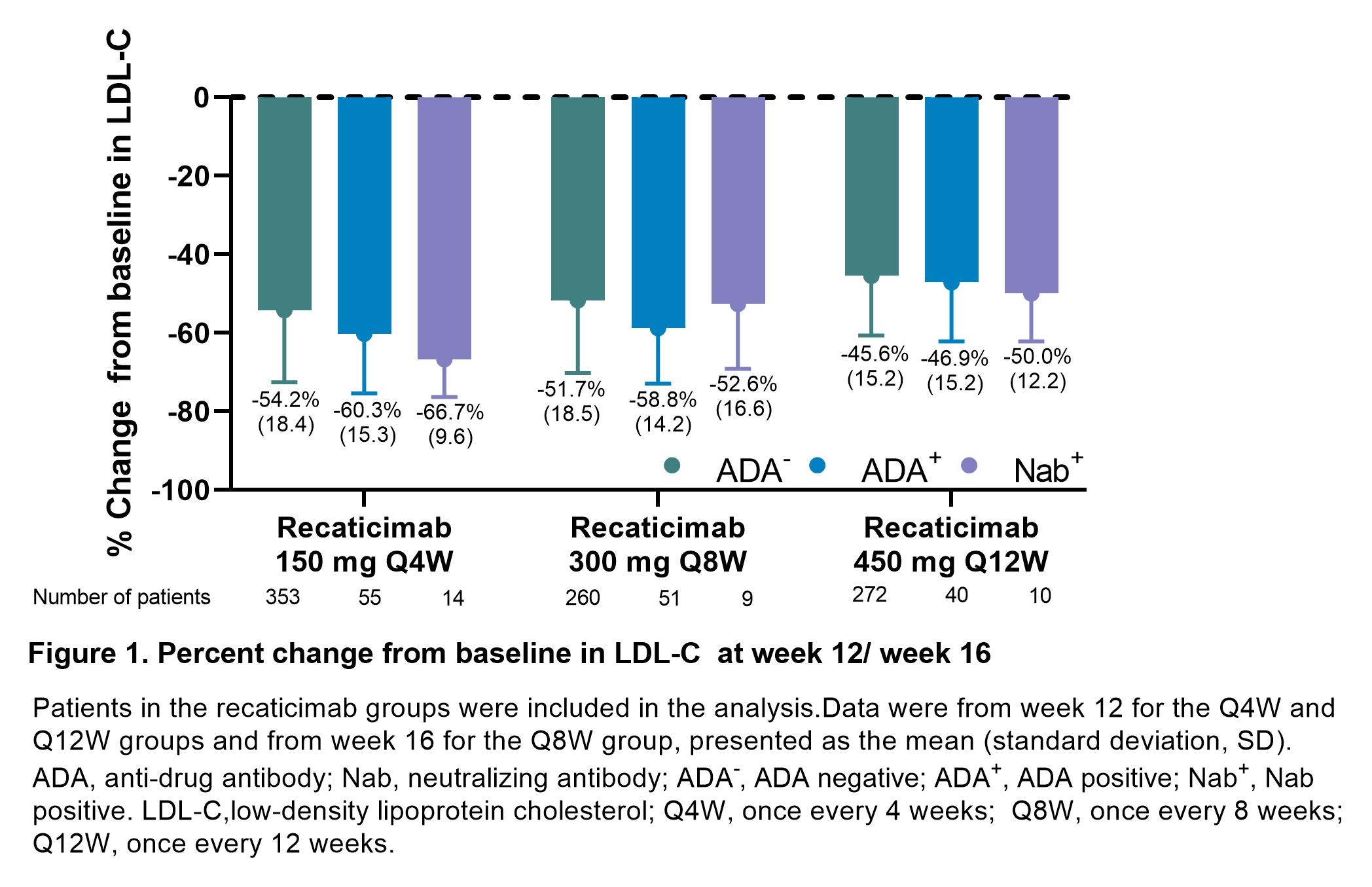
The pooled analysis was conducted using data from 3 phase III trials (REMAIN 1-3) and 1 phase Ib/II trial (NCT03944109). Patients with primary hypercholesterolemia (non-familial and heterozygous) and mixed hyperlipemia were randomized to receive subcutaneous recaticimab at doses of 150 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W), 300 mg Q8W, 450 mg Q12W, or matching placebo. Anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) were measured over time, with ADA-positive samples tested for neutralizing antibodies (Nabs). Efficacy outcome (the percent change in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol [LDL-C] from baseline at Week 12 (Q4W and Q12W groups), and Week 16 (Q8W group), and safety outcome were evaluated by ADA and Nab status.
Results:
Among 1034 patients who received recaticimab, 146 (14.1%) tested positive for treatment-emergent ADA (ADA+), and 33 (3.2%) for Nab (Nab+). In the placebo group (n=507), 10 (2.0%) were ADA+, and none were Nab+. In recaticimab-treated patients, LDL-C reductions from baseline at Week 12/16 were comparable across ADA-, ADA+, Nab+ patients for all dosing regimens (Figure 1). The incidence of treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) was 22.8% (202 of 885) in ADA- patients, 29.5% (43 of 146) in ADA+ patients, and 42.4% (14 of 33) in Nab+ patients. Injection site reactions were the most common TRAE: 2.8% (25 of 885) in ADA-, 10.3% (15 of 146) in ADA+, and 18.2% (6 of 33) in Nab+ patients. All TRAEs in the ADA+ and Nab+ groups were mild to moderate, with no serious TRAEs reported.
Conclusions:
The incidence of ADAs (14.1%) and Nabs (3.2%) following recaticimab treatment did not impact efficacy. ADA+ and Nab+ patients had a higher incidence of self-resolving injection site reactions compared to ADA- patients. These findings support the clinical use of recaticimab for lipid-lowering therapy, regardless of immunogenicity status.
Recaticimab, a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) with a novel YTE mutation, prolongs its half-life by enhancing neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) binding, making it the longest-acting anti-PCSK9 antibody. Approved for dyslipidemia management, its clinical performance concerning immunogenicity is still under study.
Aims:
To explore the impact of immunogenicity on the efficacy and safety of recaticimab in patients with dyslipidemia.
Methods:
The pooled analysis was conducted using data from 3 phase III trials (REMAIN 1-3) and 1 phase Ib/II trial (NCT03944109). Patients with primary hypercholesterolemia (non-familial and heterozygous) and mixed hyperlipemia were randomized to receive subcutaneous recaticimab at doses of 150 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W), 300 mg Q8W, 450 mg Q12W, or matching placebo. Anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) were measured over time, with ADA-positive samples tested for neutralizing antibodies (Nabs). Efficacy outcome (the percent change in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol [LDL-C] from baseline at Week 12 (Q4W and Q12W groups), and Week 16 (Q8W group), and safety outcome were evaluated by ADA and Nab status.
Results:
Among 1034 patients who received recaticimab, 146 (14.1%) tested positive for treatment-emergent ADA (ADA+), and 33 (3.2%) for Nab (Nab+). In the placebo group (n=507), 10 (2.0%) were ADA+, and none were Nab+. In recaticimab-treated patients, LDL-C reductions from baseline at Week 12/16 were comparable across ADA-, ADA+, Nab+ patients for all dosing regimens (Figure 1). The incidence of treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) was 22.8% (202 of 885) in ADA- patients, 29.5% (43 of 146) in ADA+ patients, and 42.4% (14 of 33) in Nab+ patients. Injection site reactions were the most common TRAE: 2.8% (25 of 885) in ADA-, 10.3% (15 of 146) in ADA+, and 18.2% (6 of 33) in Nab+ patients. All TRAEs in the ADA+ and Nab+ groups were mild to moderate, with no serious TRAEs reported.
Conclusions:
The incidence of ADAs (14.1%) and Nabs (3.2%) following recaticimab treatment did not impact efficacy. ADA+ and Nab+ patients had a higher incidence of self-resolving injection site reactions compared to ADA- patients. These findings support the clinical use of recaticimab for lipid-lowering therapy, regardless of immunogenicity status.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acoramidis Effect on All-Cause Mortality in Patients with p.V142I (V122I) Variant ATTR-CM: Findings From the ATTRibute-CM Study
Alexander Kevin, Bhatt Kunal, Judge Daniel, Grodin Justin, Akinboboye Olakunle, Chen Chris, Tamby Jean-francois, Castano Adam, Fox Jonathan, Fontana Marianna, Gillmore Julian, Sarswat Nitasha, Grogan Martha, Solomon Scott, Davis Margot, Cuddy Sarah, Kittleson Michelle, Shah Keyur, Griffin Jan, Ruberg Frederick, Khouri Michel
Acoramidis Lowers NT-proBNP in a Larger Proportion of ATTRibute-CM Study Participants With Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy Compared with Placebo, Independent of Atrial Fibrillation StatusMaurer Mathew, Castano Adam, Tamby Jean-francois, Fox Jonathan, Mitter Sumeet, Hanna Mazen, Sperry Brett, Alexander Kevin, Obici Laura, Poulsen Steen, Januzzi James, Witteles Ronald, Jaber Wael, Brailovsky Yevgeniy, Vogtlaender Kai