Final ID: Su4104
The impact of post-COVID syndrome on plasma endothelial, thrombotic and renal biomarkers
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Despite widespread vaccination and reduced SARS-CoV-2 pathogenicity, post-COVID syndrome (PCS) remains a significant public health issue. It is widely thought to represent a single, multi-systemic disorder, yet its pathophysiology remains poorly defined. Endothelial dysfunction and thrombosis have been proposed as central mechanisms.
Aims: To assess the long-term impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection on plasma biomarkers of endothelial, thrombotic and renal function.
Methods: Plasma samples were obtained from prospective observational cohort studies of patients previously infected with SARS-CoV-2, stratified by recovery status. Patients not previously hospitalised provided a single sample at 3–36 months post-infection (recovered: n=22; PCS: n=34-35). Post-hospitalisation patients provided samples at 6, 12, and 24 months (recovered: n=4-6; PCS: n=8-16). Commercial ELISAs and colorimetric assays quantified markers of endothelial-mediated vasomotor control (ET-1, nitrate/nitrite, prostacyclin, ADMA, arginine), thrombosis (sCD40L, P-selectin, PSGL-1, tPA, PAI-1, D-dimer) and renal injury (uromodulin, NGAL, cystatin C, TFF3, OPN). Statistical analysis used a mixed-effects model with Dunnett’s test to correct for multiple comparisons.
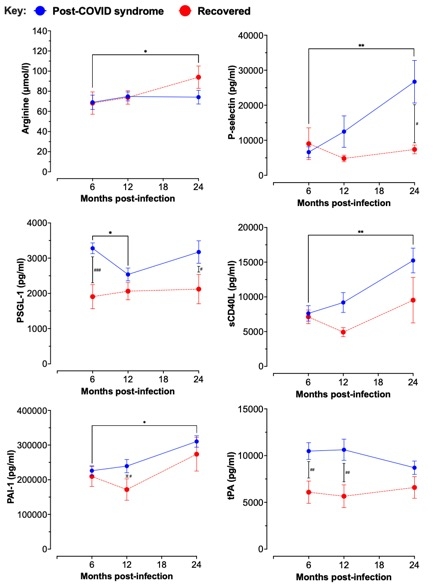
Results: In non-hospitalised cohorts, no significant differences were found between groups across any biomarker. In the post-hospitalisation cohort, arginine levels increased in the recovered group at 24 months (p=0.035; trend vs PCS group p=0.051), with no changes in other markers of endothelial function (Fig. 1). In the PCS group, higher plasma levels of P-selectin (p=0.021), PSGL-1 (p=0.0006), PAI-1 (p=0.018), tPA (p=0.006 & 0.002) and D-dimer (trend; p=0.087) were seen in comparison with the recovered group (Fig. 1). Longitudinally, P-selectin (p=0.003), sCD40L (p=0.013), and PAI-1 (p=0.017) increased between 6 and 24 months in the PCS group. Renal markers were also altered in PCS: cystatin C (p=0.014) and TFF3 (p=0.002 & 0.014) were elevated, while OPN decreased between 6 and 12 months (p=0.034).
Conclusions: Post-hospitalisation PCS is associated within increased markers of thrombosis, indicating persistent platelet and endothelial activation, impaired fibrinolysis and evidence of renal stress up to two years post-infection. We found no change in markers of vasomotor control except for arginine, the ‘recovery’ of which over time may reflect partial vascular restoration and warrants further investigation.
Aims: To assess the long-term impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection on plasma biomarkers of endothelial, thrombotic and renal function.
Methods: Plasma samples were obtained from prospective observational cohort studies of patients previously infected with SARS-CoV-2, stratified by recovery status. Patients not previously hospitalised provided a single sample at 3–36 months post-infection (recovered: n=22; PCS: n=34-35). Post-hospitalisation patients provided samples at 6, 12, and 24 months (recovered: n=4-6; PCS: n=8-16). Commercial ELISAs and colorimetric assays quantified markers of endothelial-mediated vasomotor control (ET-1, nitrate/nitrite, prostacyclin, ADMA, arginine), thrombosis (sCD40L, P-selectin, PSGL-1, tPA, PAI-1, D-dimer) and renal injury (uromodulin, NGAL, cystatin C, TFF3, OPN). Statistical analysis used a mixed-effects model with Dunnett’s test to correct for multiple comparisons.
Results: In non-hospitalised cohorts, no significant differences were found between groups across any biomarker. In the post-hospitalisation cohort, arginine levels increased in the recovered group at 24 months (p=0.035; trend vs PCS group p=0.051), with no changes in other markers of endothelial function (Fig. 1). In the PCS group, higher plasma levels of P-selectin (p=0.021), PSGL-1 (p=0.0006), PAI-1 (p=0.018), tPA (p=0.006 & 0.002) and D-dimer (trend; p=0.087) were seen in comparison with the recovered group (Fig. 1). Longitudinally, P-selectin (p=0.003), sCD40L (p=0.013), and PAI-1 (p=0.017) increased between 6 and 24 months in the PCS group. Renal markers were also altered in PCS: cystatin C (p=0.014) and TFF3 (p=0.002 & 0.014) were elevated, while OPN decreased between 6 and 12 months (p=0.034).
Conclusions: Post-hospitalisation PCS is associated within increased markers of thrombosis, indicating persistent platelet and endothelial activation, impaired fibrinolysis and evidence of renal stress up to two years post-infection. We found no change in markers of vasomotor control except for arginine, the ‘recovery’ of which over time may reflect partial vascular restoration and warrants further investigation.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adrenal Zona Glomerulosa Long Form Leptin Receptor (LepRb) Protects from Leptin-Mediated Vascular Disorders in Female Mice
Ono Yoichi, Kennard Simone, Breault David, Belin De Chantemele Eric
A Novel Tool for Evaluating Endothelial Function: Plethysmographic Flow-mediated Vasodilation (pFMD)Kishimoto Shinji, Itarashiki Tomomasa, Higashi Yukihito, Maruhashi Tatsuya, Kajikawa Masato, Mizobuchi Aya, Harada Takahiro, Yamaji Takayuki, Nakano Yukiko, Mohamad Yusoff Farina, Yada Tomohiko