Final ID: Su4105
The impact of viral infection with SARS-CoV-2 and influenza on plasma endothelial, thrombotic and renal biomarkers
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: SARS-CoV-2 and influenza infections are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events. While the underlying mechanisms remain incompletely defined, mounting evidence points towards endothelial dysfunction and thrombotic activation, caused either directly or indirectly by viral infection.
Aims: We sought to characterise the temporal effects of mild SARS-CoV-2 and H3N2 influenza infection on plasma biomarkers of endothelial, thrombotic and renal function.
Methods: Plasma samples were collected from healthy volunteers enrolled in SARS-CoV-2 (n=7-10) and H3N2 (n=7-11) human challenge studies. Samples were taken at baseline (day 0/–1) and at days 3, 7, 10, 14, and 28 post-inoculation. Commercial ELISAs/colorimetric assays were used to quantify endothelial dysfunction using biomarkers of endothelial-mediated vasomotor control (endothelin-1, nitrate/nitrite, prostacyclin, ADMA, arginine), thrombosis (sCD40L, P-selectin, PSGL-1, tPA, PAI-1, D-dimer, factor IX), and renal function (uromodulin, NGAL, cystatin C, TFF3, OPN). One-way ANOVA, or a mixed effects model, and Dunnet’s test to correct for multiple comparisons, were used to compare baseline biomarker levels with levels at subsequent timepoints.
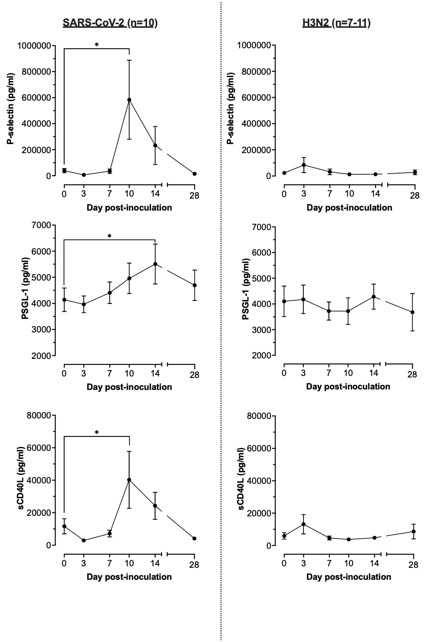
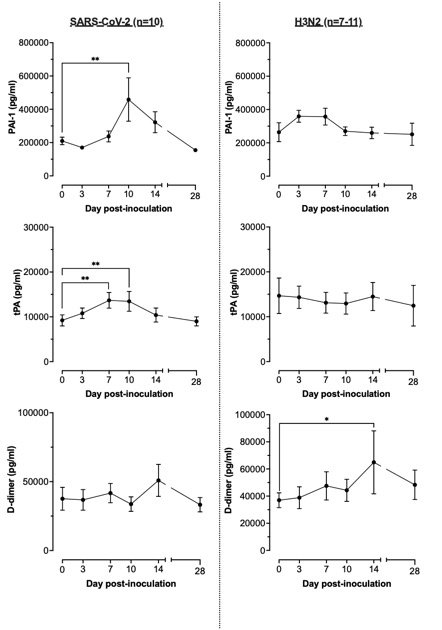
Results: Infection with SARS-CoV-2 significantly increased thrombosis biomarkers (Figs. 1 & 2): P-selectin (p=0.025), PSGL-1 (p=0.024), sCD40L (p=0.048), PAI-1 (p=0.008) and tPA (p=0.006 & 0.008) at days 7 to 14. In contrast, infection with H3N2 resulted in a significant increase in D-dimer levels at day 14 (p=0.025) and no changes in other biomarkers of thrombosis. No changes from baseline were detected in biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction in either group. Uromodulin levels declined by day 28 in the SARS-CoV-2 group (p=0.034), otherwise no changes in biomarkers of renal function were noted in either group.
Conclusions: There are two striking results of this study. Firstly, that for both H3N2 and SARS-CoV-2 infection, it was markers of platelet activation/thrombosis, without changes in endothelial or renal function, that increased after infection. Secondly, that a broader spectrum of these markers was increased in volunteers infected with SARS-CoV-2. These findings suggest distinct thrombotic mechanisms are activated by SARS-CoV-2 and H3N2 and support further investigation of thrombotic profiles in patients infected with other respiratory viruses allowing for strategies to identify and mitigate associated cardiovascular events.
Aims: We sought to characterise the temporal effects of mild SARS-CoV-2 and H3N2 influenza infection on plasma biomarkers of endothelial, thrombotic and renal function.
Methods: Plasma samples were collected from healthy volunteers enrolled in SARS-CoV-2 (n=7-10) and H3N2 (n=7-11) human challenge studies. Samples were taken at baseline (day 0/–1) and at days 3, 7, 10, 14, and 28 post-inoculation. Commercial ELISAs/colorimetric assays were used to quantify endothelial dysfunction using biomarkers of endothelial-mediated vasomotor control (endothelin-1, nitrate/nitrite, prostacyclin, ADMA, arginine), thrombosis (sCD40L, P-selectin, PSGL-1, tPA, PAI-1, D-dimer, factor IX), and renal function (uromodulin, NGAL, cystatin C, TFF3, OPN). One-way ANOVA, or a mixed effects model, and Dunnet’s test to correct for multiple comparisons, were used to compare baseline biomarker levels with levels at subsequent timepoints.
Results: Infection with SARS-CoV-2 significantly increased thrombosis biomarkers (Figs. 1 & 2): P-selectin (p=0.025), PSGL-1 (p=0.024), sCD40L (p=0.048), PAI-1 (p=0.008) and tPA (p=0.006 & 0.008) at days 7 to 14. In contrast, infection with H3N2 resulted in a significant increase in D-dimer levels at day 14 (p=0.025) and no changes in other biomarkers of thrombosis. No changes from baseline were detected in biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction in either group. Uromodulin levels declined by day 28 in the SARS-CoV-2 group (p=0.034), otherwise no changes in biomarkers of renal function were noted in either group.
Conclusions: There are two striking results of this study. Firstly, that for both H3N2 and SARS-CoV-2 infection, it was markers of platelet activation/thrombosis, without changes in endothelial or renal function, that increased after infection. Secondly, that a broader spectrum of these markers was increased in volunteers infected with SARS-CoV-2. These findings suggest distinct thrombotic mechanisms are activated by SARS-CoV-2 and H3N2 and support further investigation of thrombotic profiles in patients infected with other respiratory viruses allowing for strategies to identify and mitigate associated cardiovascular events.
More abstracts on this topic:
Atrial Fibrillation and COVID-19: Disparities in Mortality and Clinical Outcomes
Sandhu Navneet, Sandhu Onkar, Joshi Bipin
A distinct clot transcriptomic signature is associated with atrial fibrillation-derived ischemic stroke in the INSIGHT RegistrySeah Carina, Rivet Dennis, Fraser Justin, Kellner Christopher, Devarajan Alex, Vicari James, Dabney Alan, Baltan Selva, Sohrabji Farida, Pennypacker Keith, Nanda Ashish, Woodward Britton