Final ID: WMP3
A retrospective analysis of Tenecteplase vs Alteplase for the treatment of central retinal artery occlusion
Abstract Body: Introduction: There is no established acute intervention for central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) which often results in poor visual outcomes. Intravenous Alteplase (tPA) has emerged as a promising acute treatment for CRAO. Intravenous Tenecteplase (TNK) is non-inferior to tPA in the acute treatment of ischemic stroke. However, there is limited data on its use for CRAO.
Methods: Retrospective data of patients from January 2016 to February 2024 with CRAO who received TNK or tPA and a medical management (MM) matched cohort were collected, including demographics, suspected etiology of CRAO, presenting and final central visual acuity, symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH), vitreous hemorrhage, and neovascularization. In cases where the presenting central visual acuity was not quantified, it was assigned a value by the investigator based on qualitative descriptions. Visual acuity was converted to LogMAR units to enable quantitative comparison, where the ability to count fingers was assigned a value of 1.85, hand motions 2.28, light perception 2.70, and no light perception 3.00. Functional visual recovery was defined as a final visual acuity of 20/100 or better. Patients without a documented final central visual acuity were excluded from the analysis. T-test, chi-square, and ANOVA were used for statistical analysis.
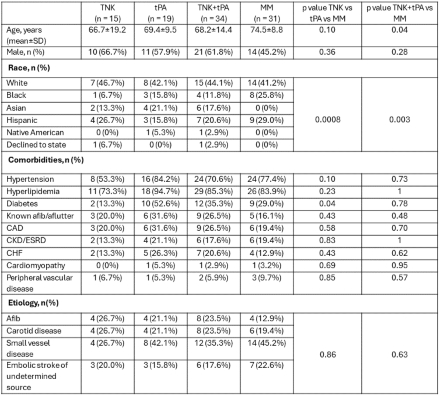
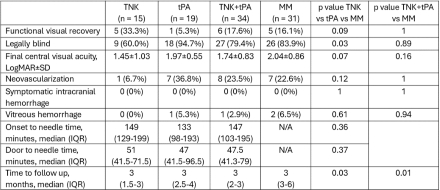
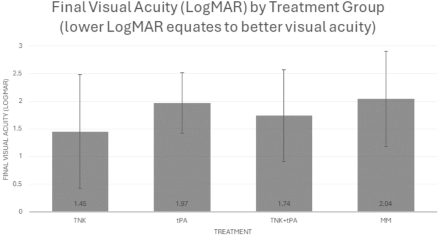
Results: A total of 15 TNK, 19 tPA, and 31 MM patients were included. MM patients were older than the thrombolytic patients (74.5±8.8 vs. 68.2±14.4 yrs) p=0.04. More patients had diabetes in tPA (52.6%) vs TNK (13.3%) vs MM (29.0%) p=0.04. There was no difference in suspected etiologies of CRAO. Functional visual recovery trended toward improvement in TNK (33.3%) vs. tPA (5.3%) vs. MM (16.1%) p=0.09. Quantitative assessment of final visual acuity by LogMAR trended toward improvement in TNK (1.45±1.03) vs. tPA (1.97±0.55) vs. MM (2.04±0.86) p=0.07. Fewer patients were legally blind in TNK (60.0%) vs. tPA (94.7%) vs. MM (83.9%) p=0.03. There was no difference in sICH, vitreous hemorrhage, or neovascularization.
Conclusions: This is the first case series comparing CRAO treated with TNK, tPA, and MM. There were fewer patients who were legally blind and there was a trend toward improved final visual acuity in the TNK group. There was no difference in sICH, vitreous hemorrhage, or neovascularization. This study adds to the growing body of evidence that TNK can be an effective and safe treatment for CRAO.
Methods: Retrospective data of patients from January 2016 to February 2024 with CRAO who received TNK or tPA and a medical management (MM) matched cohort were collected, including demographics, suspected etiology of CRAO, presenting and final central visual acuity, symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH), vitreous hemorrhage, and neovascularization. In cases where the presenting central visual acuity was not quantified, it was assigned a value by the investigator based on qualitative descriptions. Visual acuity was converted to LogMAR units to enable quantitative comparison, where the ability to count fingers was assigned a value of 1.85, hand motions 2.28, light perception 2.70, and no light perception 3.00. Functional visual recovery was defined as a final visual acuity of 20/100 or better. Patients without a documented final central visual acuity were excluded from the analysis. T-test, chi-square, and ANOVA were used for statistical analysis.
Results: A total of 15 TNK, 19 tPA, and 31 MM patients were included. MM patients were older than the thrombolytic patients (74.5±8.8 vs. 68.2±14.4 yrs) p=0.04. More patients had diabetes in tPA (52.6%) vs TNK (13.3%) vs MM (29.0%) p=0.04. There was no difference in suspected etiologies of CRAO. Functional visual recovery trended toward improvement in TNK (33.3%) vs. tPA (5.3%) vs. MM (16.1%) p=0.09. Quantitative assessment of final visual acuity by LogMAR trended toward improvement in TNK (1.45±1.03) vs. tPA (1.97±0.55) vs. MM (2.04±0.86) p=0.07. Fewer patients were legally blind in TNK (60.0%) vs. tPA (94.7%) vs. MM (83.9%) p=0.03. There was no difference in sICH, vitreous hemorrhage, or neovascularization.
Conclusions: This is the first case series comparing CRAO treated with TNK, tPA, and MM. There were fewer patients who were legally blind and there was a trend toward improved final visual acuity in the TNK group. There was no difference in sICH, vitreous hemorrhage, or neovascularization. This study adds to the growing body of evidence that TNK can be an effective and safe treatment for CRAO.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Contactless and Automated Approach to the Acute Stroke Assessment
Saadat Moh, Titus Ryan, Verkuilen Haley, Fleming Phil, Sur Sanjib, Sen Souvik
Hemorrhagic Transformation in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Diabetes: Is it Different between Alteplase and Tenecteplase?Hegde Sheetal, Hernandez Roberto, Salter Amber, Ray Bappaditya
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)