Final ID: MP658
Incidence and Causes of Sudden Deaths with History of Atrial Fibrillation and Effect of Anticoagulant/Antiplatelet Therapy on Hemorrhagic Causes: from the POST SCD Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common arrhythmia, and studies have reported increased risk of heart failure and sudden cardiac death (SCD). However, the proportion of SCDs with AF due to hemorrhage is unknown because these studies presumed cardiac/arrhythmic causes without autopsy; these are now considered presumed SCD (pSCD) by international consensus.
Research Question
To determine autopsy-defined causes of sudden death in victims with AF and on anticoagulant (AC) therapy in San Francisco (SF) County.
Methods
POST SCD is an ongoing prospective study using autopsy and clinical records to adjudicate arrhythmic vs. non-arrhythmic causes among 1,120 incident pSCDs aged 18-90 years meeting WHO criteria in SF County from 2/1/2011-1/1/2024. For rate calculations, 525 (i.e., every incident) pSCDs in the initial cohort (2/1/2011-3/1/2014) were used, with at-risk person-years estimated from US census and AF prevalence data. For analysis of causes, 595 additional pSCDs (incident cases approximately every third day) were added from the extended cohort (3/1/2014-1/1/2024). A composite of intracranial, gastrointestinal, or other hemorrhage was classified as hemorrhagic sudden deaths. Clinical records were used to identify AF and atrial flutter (AFL) diagnoses and AC or antiplatelet (AP) use.
Results
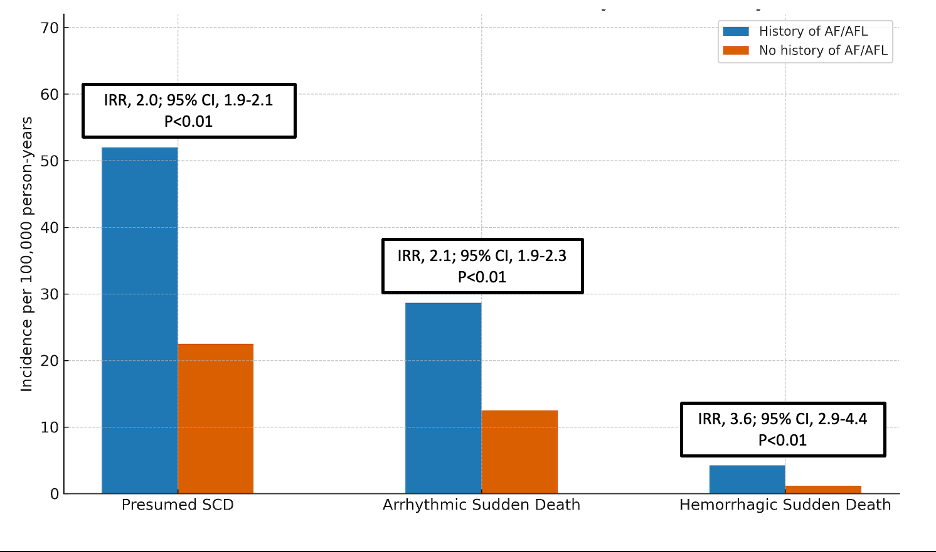
Of 1,120 total pSCDs, 78 (7%) had a diagnosis of AF/AFL; these cases were older than those without AF/AFL (70 vs 58 years, p<0.01) and 31/63 cases with CHADS2-VASC≥2 (49%) were appropriately prescribed AC. Using an estimated AF prevalence of 4.48% in SF County, 3-year age-adjusted incidence rate ratio (IRR) of hemorrhagic sudden death for individuals with AF/AFL was 3.6 (95% CI 2.9-4.4, p<0.01) vs those without AF/AFL. pSCDs with AF/AFL were more likely to die of arrhythmia secondary to cardiomyopathy (18.4% vs 8.9%, p=0.01) but not hemorrhagic sudden death (p=0.57). However, pSCDs who were prescribed AC/AP were twice as likely to have hemorrhagic sudden death vs those not on therapy (6.9% vs 3.5%, p=0.03).
Conclusion
In this 13-year countywide postmortem study of sudden deaths, individuals with AF/AFL had an over-3-fold higher age-adjusted incidence of hemorrhagic sudden death. AC or AP therapy was associated with a two-fold higher risk of hemorrhagic cause of sudden death. Because sudden deaths in AC trials for AF were presumed cardiac, the real-world risk of hemorrhagic death was likely underestimated and thus changes the risk-benefit calculus of AC for AF.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common arrhythmia, and studies have reported increased risk of heart failure and sudden cardiac death (SCD). However, the proportion of SCDs with AF due to hemorrhage is unknown because these studies presumed cardiac/arrhythmic causes without autopsy; these are now considered presumed SCD (pSCD) by international consensus.
Research Question
To determine autopsy-defined causes of sudden death in victims with AF and on anticoagulant (AC) therapy in San Francisco (SF) County.
Methods
POST SCD is an ongoing prospective study using autopsy and clinical records to adjudicate arrhythmic vs. non-arrhythmic causes among 1,120 incident pSCDs aged 18-90 years meeting WHO criteria in SF County from 2/1/2011-1/1/2024. For rate calculations, 525 (i.e., every incident) pSCDs in the initial cohort (2/1/2011-3/1/2014) were used, with at-risk person-years estimated from US census and AF prevalence data. For analysis of causes, 595 additional pSCDs (incident cases approximately every third day) were added from the extended cohort (3/1/2014-1/1/2024). A composite of intracranial, gastrointestinal, or other hemorrhage was classified as hemorrhagic sudden deaths. Clinical records were used to identify AF and atrial flutter (AFL) diagnoses and AC or antiplatelet (AP) use.
Results
Of 1,120 total pSCDs, 78 (7%) had a diagnosis of AF/AFL; these cases were older than those without AF/AFL (70 vs 58 years, p<0.01) and 31/63 cases with CHADS2-VASC≥2 (49%) were appropriately prescribed AC. Using an estimated AF prevalence of 4.48% in SF County, 3-year age-adjusted incidence rate ratio (IRR) of hemorrhagic sudden death for individuals with AF/AFL was 3.6 (95% CI 2.9-4.4, p<0.01) vs those without AF/AFL. pSCDs with AF/AFL were more likely to die of arrhythmia secondary to cardiomyopathy (18.4% vs 8.9%, p=0.01) but not hemorrhagic sudden death (p=0.57). However, pSCDs who were prescribed AC/AP were twice as likely to have hemorrhagic sudden death vs those not on therapy (6.9% vs 3.5%, p=0.03).
Conclusion
In this 13-year countywide postmortem study of sudden deaths, individuals with AF/AFL had an over-3-fold higher age-adjusted incidence of hemorrhagic sudden death. AC or AP therapy was associated with a two-fold higher risk of hemorrhagic cause of sudden death. Because sudden deaths in AC trials for AF were presumed cardiac, the real-world risk of hemorrhagic death was likely underestimated and thus changes the risk-benefit calculus of AC for AF.
More abstracts on this topic:
Abdominal Counter-Constriction Versus Abdominal Binding as Hemodynamic Adjuncts to Circumferential Thoracic Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Paradis Aidan, Paradis Norman, Gaddy David, Moodie Karen, Mader Timothy, Dufresne Alexandre, Couturier Christine, Dufresne Simon, Davis Daniel, Sims Christopher
Antithrombotic trends before and after publication of randomized clinical trials in cervical artery dissection: A secondary analysis of the STOP-CAD StudyPenckofer Mary, Salehi Omran Setareh, Seiffge David, Arnold Marcel, Marialuisa Zedde, Zubair Adeel, Marto Joao Pedro, Ghannam Malik, Engelter Stefan, Traenka Christopher, Mac Grory Brian, Shu Liqi, Kam Wayneho, Elnazeir Marwa, Romoli Michele, Saleh Velez Faddi, Siegler James, Strelecky Lukas, Yaghi Shadi, Henninger Nils, Muppa Jayachandra, Bakradze Ekaterina, Heldner Mirjam, Katheryna Antonenko