Final ID: Sa2035
Cardiovascular Outcomes of Oral Semaglutide in High Risk Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular events, particularly in high-risk patients—those with coexisting cardiovascular disease (CVD) or chronic kidney disease (CKD). Oral semaglutide, a novel glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, has demonstrated strong efficacy in glycemic control and potential cardiovascular benefits in T2DM. However, its impact on cardiovascular outcomes in T2DM patients with coexisting CVD or CKD remains to be fully elucidated.
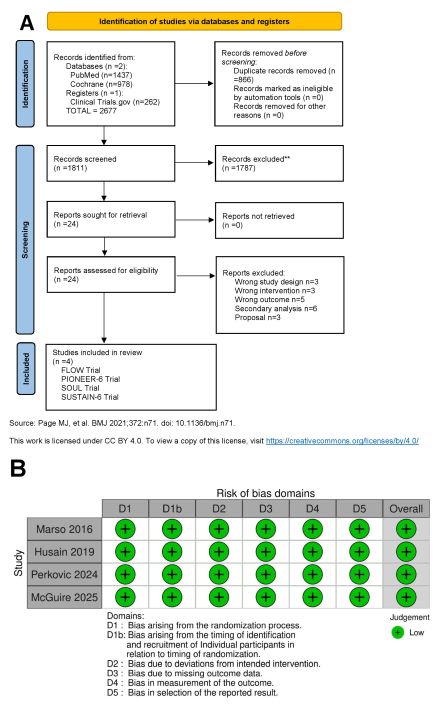
Methods: A comprehensive literature search of PubMed, Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov was conducted to identify randomized, placebo-controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating oral semaglutide in T2DM patients aged over 50 years with either CVD or CKD. Primary outcomes included all-cause mortality, major cardiovascular events, non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), cardiovascular death, and non-fatal stroke. The secondary outcomes assessed were adverse events of special interest, such as malignant neoplasms and acute pancreatitis. A random-effects model using the Mantel-Haenszel method was used to calculate pooled hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
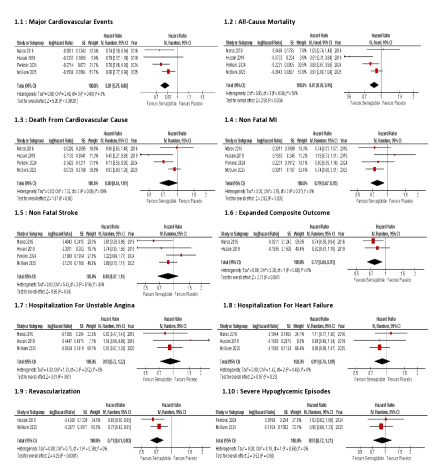
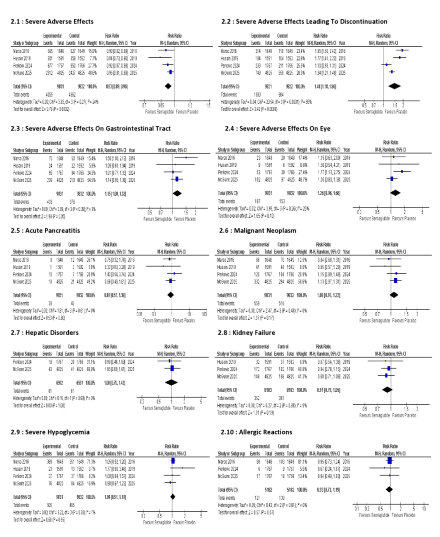
Results: Four RCTs comprising 19,663 patients (9,831 in the semaglutide group; 9,832 in the placebo group) were included. Oral semaglutide significantly reduced all-cause mortality (HR: 0.87; 95% CI: 0.78–0.95; p = 0.004), major cardiovascular events (HR: 0.81; 95% CI: 0.75–0.88; p < 0.00001), and non-fatal MI (HR: 0.79; 95% CI: 0.67–0.93; p = 0.005) compared to placebo. No significant differences were observed for cardiovascular death (HR: 0.80; 95% CI: 0.64–1.01), non-fatal stroke (HR: 0.88; 95% CI: 0.67–1.15), or heart failure hospitalization (HR: 0.91; 95% CI: 0.76–1.09). All adverse events of special interest, including malignant neoplasms (RR: 1.08; p = 0.17) and acute pancreatitis (RR: 0.89; p = 0.60), did not differ significantly between groups.
Conclusion: Oral semaglutide is associated with significant reductions in all-cause mortality, major cardiovascular events, and non-fatal myocardial infarction in high-risk T2DM patients with CVD or CKD, supporting its role as a cardioprotective agent in this population. Importantly, semaglutide did not increase the risk of serious adverse events, underscoring its safety. These findings support broader consideration of oral semaglutide in cardiovascular risk management for high-risk T2DM patients.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search of PubMed, Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov was conducted to identify randomized, placebo-controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating oral semaglutide in T2DM patients aged over 50 years with either CVD or CKD. Primary outcomes included all-cause mortality, major cardiovascular events, non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), cardiovascular death, and non-fatal stroke. The secondary outcomes assessed were adverse events of special interest, such as malignant neoplasms and acute pancreatitis. A random-effects model using the Mantel-Haenszel method was used to calculate pooled hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results: Four RCTs comprising 19,663 patients (9,831 in the semaglutide group; 9,832 in the placebo group) were included. Oral semaglutide significantly reduced all-cause mortality (HR: 0.87; 95% CI: 0.78–0.95; p = 0.004), major cardiovascular events (HR: 0.81; 95% CI: 0.75–0.88; p < 0.00001), and non-fatal MI (HR: 0.79; 95% CI: 0.67–0.93; p = 0.005) compared to placebo. No significant differences were observed for cardiovascular death (HR: 0.80; 95% CI: 0.64–1.01), non-fatal stroke (HR: 0.88; 95% CI: 0.67–1.15), or heart failure hospitalization (HR: 0.91; 95% CI: 0.76–1.09). All adverse events of special interest, including malignant neoplasms (RR: 1.08; p = 0.17) and acute pancreatitis (RR: 0.89; p = 0.60), did not differ significantly between groups.
Conclusion: Oral semaglutide is associated with significant reductions in all-cause mortality, major cardiovascular events, and non-fatal myocardial infarction in high-risk T2DM patients with CVD or CKD, supporting its role as a cardioprotective agent in this population. Importantly, semaglutide did not increase the risk of serious adverse events, underscoring its safety. These findings support broader consideration of oral semaglutide in cardiovascular risk management for high-risk T2DM patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Real-world Evaluation of Longitudinal Healthcare Expenses in a Health System Registry of Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease Enabled by the 21st Century Cures Act
Dhingra Lovedeep, Aminorroaya Arya, Pedroso Aline, Rajpura Jigar, Mehanna Sherif, Tonnu-mihara Ivy, Khera Rohan
Arteriovenous fistula creation results in cardiac dysfunction and remodeling in a uremic pig modelKane Jamie, Collins Jeremy, Lee Timmy, Misra Sanjay, Singh Prabh, Kilari Sreenivasulu, Baranwal Gaurav, Naskar Atanu, Montonye Dan, Lutgens Esther, Wang Ying, Negm Ahmed