Final ID: Su2063
Fish-Eye Disease: A Case Report
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Description of Case:
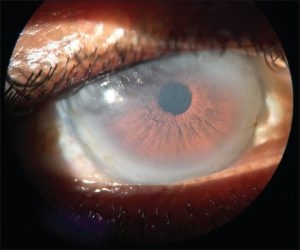
A 26-year-old female was referred to cardiology with bilateral corneal opacifications of four years’ duration, with no change in her visual acuity. Her workup revealed a high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) level of less than 10 mg/dL and a low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level of 182 mg/dL, prompting genetic evaluation for disorders of lipid metabolism. She was found to have a heterozygous mutation, c.440C>T (p.Thr147Ile), and variant of uncertain significance, c.715G>A (p.Gly239Ser) in the lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) gene. Additional studies showed low-normal serum cholesterol esters and no evidence of hematologic abnormalities or renal dysfunction. Based on these findings and her corneal opacifications, a clinical diagnosis of partial LCAT deficiency, or Fish-Eye Disease (FED), was made. Given her lipid abnormalities and the increased risk of atherosclerosis associated with FED, a high-potency statin was prescribed. Her LDL-C decreased from 182 mg/dL to 124 mg/dL.
Discussion:
FED is an autosomal recessive disorder of lipid metabolism caused by mutations in the LCAT gene, resulting in partial loss of enzymatic activity. LCAT catalyzes the esterification of free cholesterol, a key step in reverse cholesterol transport; esterification is lost in HDL-C (i.e., alpha activity) and conserved in lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein B (i.e., beta activity). Consequently, FED is biochemically characterized by reduced HDL-C and plasma cholesterol esters and elevated LDL-C, very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, and/or plasma unesterified cholesterol. Clinically, these patients typically present with worsening corneal opacities and decreased visual acuity and are at increased risk of atherosclerosis due to preserved beta activity. In contrast, patients may have complete loss of LCAT activity and present with more severe sequelae, a disease known as familial LCAT deficiency (FLD). Absent LCAT activity leads to unesterified cholesterol accumulation, which disrupts red blood cell membranes and deposits in the renal mesangium, leading to hemolytic anemia and renal dysfunction. It is therefore important to promptly determine the degree of LCAT activity loss and manage patients accordingly. Measuring LCAT activity, both alpha and beta, is the best diagnostic test. FED should be treated primarily with lipid-lowering medications, whereas FLD requires monitoring for anemia and renal dysfunction.
A 26-year-old female was referred to cardiology with bilateral corneal opacifications of four years’ duration, with no change in her visual acuity. Her workup revealed a high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) level of less than 10 mg/dL and a low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level of 182 mg/dL, prompting genetic evaluation for disorders of lipid metabolism. She was found to have a heterozygous mutation, c.440C>T (p.Thr147Ile), and variant of uncertain significance, c.715G>A (p.Gly239Ser) in the lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) gene. Additional studies showed low-normal serum cholesterol esters and no evidence of hematologic abnormalities or renal dysfunction. Based on these findings and her corneal opacifications, a clinical diagnosis of partial LCAT deficiency, or Fish-Eye Disease (FED), was made. Given her lipid abnormalities and the increased risk of atherosclerosis associated with FED, a high-potency statin was prescribed. Her LDL-C decreased from 182 mg/dL to 124 mg/dL.
Discussion:
FED is an autosomal recessive disorder of lipid metabolism caused by mutations in the LCAT gene, resulting in partial loss of enzymatic activity. LCAT catalyzes the esterification of free cholesterol, a key step in reverse cholesterol transport; esterification is lost in HDL-C (i.e., alpha activity) and conserved in lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein B (i.e., beta activity). Consequently, FED is biochemically characterized by reduced HDL-C and plasma cholesterol esters and elevated LDL-C, very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, and/or plasma unesterified cholesterol. Clinically, these patients typically present with worsening corneal opacities and decreased visual acuity and are at increased risk of atherosclerosis due to preserved beta activity. In contrast, patients may have complete loss of LCAT activity and present with more severe sequelae, a disease known as familial LCAT deficiency (FLD). Absent LCAT activity leads to unesterified cholesterol accumulation, which disrupts red blood cell membranes and deposits in the renal mesangium, leading to hemolytic anemia and renal dysfunction. It is therefore important to promptly determine the degree of LCAT activity loss and manage patients accordingly. Measuring LCAT activity, both alpha and beta, is the best diagnostic test. FED should be treated primarily with lipid-lowering medications, whereas FLD requires monitoring for anemia and renal dysfunction.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Genome-wide CRISPRi Screen Implicates Coronary Artery Disease GWAS Genes as Key Regulators of Adventitial Fibroblast Proliferation
Jackson William, Zhu Ashley, Gu Wenduo, Berezowitz Alexa, Iyer Meghana, Cheng Paul
A Novel Approach to Manage Hypercholesterolemia: The Veterans Affairs Lipid Optimization Reimagined Quality Improvement (VALOR-QI) ProgramDjousse Luc, Leesch Tharen, Pena David, Gaziano Michael, Ward Rachel, Wellman Helen, Yel Nedim, Santos Abigail, Delgrande Jen, Fink Abigail, Colson Kristin, Pan Eddie