Final ID: MP2174
Comparative Study of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Prediction: Conventional QRISK3 vs. Enhanced Machine Learning Models Combined with Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) Algorithm
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is one of the biggest causes of mortality worldwide. Risk stratification for early detection is essential for the primary prevention of CAD. QRISK3 is known to overestimate future CAD risk in some populations, resulting in unnecessary preventive treatment and reduced cost-effectiveness and safety. Combining machine learning model with the metaheuristic optimisation approach using the PSO algorithm may outperform QRISK3 in predicting CAD. It improves performance by selecting the best-performing subset of features related to clinical outcomes.
Research Question Does the performance of Machine Learning Models Combined with PSO Algorithm for Feature Selection as a Metaheuristic Optimisation Approach in Predicting Coronary Arterial Disease using the UK Biobank dataset outperform the QRISK3 calculator?
Aims This study is to assess the accuracy of QRISK3 in predicting CAD using the UK Biobank dataset. It aims to evaluate the efficacy of machine learning models on the identical dataset for predicting CAD. The work utilises the PSO algorithm for feature selection to identify the optimal subset of features from the UK Biobank dataset.
Methods This study utilises data from the UK Biobank. The dataset consists of 348,015 participants aged 24-84 with no prior diagnosis of CAD. The performance of both QRISK3 and machine learning models was evaluated separately using ROC analysis. Several machine learning models were employed: Logistic Regression, Decision Tree, Random Forest, Naïve Bayes, and Gradient Boosting. The dataset was split into training and test sets with a ratio of 4:1 for the machine learning models. Each model has been developed by adding a PSO algorithm to enhance the model's classification accuracy.
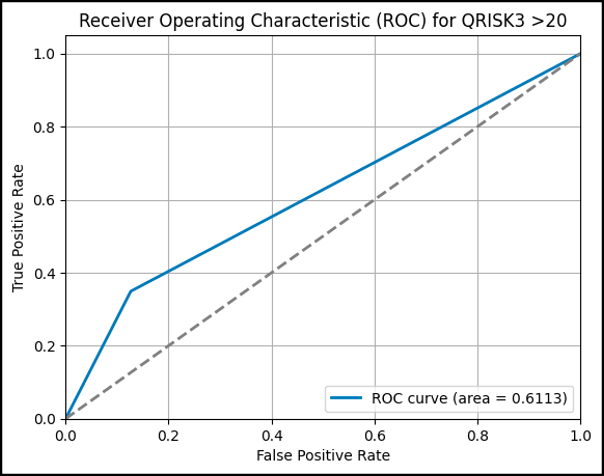
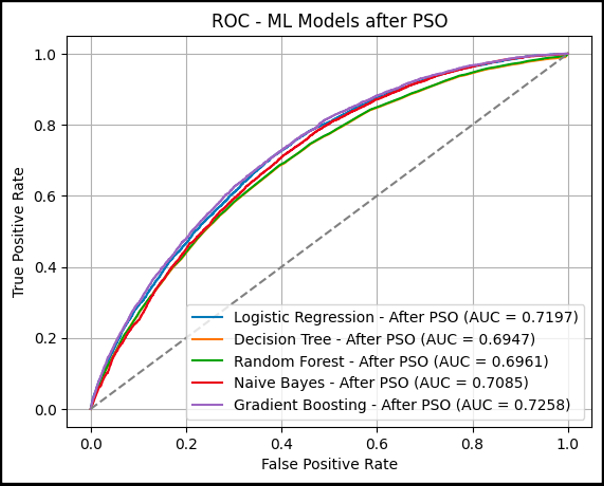
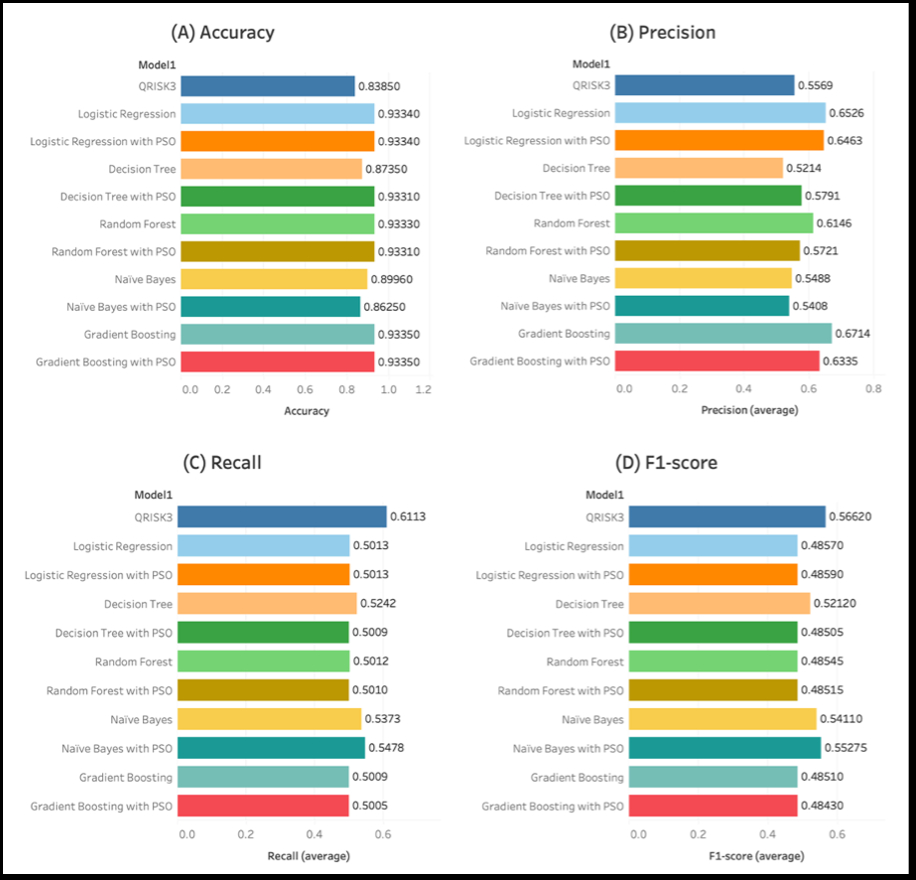
Results Out of the total 348,015 participants, 23,136 individuals (6.64%) were diagnosed with CAD within 10 years following their first visit, while 324,879 individuals (93.4%) did not develop CAD. The AUC value of the QRISK3 prediction is 0.6113, while the combined machine learning models using the PSO algorithm using the gradient boosting model achieve an AUC of 0.7258, showing better performance.
Conclusions This study shows hybrid machine learning models optimised with the PSO algorithm can better predict CAD than QRISK3. These ML models can effectively identify high-risk CAD patients, allowing for more personalised preventative strategies and supporting policymakers in implementing lifestyle change recommendations.
Research Question Does the performance of Machine Learning Models Combined with PSO Algorithm for Feature Selection as a Metaheuristic Optimisation Approach in Predicting Coronary Arterial Disease using the UK Biobank dataset outperform the QRISK3 calculator?
Aims This study is to assess the accuracy of QRISK3 in predicting CAD using the UK Biobank dataset. It aims to evaluate the efficacy of machine learning models on the identical dataset for predicting CAD. The work utilises the PSO algorithm for feature selection to identify the optimal subset of features from the UK Biobank dataset.
Methods This study utilises data from the UK Biobank. The dataset consists of 348,015 participants aged 24-84 with no prior diagnosis of CAD. The performance of both QRISK3 and machine learning models was evaluated separately using ROC analysis. Several machine learning models were employed: Logistic Regression, Decision Tree, Random Forest, Naïve Bayes, and Gradient Boosting. The dataset was split into training and test sets with a ratio of 4:1 for the machine learning models. Each model has been developed by adding a PSO algorithm to enhance the model's classification accuracy.
Results Out of the total 348,015 participants, 23,136 individuals (6.64%) were diagnosed with CAD within 10 years following their first visit, while 324,879 individuals (93.4%) did not develop CAD. The AUC value of the QRISK3 prediction is 0.6113, while the combined machine learning models using the PSO algorithm using the gradient boosting model achieve an AUC of 0.7258, showing better performance.
Conclusions This study shows hybrid machine learning models optimised with the PSO algorithm can better predict CAD than QRISK3. These ML models can effectively identify high-risk CAD patients, allowing for more personalised preventative strategies and supporting policymakers in implementing lifestyle change recommendations.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Rare Case of Sequential Impella Mechanical Failures due to Infective Endocarditis Vegetations
Sawalski Cathryn, Seu Michelle, Darki Amir
Association of African Genetic Ancestry with Lipid Profile and Dyslipidemias in the Tobago Health StudyBeresford Ruel, Miljkovic Iva, Zmuda Joseph, Cvejkus Ryan, Wheeler Victor, Kuipers Allison