Final ID: Su3100
Platelet Transcriptomics-Enabled Identification of Acute Coronary Occlusion: A Risk Stratification Tool for Guiding Early Revascularization in NSTEMI
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) results from the rupture of coronary artery plaques and is driven by platelet activation, leading to non-obstructive thrombosis. Electrocardiographic (ECG) manifestations typically include ST-segment depression or T-wave inversion. However, a subgroup of ECG-diagnosed NSTEMI patients exhibits acute total occlusion (ATO) of culprit vessels. Current diagnostic tools lack the sensitivity to identify these patients, potentially delaying revascularization and contributing to adverse outcomes. Although platelet gene has been investigated as a liquid biomarker in oncology and pulmonary hypertension, its potential for early detection of ATO in NSTEMI patients remains unexplored.
Research Questions:
To develop a machine learning (ML) model integrating clinical parameters and platelet differential genes for early identification of ATO in NSTEMI patients.
Methods:
Peripheral blood was collected from 69 NSTEMI patients at admission. Platelet RNA-seq was performed to generate transcriptomic profiles. Coronary angiography divided patients into ATO and non-ATO groups. Based on LASSO-selected clinical features and platelet transcriptomes, three prediction models based on random forests were constructed. developed.: Clinical model, PLT model, and combined clinical-PLT (Final) model. Model discrimination was evaluated using AUC and compared with the published CAR Score model. Calibration curves and decision curve analysis (DCA) was used to assess the Final model’s calibration accuracy and clinical net benefit.
Results:
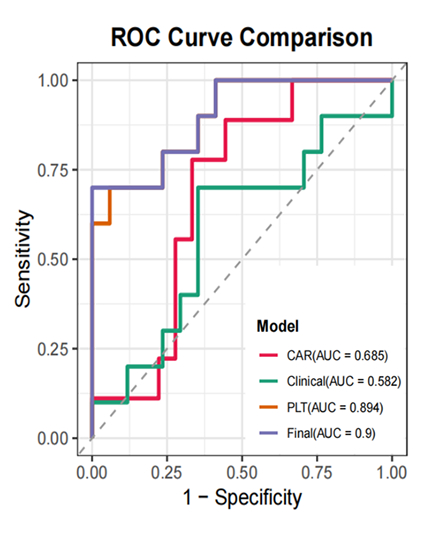
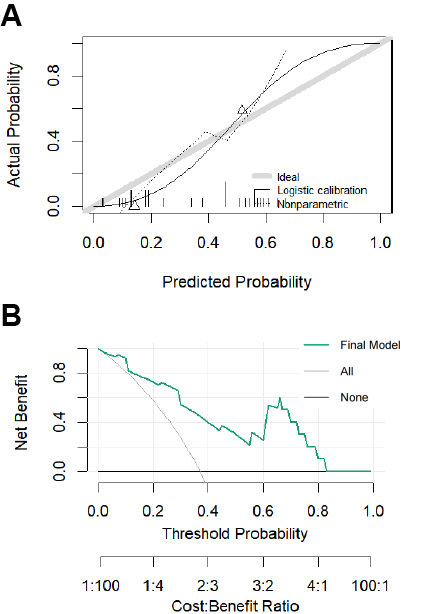
The study included 69 patients with NSTEMI, 26 patients (37.7%) had ATO of culprit vessels confirmed by coronary angiography. The Final model demonstrated superior predictive performance (AUC = 0.900). It significantly outperformed the clinical model (AUC = 0.582), the PLT model (AUC = 0.894), and the previously reported CAR model (AUC = 0.685). Calibration curves indicated that the Final model was well-calibrated (Brier score=0.157, Emax=0.288), and DCA further demonstrated clinical net benefit.
Conclusion:
This study integrates platelet transcriptomics and clinical data to establish a ML model that identifies key biomarkers and clinical features for recognizing ATO in NSTEMI. The model demonstrates reliable diagnostic accuracy and clinical applicability, providing a potential diagnostic tool to guide emergency revascularization decisions in ATO patients.
Non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) results from the rupture of coronary artery plaques and is driven by platelet activation, leading to non-obstructive thrombosis. Electrocardiographic (ECG) manifestations typically include ST-segment depression or T-wave inversion. However, a subgroup of ECG-diagnosed NSTEMI patients exhibits acute total occlusion (ATO) of culprit vessels. Current diagnostic tools lack the sensitivity to identify these patients, potentially delaying revascularization and contributing to adverse outcomes. Although platelet gene has been investigated as a liquid biomarker in oncology and pulmonary hypertension, its potential for early detection of ATO in NSTEMI patients remains unexplored.
Research Questions:
To develop a machine learning (ML) model integrating clinical parameters and platelet differential genes for early identification of ATO in NSTEMI patients.
Methods:
Peripheral blood was collected from 69 NSTEMI patients at admission. Platelet RNA-seq was performed to generate transcriptomic profiles. Coronary angiography divided patients into ATO and non-ATO groups. Based on LASSO-selected clinical features and platelet transcriptomes, three prediction models based on random forests were constructed. developed.: Clinical model, PLT model, and combined clinical-PLT (Final) model. Model discrimination was evaluated using AUC and compared with the published CAR Score model. Calibration curves and decision curve analysis (DCA) was used to assess the Final model’s calibration accuracy and clinical net benefit.
Results:
The study included 69 patients with NSTEMI, 26 patients (37.7%) had ATO of culprit vessels confirmed by coronary angiography. The Final model demonstrated superior predictive performance (AUC = 0.900). It significantly outperformed the clinical model (AUC = 0.582), the PLT model (AUC = 0.894), and the previously reported CAR model (AUC = 0.685). Calibration curves indicated that the Final model was well-calibrated (Brier score=0.157, Emax=0.288), and DCA further demonstrated clinical net benefit.
Conclusion:
This study integrates platelet transcriptomics and clinical data to establish a ML model that identifies key biomarkers and clinical features for recognizing ATO in NSTEMI. The model demonstrates reliable diagnostic accuracy and clinical applicability, providing a potential diagnostic tool to guide emergency revascularization decisions in ATO patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
A multi-proteomic Risk Score Predicts Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Angina and Non-obstructive Coronary Artery Disease
Huang Jingwen, Lodhi Rafia, Lodhi Saleha, Eldaidamouni Ahmed, Hritani Wesam, Hasan Muhammet, Haroun Nisreen, Quyyumi Arshed, Mehta Puja, Leon Ana, Ko Yi-an, Yang Huiying, Medina-inojosa Jose, Ahmed Taha, Harris Kristen, Alkhoder Ayman, Al Kasem Mahmoud
Advanced Diagnosis of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with AI-ECG and Differences Based on Race and SubtypeLewontin Myra, Perry Allison, Amos Kaitlyn, Ayers Michael, Kaplan Emily, Bilchick Kenneth, Barber Anita, Bivona Derek, Kramer Christopher, Parrish Anna, Mcclean Karen, Thomas Matthew