Final ID: Su3101
Platelet Transcriptomic for Coronary Artery Disease Diagnosis Using Machine Learning
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Non-invasive assessment of coronary artery disease (CAD) in patients with suspected angina is essential for guiding clinical management strategies. However, current non-invasive diagnostic models have limited accuracy, while invasive coronary angiography (ICA) carries procedural risks and contributes to unnecessary healthcare costs. Therefore, there is a critical need for a safe, cost-effective, and accurate non-invasive method to detect the presence of CAD. Platelet transcriptomes, which display distinct expression patterns in cardiovascular diseases, offer a promising opportunity for molecular-based, non-invasive diagnosis.
Research Objective:
This study aims to analyze platelet transcriptomic changes and develop a non-invasive model for CAD diagnosis by applying a machine learning (ML) approach to accurately assess the presence of CAD.
Methods:
This study included 291 patients with suspected angina undergoing ICA. Platelet bulk-RNA sequencing with DESeq2 differential analysis was used to compare the platelet features between 189 CAD patients with coronary stenosis ≥ 50% and 102 patients without coronary stenosis < 50%. LASSO regression algorithms identified CAD-associated genes. ML model was constructed based on the LASSO regression algorithm: PLT model (utilizing solely platelet transcriptomic features), Clinical risk factors model (age, gender, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, smoking), PLT + Clinical risk factors model, updated Diamond-Forrester (UDF) model. Diagnostic performance was assessed and compared using AUC.
Results:
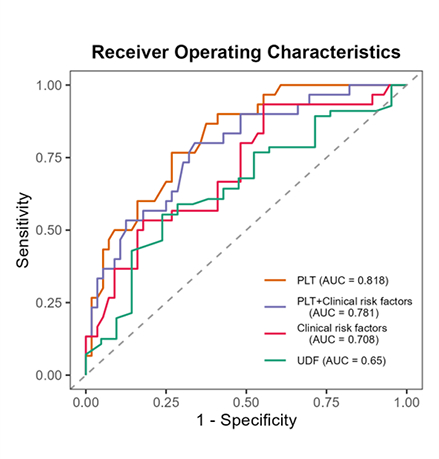
A total of 287 differentially expressed genes were identified between patients with coronary stenosis ≥ 50%) and those without coronary stenosis < 50%. The PLT model exhibited a sensitivity of 0.73, specificity of 0.77, and an AUC of 0.818 (95% CI, 0.73-0.90), outperforming the UDF model with an AUC of 0.625 (95% CI, 0.51-0.78), the Clinical risk factors model with an AUC of 0.708 (95% CI, 0.59-0.82), and the PLT + Clinical risk factors model with an AUC of 0.78 (95% CI, 0.68-0.88). Collectively, the PLT model demonstrates strong predictive accuracy.
Conclusion:
This pilot study, using a machine learning model based on platelet transcriptomic features, suggests a potential role for platelet transcriptomic as a non-invasive approach for the diagnosis of CAD.
Non-invasive assessment of coronary artery disease (CAD) in patients with suspected angina is essential for guiding clinical management strategies. However, current non-invasive diagnostic models have limited accuracy, while invasive coronary angiography (ICA) carries procedural risks and contributes to unnecessary healthcare costs. Therefore, there is a critical need for a safe, cost-effective, and accurate non-invasive method to detect the presence of CAD. Platelet transcriptomes, which display distinct expression patterns in cardiovascular diseases, offer a promising opportunity for molecular-based, non-invasive diagnosis.
Research Objective:
This study aims to analyze platelet transcriptomic changes and develop a non-invasive model for CAD diagnosis by applying a machine learning (ML) approach to accurately assess the presence of CAD.
Methods:
This study included 291 patients with suspected angina undergoing ICA. Platelet bulk-RNA sequencing with DESeq2 differential analysis was used to compare the platelet features between 189 CAD patients with coronary stenosis ≥ 50% and 102 patients without coronary stenosis < 50%. LASSO regression algorithms identified CAD-associated genes. ML model was constructed based on the LASSO regression algorithm: PLT model (utilizing solely platelet transcriptomic features), Clinical risk factors model (age, gender, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, smoking), PLT + Clinical risk factors model, updated Diamond-Forrester (UDF) model. Diagnostic performance was assessed and compared using AUC.
Results:
A total of 287 differentially expressed genes were identified between patients with coronary stenosis ≥ 50%) and those without coronary stenosis < 50%. The PLT model exhibited a sensitivity of 0.73, specificity of 0.77, and an AUC of 0.818 (95% CI, 0.73-0.90), outperforming the UDF model with an AUC of 0.625 (95% CI, 0.51-0.78), the Clinical risk factors model with an AUC of 0.708 (95% CI, 0.59-0.82), and the PLT + Clinical risk factors model with an AUC of 0.78 (95% CI, 0.68-0.88). Collectively, the PLT model demonstrates strong predictive accuracy.
Conclusion:
This pilot study, using a machine learning model based on platelet transcriptomic features, suggests a potential role for platelet transcriptomic as a non-invasive approach for the diagnosis of CAD.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Machine Learning-based Adverse Cardiovascular Events Risk Algorithm For Cancer Patients Treated With Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Wahi Shawn, Cross James, Mora Ruben, Im Yunju, Kwan Jennifer
A machine learning approach to classifying ischemic stroke etiology using variables available in the Get-with-the-Guidelines Stroke RegistryLee Ho-joon, Schwamm Lee, Turner Ashby, De Havenon Adam, Kamel Hooman, Brandt Cynthia, Zhao Hongyu, Krumholz Harlan, Sharma Richa