Final ID: Sa2097
Blood Biochemical Responses to Acute Endurance and Resistance Exercise: Findings from the Molecular Transducers of Physical Activity Consortium (MoTrPAC)
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Exercise is a robust stimulus that impacts numerous organ systems; however, the molecular mechanisms underlying these effects remain unclear. We performed multi-omic profiling in blood samples in response to endurance and resistance exercise in MoTrPAC participants to study the effects of acute exercise.
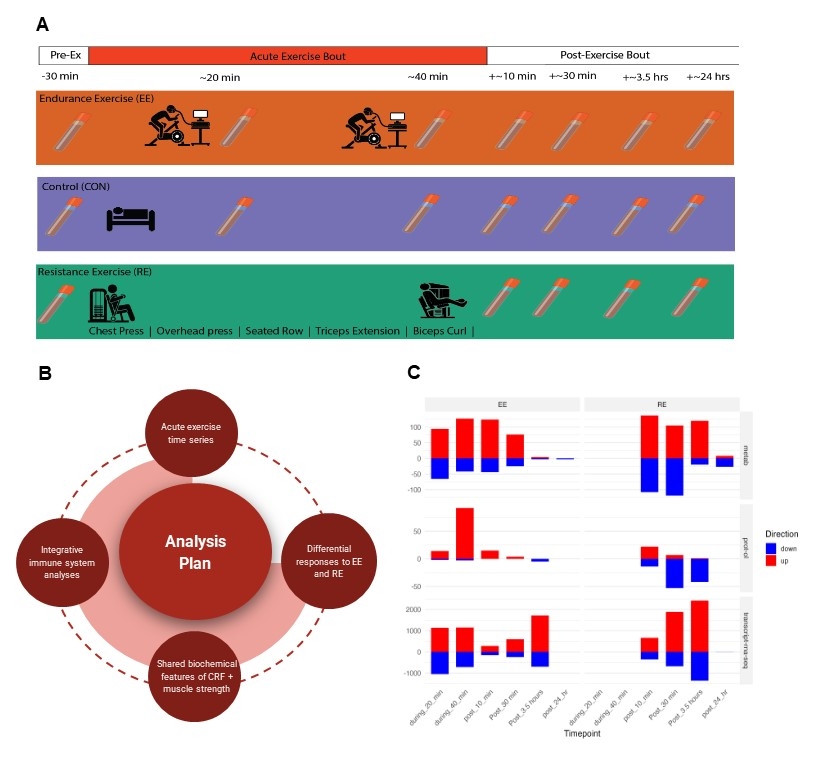
Methods: Healthy, sedentary adults were randomized to endurance exercise (EE, N=65; 40 min cycle ergometry at 65% VO2max), resistance exercise (RE, N=72; 8-exercises, 3 sets of 10 repetitions), or a non-exercise control group (CON, N=37). Plasma and whole blood samples were collected at up to 7 different timepoints [baseline, during EE and CON (20 and 40 min), and post-exercise (10 min, 30 min, 3.5 hrs, and 24 hrs) in EE, RE, and CON. Plasma proteomics (Olink, 1.5K assay), targeted LC-MS metabolomics, and whole blood transcriptomics (PAXgene) were performed (Figure 1). Differential and enrichment analyses were used to identify molecular responses and biochemical pathways according to exercise stimulus.
Results: Participants were 41 (±15) years old (72% female; BMI 26.9 kg/m2 (± 4.0)). Overall, 189 proteins 447 metabolites, and 7066 transcripts changed in response to EE or RE (Fig. 1). Nearly all (97%) of the plasma proteins that changed during EE (40 min) increased and rapidly resolved by early recovery (30 min). RE led to more sustained proteomic changes post-exercise (10 min-3.5 hrs), including a higher percentage of secreted and/or hormonal proteins (e.g. fibroblast growth factor 21 [FGF21] and pro-adrenomedullin [ADM]). In general, EE and RE led to similar directional effects on proteins, however RE demonstrated a greater magnitude of effect. In contrast, several acylcarnitines and fatty acids demonstrated discordant changes in EE compared to RE in the early exercise recovery period that paralleled muscle metabolomic changes. Whole blood transcriptional changes reflected processes of angiogenesis and tissue repair in enrichment analyses (VEGF, IL-6, and HSP90 pathways) in both EE and RE, whereas differential immune cell responses were observed across exercise modes (e.g. RE elicited an inhibitory response on B-cell mobilization).
Conclusions: Acute exercise induces widespread molecular responses in human blood. Modality-specific temporal biochemical patterns reveal new insights into the systemic effects of endurance and resistance exercise.
Methods: Healthy, sedentary adults were randomized to endurance exercise (EE, N=65; 40 min cycle ergometry at 65% VO2max), resistance exercise (RE, N=72; 8-exercises, 3 sets of 10 repetitions), or a non-exercise control group (CON, N=37). Plasma and whole blood samples were collected at up to 7 different timepoints [baseline, during EE and CON (20 and 40 min), and post-exercise (10 min, 30 min, 3.5 hrs, and 24 hrs) in EE, RE, and CON. Plasma proteomics (Olink, 1.5K assay), targeted LC-MS metabolomics, and whole blood transcriptomics (PAXgene) were performed (Figure 1). Differential and enrichment analyses were used to identify molecular responses and biochemical pathways according to exercise stimulus.
Results: Participants were 41 (±15) years old (72% female; BMI 26.9 kg/m2 (± 4.0)). Overall, 189 proteins 447 metabolites, and 7066 transcripts changed in response to EE or RE (Fig. 1). Nearly all (97%) of the plasma proteins that changed during EE (40 min) increased and rapidly resolved by early recovery (30 min). RE led to more sustained proteomic changes post-exercise (10 min-3.5 hrs), including a higher percentage of secreted and/or hormonal proteins (e.g. fibroblast growth factor 21 [FGF21] and pro-adrenomedullin [ADM]). In general, EE and RE led to similar directional effects on proteins, however RE demonstrated a greater magnitude of effect. In contrast, several acylcarnitines and fatty acids demonstrated discordant changes in EE compared to RE in the early exercise recovery period that paralleled muscle metabolomic changes. Whole blood transcriptional changes reflected processes of angiogenesis and tissue repair in enrichment analyses (VEGF, IL-6, and HSP90 pathways) in both EE and RE, whereas differential immune cell responses were observed across exercise modes (e.g. RE elicited an inhibitory response on B-cell mobilization).
Conclusions: Acute exercise induces widespread molecular responses in human blood. Modality-specific temporal biochemical patterns reveal new insights into the systemic effects of endurance and resistance exercise.
More abstracts on this topic:
Relationship between hemodynamics and oxygen consumption in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy during maximal stress testing
Parrish Jonathan, Macgowan Guy, Jakovljevic Djordje, Charman Sarah, Blain Alasdair, Okwose Nduka, Fuller Amy, Alyahya Alaa, Russell Sophie, Eggett Christopher, Luke Peter, Bailey Kristian
Aerobic Capacity of Adults with Fontan Palliation: Disease-specific Reference Values and Relationship to OutcomesAli Ahmed, Goda Ahmed, Abozied Omar, Egbe Alexander