Final ID: Su2040
Lean Body Mass Index: A Valuable Predictor of Coronary Artery Disease Severity Stratified by the Computed Tomography–derived SYNTAX Score
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Body composition indicators (BCIs) are metrics for assessing the components of the body, such as waist circumference (WC), body mass index (BMI), lean body mass index (LBMI), and visceral-to-subcutaneous fat area ratio (V/S ratio), and are considered associational factors of coronary artery disease (CAD). LBMI is a convenient marker of frailty and sarcopenia and can be calculated using an estimation formula that requires only an individual’s height and weight. Recently, abdominal fat distribution (AFD) assessed by the V/S ratio has been determined as one of the important risk factors for CAD. However, studies investigating the relationship between BCIs and CAD severity are limited. The computed tomography (CT)–derived SYNTAX score (CT-SX score) is a feasible method for grading CAD severity based on the coronary CT angiography (CTA) findings. This study aimed to evaluate the association between BCIs and CAD severity using the CT-SX score.
Methods: We enrolled 931 consecutive patients with suspected CAD who underwent CTA. Plain abdominal CT was also performed at the umbilical level to measure WC by tracing the body contour and to calculate the V/S ratio to assess the AFD. The severity of coronary artery stenosis was assessed using CTA, with significant stenosis defined as a stenosis diameter of ≥50%. The CT-SX score was calculated in patients with >1 significant stenosis. Each stenotic lesion was assessed to calculate the CT-SX score, following the same methodology as the invasive coronary angiography assessment. Finally, the relationship between the BCIs (i.e., WC, BMI, LBMI, and V/S ratios) and the CT-SX score was evaluated.
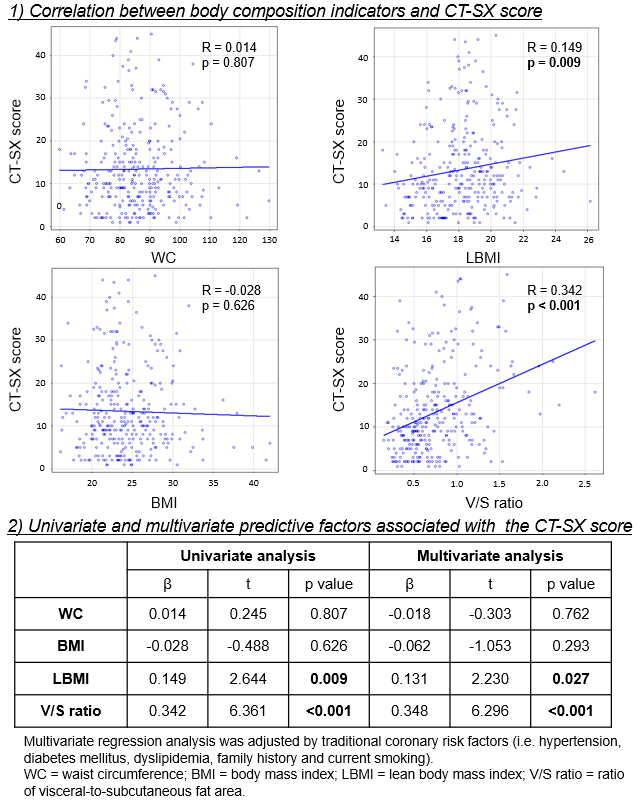
Results: Of the 931 patients enrolled, 308 (33.1%) had ≥1 significant stenosis. Although WC and BMI had no association with the CT-SX score, strong correlations were observed between the CT-SX score and the factors LBMI and V/S ratio. In the multivariate regression analysis after adjusting for traditional coronary risk factors, LBMI and V/S ratio remained as the independent predictors of CAD severity based on the CT-SX score (Figure).
Conclusions: The findings suggest that among the BCIs studied, only LBMI and the V/S ratio are strong predictors of CAD severity, as stratified by the CT-SX score. Because the estimated LBMI can be more easily assessed than the V/S ratio, the former may be a valuable predictor of CAD severity in daily clinical practice.
Methods: We enrolled 931 consecutive patients with suspected CAD who underwent CTA. Plain abdominal CT was also performed at the umbilical level to measure WC by tracing the body contour and to calculate the V/S ratio to assess the AFD. The severity of coronary artery stenosis was assessed using CTA, with significant stenosis defined as a stenosis diameter of ≥50%. The CT-SX score was calculated in patients with >1 significant stenosis. Each stenotic lesion was assessed to calculate the CT-SX score, following the same methodology as the invasive coronary angiography assessment. Finally, the relationship between the BCIs (i.e., WC, BMI, LBMI, and V/S ratios) and the CT-SX score was evaluated.
Results: Of the 931 patients enrolled, 308 (33.1%) had ≥1 significant stenosis. Although WC and BMI had no association with the CT-SX score, strong correlations were observed between the CT-SX score and the factors LBMI and V/S ratio. In the multivariate regression analysis after adjusting for traditional coronary risk factors, LBMI and V/S ratio remained as the independent predictors of CAD severity based on the CT-SX score (Figure).
Conclusions: The findings suggest that among the BCIs studied, only LBMI and the V/S ratio are strong predictors of CAD severity, as stratified by the CT-SX score. Because the estimated LBMI can be more easily assessed than the V/S ratio, the former may be a valuable predictor of CAD severity in daily clinical practice.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Transient Cortical Blindness occurring during Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angiography for Acute Coronary Syndrome.
Adelakun Adeniyi, Farouji Iyad, Haddad Ahmad, Szwed Stanley
Adiposomal microRNAs Mediate Vascular Dysfunction in Obesity-Associated Type 2 DiabetesMirza Imaduddin, Morsy Mohammed, Levitan Irena, Raj Usha, Mahmoud Abeer