Final ID: MP2301
Efficacy of eHealth-Enabled versus Traditional Cardiac Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 26 Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) is a key component of secondary prevention in cardiovascular disease, improving quality of life and reducing events. However, participation in traditional, center-based CR remains low due to accessibility and logistical issues. Advances in eHealth have enabled alternative CR models, including digital (e.g., apps, telerehabilitation, SMS) and hybrid approaches (combining digital and in-person formats). The comparative effectiveness of eHealth CR versus traditional CR remains inconclusive. This meta-analysis evaluates the impact of eHealth CR compared to traditional CR on clinical outcomes in adults undergoing cardiac rehabilitation.
Methods
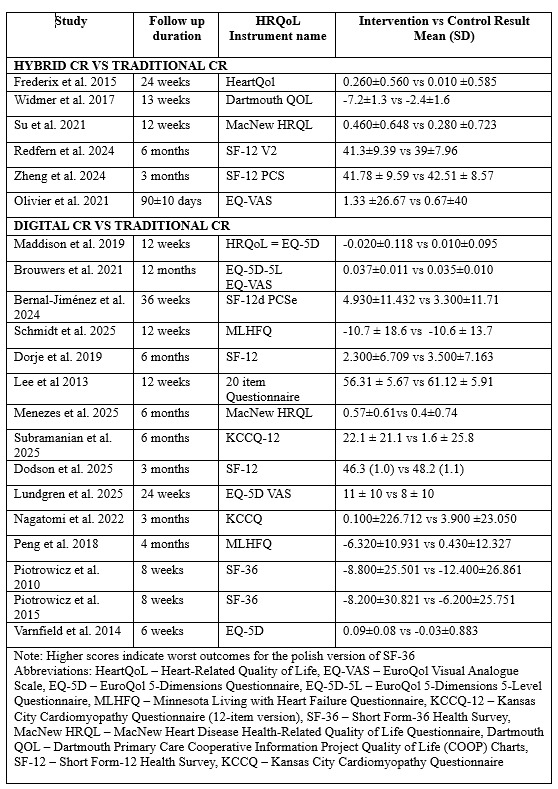
This review is registered with PROSPERO CRD420251062774. Following PRISMA guidelines, a comprehensive search of PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar was conducted from inception to May 2025. RCTs were included comparing digital or hybrid CR with traditional CR or usual care in adult patients (age ≥18 years) with heart disease initiating rehabilitation. Primary outcomes were functional capacity (e.g., peak VO2, 6-MWT) and HRQoL. Secondary outcomes included psychological well-being and cardiometabolic markers (BMI, SBP, DBP, resting HR, HbA1c, and lipid levels). The random-effects model calculated mean differences (MD) with 95% CI. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
Results
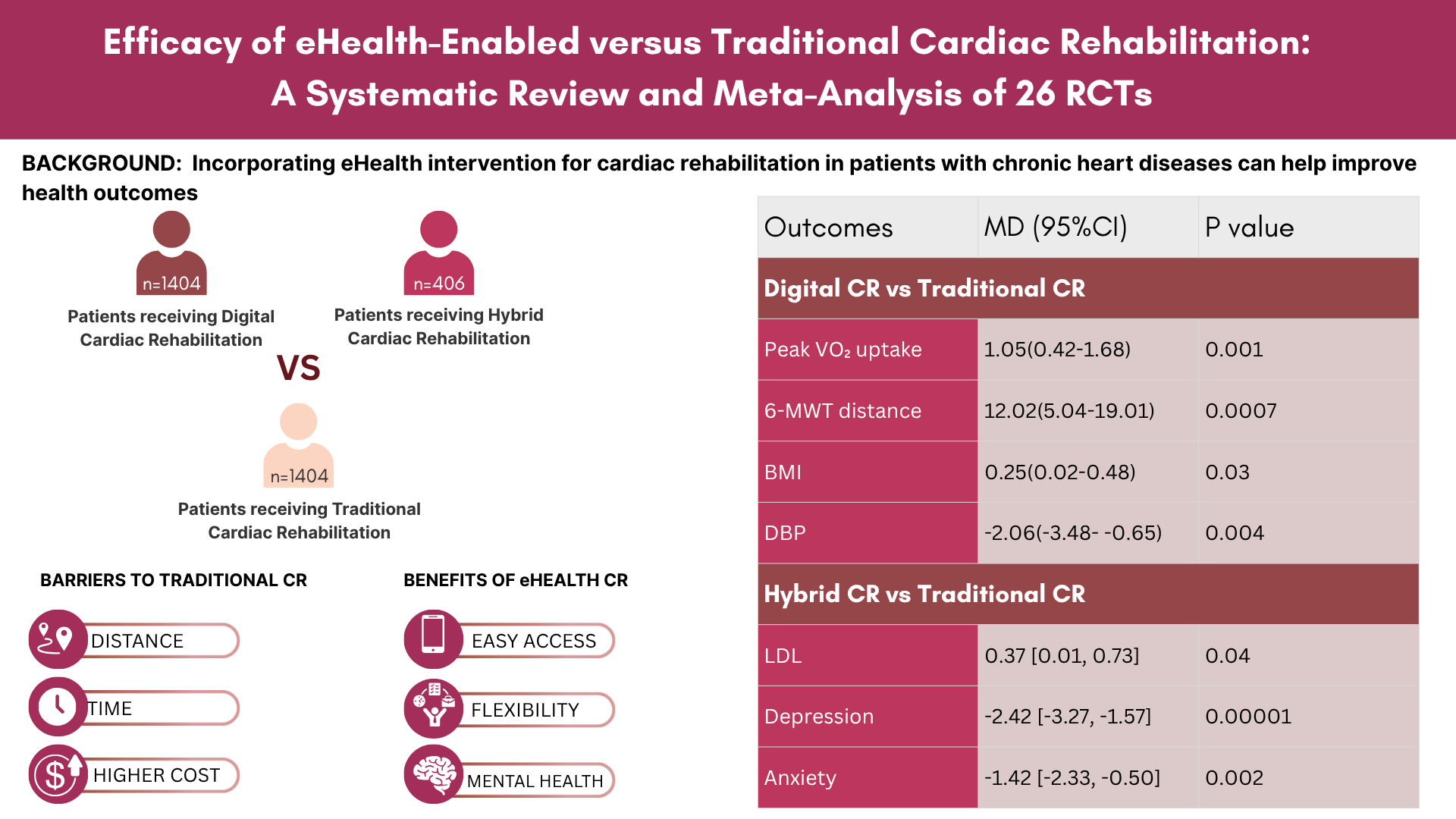
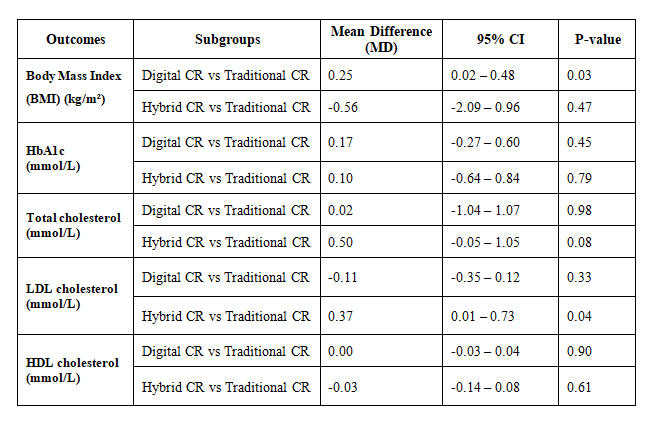
A total of 26 RCTs met the inclusion criteria, including 3,214 patients with MI, CAD, HF, or those who had undergone revascularization. Meta-analysis demonstrated that digital CR significantly improved peak VO2 uptake (MD: 1.05; 95% CI: 0.42-1.68; P = 0.001) and 6-MWT distance (MD: 12.02; 95% CI: 5.04-19.01; P = 0.0007) compared with traditional CR. No significant differences were observed between hybrid CR and traditional CR for primary outcomes. Digital CR was also associated with significant reductions in DBP (MD: -2.06; 95% CI: -3.48- -0.65; P = 0.004) and BMI (MD: 0.25; 95% CI: 0.02-0.48; P = 0.03) relative to traditional CR. Hybrid CR significantly reduced LDL cholesterol, depression and anxiety scores compared to traditional CR. No significant differences were identified between eHealth and traditional CR in SBP, HR, HbA1c, or lipid levels.
Conclusion
Digital CR significantly improves functional capacity and selective cardiometabolic outcomes compared to traditional CR. Hybrid CR shows greater benefits for mental well-being. These findings support the integration of eHealth in modern CR programs.
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) is a key component of secondary prevention in cardiovascular disease, improving quality of life and reducing events. However, participation in traditional, center-based CR remains low due to accessibility and logistical issues. Advances in eHealth have enabled alternative CR models, including digital (e.g., apps, telerehabilitation, SMS) and hybrid approaches (combining digital and in-person formats). The comparative effectiveness of eHealth CR versus traditional CR remains inconclusive. This meta-analysis evaluates the impact of eHealth CR compared to traditional CR on clinical outcomes in adults undergoing cardiac rehabilitation.
Methods
This review is registered with PROSPERO CRD420251062774. Following PRISMA guidelines, a comprehensive search of PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar was conducted from inception to May 2025. RCTs were included comparing digital or hybrid CR with traditional CR or usual care in adult patients (age ≥18 years) with heart disease initiating rehabilitation. Primary outcomes were functional capacity (e.g., peak VO2, 6-MWT) and HRQoL. Secondary outcomes included psychological well-being and cardiometabolic markers (BMI, SBP, DBP, resting HR, HbA1c, and lipid levels). The random-effects model calculated mean differences (MD) with 95% CI. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
Results
A total of 26 RCTs met the inclusion criteria, including 3,214 patients with MI, CAD, HF, or those who had undergone revascularization. Meta-analysis demonstrated that digital CR significantly improved peak VO2 uptake (MD: 1.05; 95% CI: 0.42-1.68; P = 0.001) and 6-MWT distance (MD: 12.02; 95% CI: 5.04-19.01; P = 0.0007) compared with traditional CR. No significant differences were observed between hybrid CR and traditional CR for primary outcomes. Digital CR was also associated with significant reductions in DBP (MD: -2.06; 95% CI: -3.48- -0.65; P = 0.004) and BMI (MD: 0.25; 95% CI: 0.02-0.48; P = 0.03) relative to traditional CR. Hybrid CR significantly reduced LDL cholesterol, depression and anxiety scores compared to traditional CR. No significant differences were identified between eHealth and traditional CR in SBP, HR, HbA1c, or lipid levels.
Conclusion
Digital CR significantly improves functional capacity and selective cardiometabolic outcomes compared to traditional CR. Hybrid CR shows greater benefits for mental well-being. These findings support the integration of eHealth in modern CR programs.
More abstracts on this topic:
Center-Based, Home-Based, and Technology-Enhanced Cardiac Rehabilitation Equally Reduce Mortality Risk in Veterans
Shah Amit, Li Louis, Aggarwal Vinod, Zafari Abarmard, Park Linda, Harzand Arash
Activities of Daily Living (ADLs) in Adults with Heart Failure Compared with Cancer: Analysis of Medicare Health Outcomes Survey DataPedamallu Havisha, Khan Sadiya, Haywood Carol, Baldridge Abigail, Grady Kathleen, Goyal Parag, Fonarow Gregg, Lagu Tara, Ahmad Faraz