Final ID: Su3014
Comparative cardiovascular efficacy of empagliflozin and dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background
The favorable safety profile of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, notably empagliflozin and dapagliflozin, make them a suitable treatment option for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, their comparative efficacy and cardiovascular (CV) benefits still remain unclear. This meta-analysis aims to compare the CV outcomes between Dapagliflozin and Empagliflozin in T2DM patients, exploring their varying effectiveness.
Methods
A comprehensive search of electronic databases, PubMed, Embase, and Google Scholar was conducted from inception till May 2024. The study was conducted adhering to the PRISMA guidelines. Following a thorough screening and quality assessment, primary outcomes including major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), cardiovascular (CV) mortality, and all-cause death along with secondary outcomes including stroke, myocardial infarction (MI), and heart failure (HF), were extracted. The random effects model was used to pool the odds ratio (OR) along with the corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for all outcomes. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
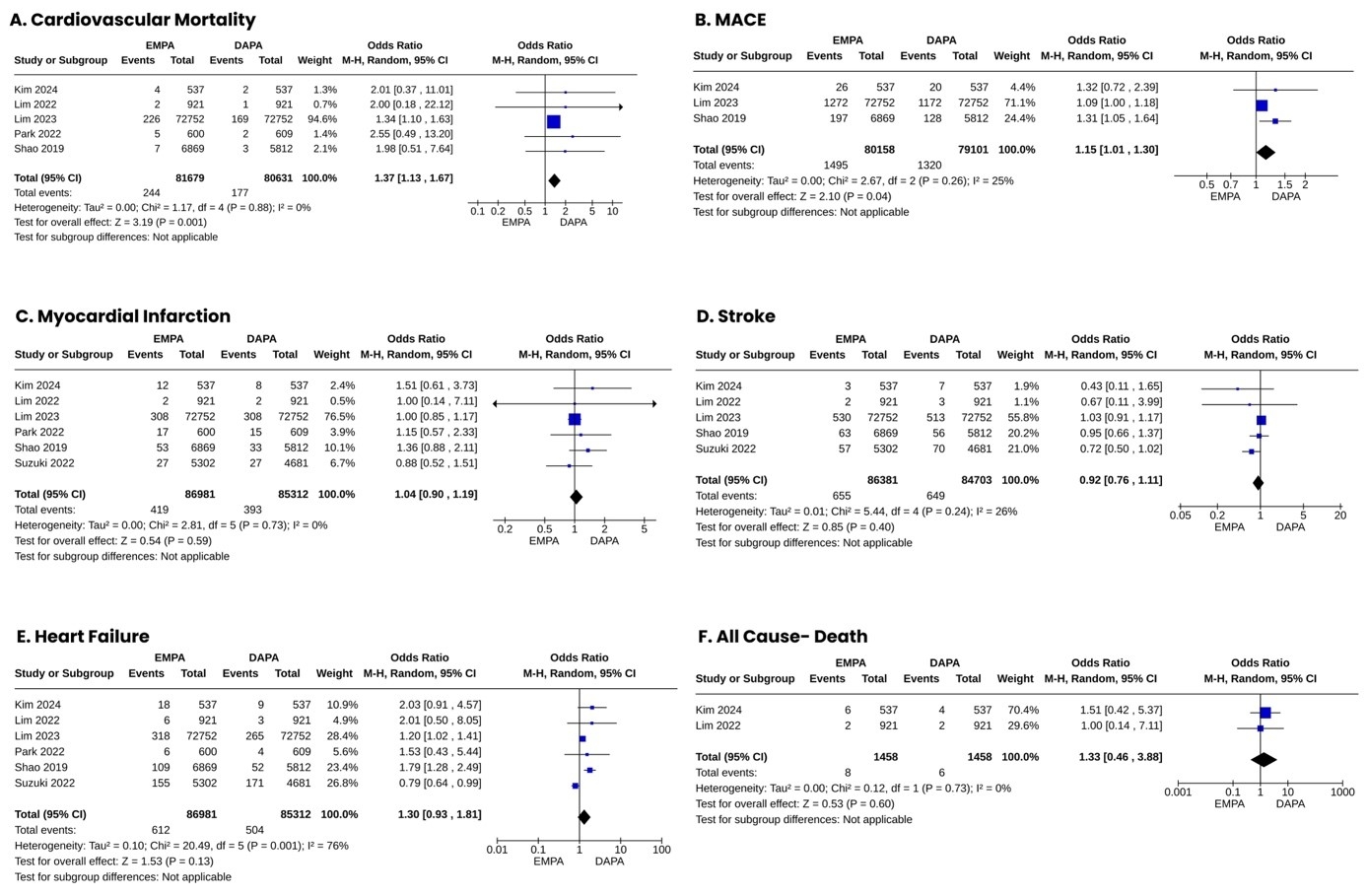
We pooled 6 studies with a total of 172,293 participants. The evaluation of pool results showed a significant association between the use of empagliflozin and dapagliflozin for reducing CV mortality (OR 1.15, 95 % CI 1.01- 1.30; p=0.04) and MACE (OR 1.15, 95 % CI 1.01- 1.30; p=0.04). However, we found no statistically significant difference between the two drugs for reducing MI (OR 1.04, 95 % CI 0.90- 1.19; p=0.59), Stroke (OR 0.92, 95 % CI 0.76- 1.11; p=0.40), HF (OR 1.30, 95 % CI 0.93- 1.81; p=0.13) and all-cause death (OR 1.33, 95 % CI 0.46- 3.88; p=0.60). After running the sensitivity analysis, a statistically significant result was observed between use of empagliflozin and dapagliflozin for HF (OR 1.47, 95 % CI 1.13- 1.90; p=0.004).
Conclusion
The use of dapagliflozin significantly reduces CV mortality and MACE when compared with empagliflozin. However, the incidence of MI, stroke, HF, and all-cause death is comparable across the two groups. Our results should be considered hypothesis generating and evidence from large-scale multi-centric randomized controlled trials (RCTs) is required to reach a definitive conclusion
Background
The favorable safety profile of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, notably empagliflozin and dapagliflozin, make them a suitable treatment option for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, their comparative efficacy and cardiovascular (CV) benefits still remain unclear. This meta-analysis aims to compare the CV outcomes between Dapagliflozin and Empagliflozin in T2DM patients, exploring their varying effectiveness.
Methods
A comprehensive search of electronic databases, PubMed, Embase, and Google Scholar was conducted from inception till May 2024. The study was conducted adhering to the PRISMA guidelines. Following a thorough screening and quality assessment, primary outcomes including major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), cardiovascular (CV) mortality, and all-cause death along with secondary outcomes including stroke, myocardial infarction (MI), and heart failure (HF), were extracted. The random effects model was used to pool the odds ratio (OR) along with the corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for all outcomes. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
We pooled 6 studies with a total of 172,293 participants. The evaluation of pool results showed a significant association between the use of empagliflozin and dapagliflozin for reducing CV mortality (OR 1.15, 95 % CI 1.01- 1.30; p=0.04) and MACE (OR 1.15, 95 % CI 1.01- 1.30; p=0.04). However, we found no statistically significant difference between the two drugs for reducing MI (OR 1.04, 95 % CI 0.90- 1.19; p=0.59), Stroke (OR 0.92, 95 % CI 0.76- 1.11; p=0.40), HF (OR 1.30, 95 % CI 0.93- 1.81; p=0.13) and all-cause death (OR 1.33, 95 % CI 0.46- 3.88; p=0.60). After running the sensitivity analysis, a statistically significant result was observed between use of empagliflozin and dapagliflozin for HF (OR 1.47, 95 % CI 1.13- 1.90; p=0.004).
Conclusion
The use of dapagliflozin significantly reduces CV mortality and MACE when compared with empagliflozin. However, the incidence of MI, stroke, HF, and all-cause death is comparable across the two groups. Our results should be considered hypothesis generating and evidence from large-scale multi-centric randomized controlled trials (RCTs) is required to reach a definitive conclusion
More abstracts on this topic:
A pharmacist-led, population health approach to optimizing care in patients with hypertension and type II diabetes mellitus in minority groups
Doyle Julie, Haftel Elizabeth, Monroe Janet, Chen Zsu-zsu, Benson Mark, Yankama Tuyen, Adam Atif, Rubin Rochelle
Adipocyte-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Enriched with NNMT Inhibit Angiogenesis Post-Myocardial Infarction in DiabetesRen Hang, Cao Liwen, Zhao Zhenkun, Huang Ying, Pan Zhongjing, Cheng Liangfen, Gan Lu