Final ID: MP1488
The Association between Non-High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level and Coronary Fatty Plaque Regression
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Regression of coronary fatty plaque, the type most prone to rupture and cause acute coronary syndromes, is associated with fewer cardiovascular events. A baseline non-HDL-C level ≤100 mg/dL predicted regression of fatty plaque at 30 months; however, to our knowledge, no data exist on the association between non-HDL-C level and percent of fatty plaque regression.
Research Question: Is there a target for coronary plaque regression and progression by non-HDL-C level?
Methods: Data from the Slowing HEART diSease with lifestyle and omega-3 fatty acids (HEARTS) trial, a randomized clinical trial, was analyzed. A total of 240 coronary artery disease (CAD) subjects on statin therapy were randomized to 3.36 g of omega-3 fatty acids daily for 30 months or none. Coronary plaque subtypes were quantitated with coronary computed tomographic angiography, and lipids and inflammatory markers were measured at baseline and 30-month follow-up. Significant interaction was found between hypertension and treatment arm in the prediction of plaque (p=0.008); thus, subjects were stratified by blood pressure status.
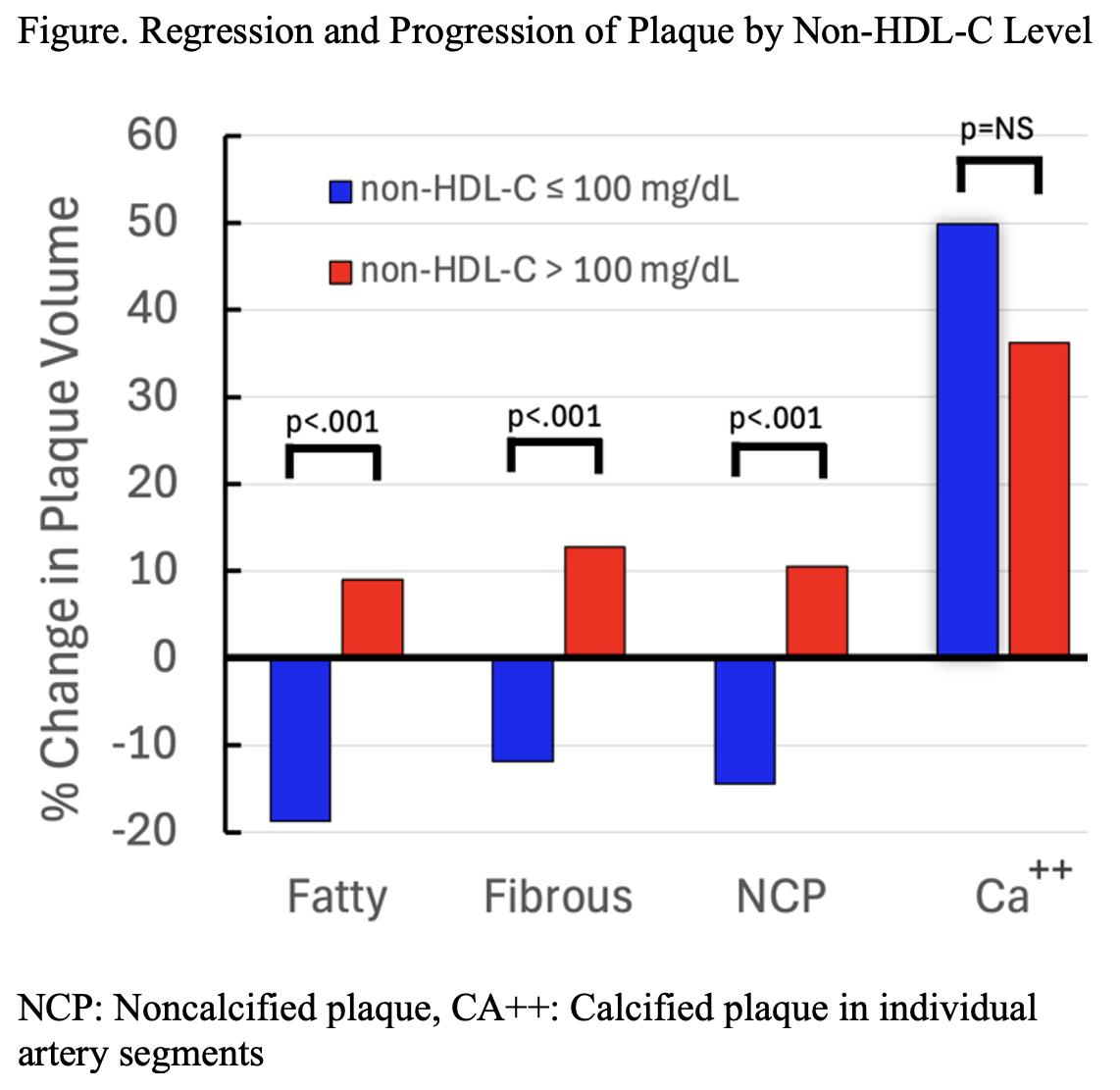
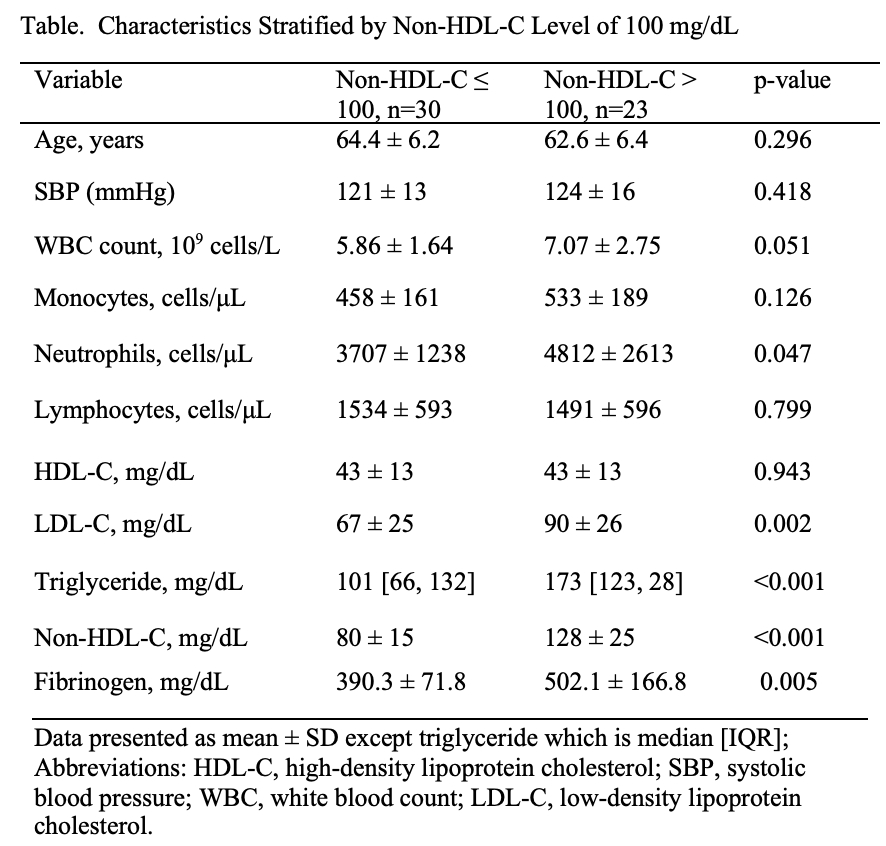
Results: Subjects (n=53) in whom non-HDL-C ≤100 mg/dL predicted plaque regression were in the control group; all had well-controlled hypertension. Median age was 63.6 years and 43 were male (81.1%). Those with non-HDL-C level ≤100 mg/dL had median fatty plaque regression of 18.8% [IQR: 6.9, 30.8] compared to median progression of 9.0% [7.3, 23.2] with non-HDL-C level >100 mg/dL (Figure). Those with non-HDL-C level >100 mg/dL had significantly higher levels of inflammatory markers: neutrophil count (p=0.047) and fibrinogen level (p=0.005) (Table). Mean LDL-C levels in the two non-HDL-C groups were 67±25 vs 90±26, respectively (p=0.002).
Conclusions: A non-HDL-C ≤100 mg/dL is a potential treatment target to achieve up to 18.8% fatty plaque regression in CAD subjects with well-controlled hypertension on statin therapy. The higher levels of inflammation in non-HDL-C >100 mg/dL suggest that inflammation may underlie the mechanism for plaque progression. The results also identify LDL-C levels at which regression and progression occur. Further study in this group, which appears to be the first report of plaque regression and progression by non-HDL-C and LDL-C levels, may identify mechanisms and reveal strategies to achieve regression of coronary plaque and prevent acute coronary syndromes.
Research Question: Is there a target for coronary plaque regression and progression by non-HDL-C level?
Methods: Data from the Slowing HEART diSease with lifestyle and omega-3 fatty acids (HEARTS) trial, a randomized clinical trial, was analyzed. A total of 240 coronary artery disease (CAD) subjects on statin therapy were randomized to 3.36 g of omega-3 fatty acids daily for 30 months or none. Coronary plaque subtypes were quantitated with coronary computed tomographic angiography, and lipids and inflammatory markers were measured at baseline and 30-month follow-up. Significant interaction was found between hypertension and treatment arm in the prediction of plaque (p=0.008); thus, subjects were stratified by blood pressure status.
Results: Subjects (n=53) in whom non-HDL-C ≤100 mg/dL predicted plaque regression were in the control group; all had well-controlled hypertension. Median age was 63.6 years and 43 were male (81.1%). Those with non-HDL-C level ≤100 mg/dL had median fatty plaque regression of 18.8% [IQR: 6.9, 30.8] compared to median progression of 9.0% [7.3, 23.2] with non-HDL-C level >100 mg/dL (Figure). Those with non-HDL-C level >100 mg/dL had significantly higher levels of inflammatory markers: neutrophil count (p=0.047) and fibrinogen level (p=0.005) (Table). Mean LDL-C levels in the two non-HDL-C groups were 67±25 vs 90±26, respectively (p=0.002).
Conclusions: A non-HDL-C ≤100 mg/dL is a potential treatment target to achieve up to 18.8% fatty plaque regression in CAD subjects with well-controlled hypertension on statin therapy. The higher levels of inflammation in non-HDL-C >100 mg/dL suggest that inflammation may underlie the mechanism for plaque progression. The results also identify LDL-C levels at which regression and progression occur. Further study in this group, which appears to be the first report of plaque regression and progression by non-HDL-C and LDL-C levels, may identify mechanisms and reveal strategies to achieve regression of coronary plaque and prevent acute coronary syndromes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Aortic Growth Mapping to Examine Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Heritable Thoracic Aortic Disease and Variants of Unknown Significance
Campello Carlos Alberto, Ramesh Vedika, Marway Prabhvir, Hofmann Bowman Marion, Aatre Rajani, Burris Nicholas
Accumulation of Epicardial Adipose Tissue as a Marker of Diastolic Dysfunction in Patients With Preserved Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Undergoing Coronary Computed Tomography AngiographIshikawa Hirotoshi, Kasayuki Noriaki, Fukuda Daiju, Otsuka Kenichiro, Sugiyama Takatoshi, Yamaura Hiroki, Hojo Kana, Kawa Yoshinori, Shintani Ako, Ito Asahiro, Yamazaki Takanori