Final ID: MP2204
The Association between C-Reactive Protein-Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Metabolic syndrome is characterized by an interplay of risk factors mediated by a chronic state of inflammation and is strongly linked to increased cardiovascular (CV) mortality. C-Reactive Protein-Triglyceride-Glucose Index (CTI) has recently emerged as a marker for both insulin resistance and systemic inflammation, both of which are established contributors to cardiovascular disease.
Research Question: Does CTI predict CV mortality in patients with metabolic syndrome?
Methods: The NHANES database was used from 1999 to 2010, and data on mortality follow-up through December 31st, 2019 was analyzed. Patients with metabolic syndrome were identified by stratifying individuals aged ≥20 years meeting ≥3 of the 5 metabolic syndrome criteria. CTI was derived using the formula 0.412 × ln(CRP [mg/L]) + ln(Triglycerides [mg/dL] × Fasting Glucose [mg/dL])/2. The incidence of coronary heart disease (CHD) and CV mortality were assessed. CTI was tested as a continuous variable and by quartiles. A Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and multivariate Cox proportional hazards models were performed to assess the relationship between CTI and CV mortality.
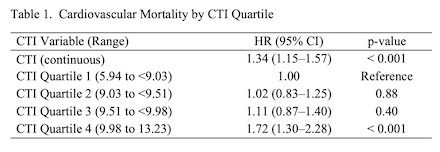
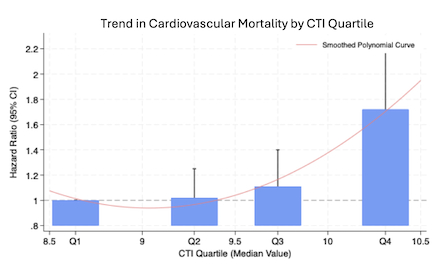
Results: A total of 10,421 patients with metabolic syndrome were identified. The mean age of the population was 57.0±17.2 years, of which 51.9% were female. The incidence of CHD was 13.0%. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed a significant difference in CV mortality across the 4 CTI quartiles (p<0.001) (Table 1). Notably, when CTI was modeled as a continuous variable, each one-unit increase in CTI was associated with a 34% higher CV mortality (HR = 1.34, 95% CI: 1.15–1.57, p<0.001). Cox regression analysis of CTI by quartiles showed a nonsignificant increase in CV mortality in quartile 2 (HR = 1.02, 95% CI: 0.83–1.25, p=0.88) and quartile 3 (HR = 1.11, 95% CI: 0.87–1.40, p=0.40) compared with the lowest quartile 1 (Figure 1). However, patients in quartile 4 had significantly higher CV mortality, with a hazard ratio of 1.72 (95% CI: 1.30–2.28, p<0.001).
Conclusion: CTI is a positive predictor of cardiovascular mortality in patients with metabolic syndrome. Our findings suggest that metabolic syndrome patients with higher insulin resistance and systemic inflammation have higher CV mortality. The current study underscores the need for further research into the clinical applicability of CTI as a strong quantitative measure of cardiovascular risk assessment.
Research Question: Does CTI predict CV mortality in patients with metabolic syndrome?
Methods: The NHANES database was used from 1999 to 2010, and data on mortality follow-up through December 31st, 2019 was analyzed. Patients with metabolic syndrome were identified by stratifying individuals aged ≥20 years meeting ≥3 of the 5 metabolic syndrome criteria. CTI was derived using the formula 0.412 × ln(CRP [mg/L]) + ln(Triglycerides [mg/dL] × Fasting Glucose [mg/dL])/2. The incidence of coronary heart disease (CHD) and CV mortality were assessed. CTI was tested as a continuous variable and by quartiles. A Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and multivariate Cox proportional hazards models were performed to assess the relationship between CTI and CV mortality.
Results: A total of 10,421 patients with metabolic syndrome were identified. The mean age of the population was 57.0±17.2 years, of which 51.9% were female. The incidence of CHD was 13.0%. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed a significant difference in CV mortality across the 4 CTI quartiles (p<0.001) (Table 1). Notably, when CTI was modeled as a continuous variable, each one-unit increase in CTI was associated with a 34% higher CV mortality (HR = 1.34, 95% CI: 1.15–1.57, p<0.001). Cox regression analysis of CTI by quartiles showed a nonsignificant increase in CV mortality in quartile 2 (HR = 1.02, 95% CI: 0.83–1.25, p=0.88) and quartile 3 (HR = 1.11, 95% CI: 0.87–1.40, p=0.40) compared with the lowest quartile 1 (Figure 1). However, patients in quartile 4 had significantly higher CV mortality, with a hazard ratio of 1.72 (95% CI: 1.30–2.28, p<0.001).
Conclusion: CTI is a positive predictor of cardiovascular mortality in patients with metabolic syndrome. Our findings suggest that metabolic syndrome patients with higher insulin resistance and systemic inflammation have higher CV mortality. The current study underscores the need for further research into the clinical applicability of CTI as a strong quantitative measure of cardiovascular risk assessment.
More abstracts on this topic:
A major uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate impairs macrophage efferocytosis and accelerates atherogenesis: a potential mechanism for cardiovascular risk in chronic kidney disease
Jha Prabhash, Kasai Taku, Vromman Amelie, Holden Rachel, Libby Peter, Tabas Ira, Singh Sasha, Aikawa Elena, Aikawa Masanori, Lupieri Adrien, Sonawane Abhijeet, Le Thanh-dat, Becker-greene Dakota, Chelvanambi Sarvesh, Turner Mandy, Nakamura Yuto, Passos Livia
A multi-proteomic Risk Score Predicts Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Angina and Non-obstructive Coronary Artery DiseaseHuang Jingwen, Lodhi Rafia, Lodhi Saleha, Eldaidamouni Ahmed, Hritani Wesam, Hasan Muhammet, Haroun Nisreen, Quyyumi Arshed, Mehta Puja, Leon Ana, Ko Yi-an, Yang Huiying, Medina-inojosa Jose, Ahmed Taha, Harris Kristen, Alkhoder Ayman, Al Kasem Mahmoud