Final ID: MP508
Hormonal Therapy and the Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases Among Men with Prostate Cancer
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
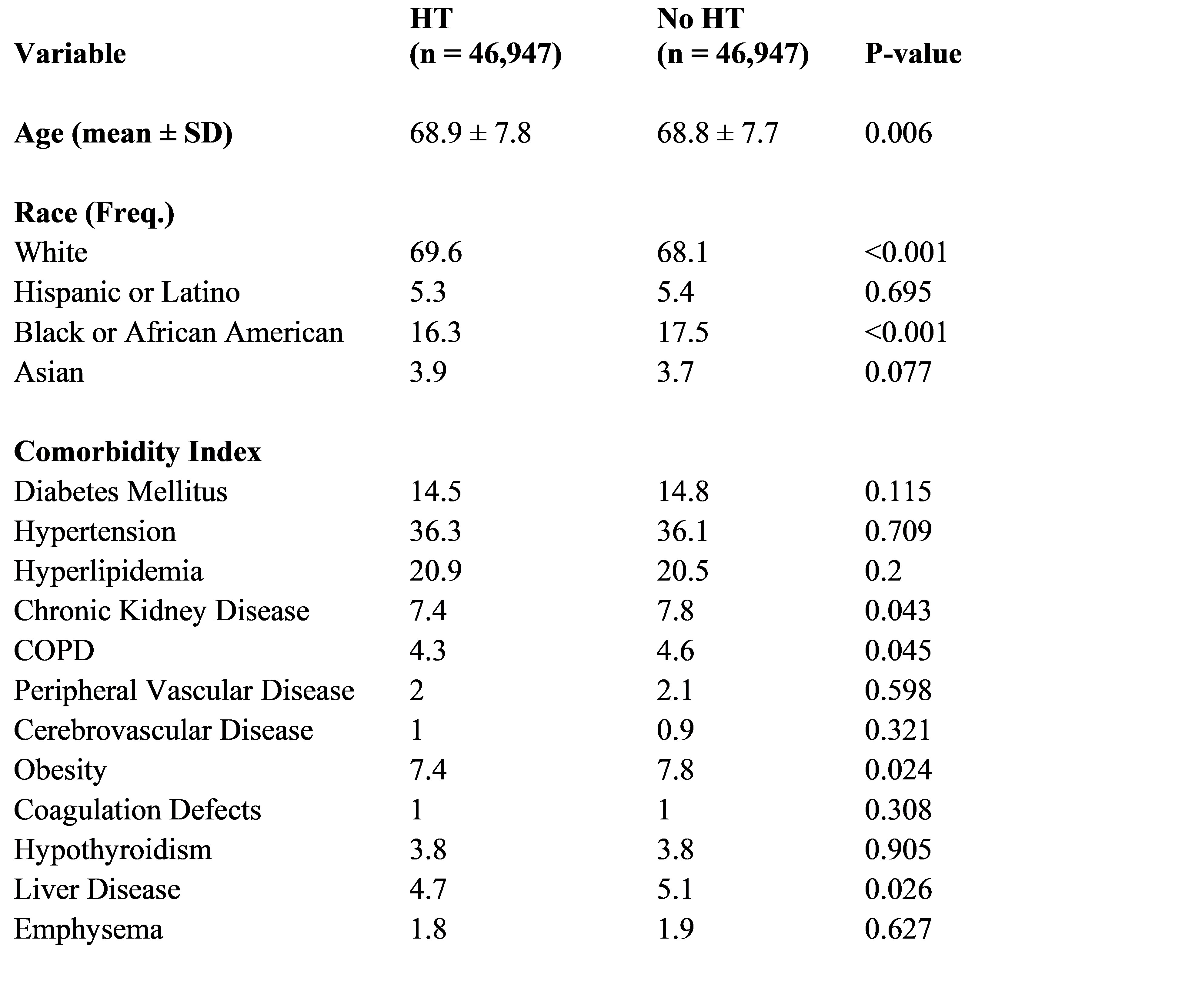
Hormonal therapy (HT) is a cornerstone of prostate cancer treatment; however, its potential cardiovascular risks remain a clinical concern. This study evaluated the incidence of cardiovascular events among prostate cancer patients treated with HT compared to those managed with prostatectomy or radiation alone.
Hypothesis
We hypothesized that hormonal therapy in men with prostate cancer would be associated with an increased risk of major cardiovascular events at 1, 2, and 3 years of follow-up compared to those not receiving hormonal therapy.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study was conducted using TriNetX. Male patients aged ≥50 years diagnosed with prostate cancer between 2010 and 2024 were included. Patients were stratified by receipt of HT versus no HT (prostatectomy or radiation only). Propensity score matching (1:1) was used to balance demographics and comorbidities. Outcomes included acute myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, cardiomyopathy, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, and chronic ischemic heart disease. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Cox proportional hazards models estimated 1-, 2-, and 3-year risks.
Results
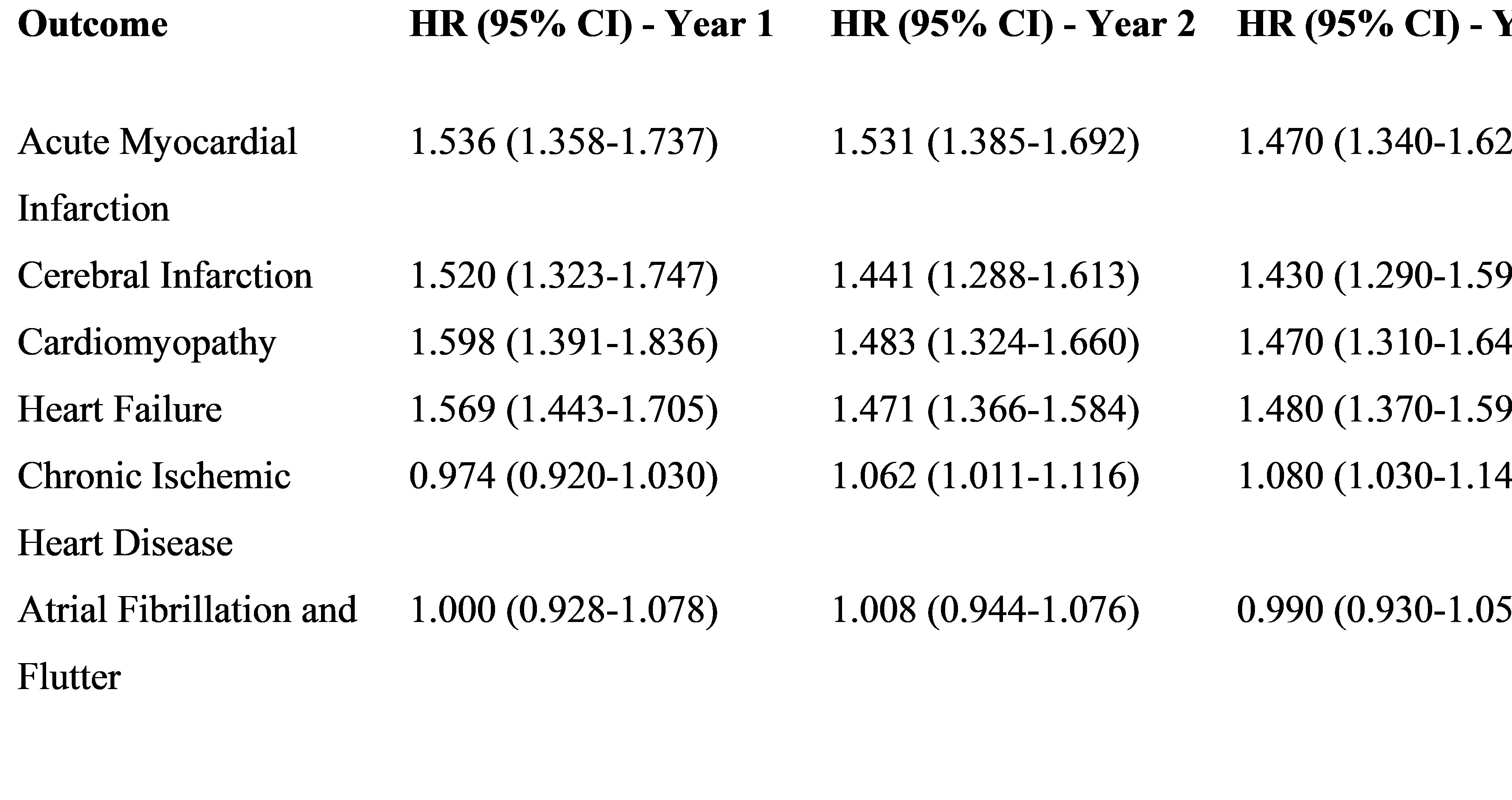
After matching (n = 46,947 per group), HT was associated with increased risks of myocardial infarction (HR 1.54), cerebral infarction (HR 1.52), cardiomyopathy (HR 1.60), and heart failure (HR 1.57) at Year 1 (all p < 0.001). These associations persisted through Years 2 and 3 (HRs 1.43–1.54). Chronic ischemic heart disease showed modest but significant risk at Years 2 and 3. No significant differences were observed for atrial fibrillation. Kaplan-Meier curves showed lower event-free survival with HT across significant outcomes.
Conclusions
HT in prostate cancer is associated with sustained increased cardiovascular risks over 3 years. These findings highlight the need for long-term cardiovascular monitoring and incorporation of preventive strategies in shared treatment planning.
Hormonal therapy (HT) is a cornerstone of prostate cancer treatment; however, its potential cardiovascular risks remain a clinical concern. This study evaluated the incidence of cardiovascular events among prostate cancer patients treated with HT compared to those managed with prostatectomy or radiation alone.
Hypothesis
We hypothesized that hormonal therapy in men with prostate cancer would be associated with an increased risk of major cardiovascular events at 1, 2, and 3 years of follow-up compared to those not receiving hormonal therapy.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study was conducted using TriNetX. Male patients aged ≥50 years diagnosed with prostate cancer between 2010 and 2024 were included. Patients were stratified by receipt of HT versus no HT (prostatectomy or radiation only). Propensity score matching (1:1) was used to balance demographics and comorbidities. Outcomes included acute myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, cardiomyopathy, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, and chronic ischemic heart disease. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Cox proportional hazards models estimated 1-, 2-, and 3-year risks.
Results
After matching (n = 46,947 per group), HT was associated with increased risks of myocardial infarction (HR 1.54), cerebral infarction (HR 1.52), cardiomyopathy (HR 1.60), and heart failure (HR 1.57) at Year 1 (all p < 0.001). These associations persisted through Years 2 and 3 (HRs 1.43–1.54). Chronic ischemic heart disease showed modest but significant risk at Years 2 and 3. No significant differences were observed for atrial fibrillation. Kaplan-Meier curves showed lower event-free survival with HT across significant outcomes.
Conclusions
HT in prostate cancer is associated with sustained increased cardiovascular risks over 3 years. These findings highlight the need for long-term cardiovascular monitoring and incorporation of preventive strategies in shared treatment planning.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Cardioprotective Mechanism in Myocardial Reperfusion Injury: Dual Neutrophil Modulation and ROS/HOCl Scavenging by an Atypical Chemokine
Zwissler Leon, Bernhagen Juergen, Cabrera-fuentes Hector Alejandro, Hernandez Resendiz Sauri, Yap En Ping, Schindler Lisa, Zhang Zhishen, Dickerhof Nina, Hampton Mark, Liehn Elisa, Hausenloy Derek
A Novel Multivariate Scoring System for Diagnosing Post-Myocardial Infarction Pericarditis Following Percutaneous Coronary InterventionBolaji Olayiwola, Omoru Okiemute, Upreti Prakash, Echari Blanche, Shoar Saeed, Basit Jawad, Alraies M Chadi