Final ID: Su2087
Outcomes of catheter ablation in cardiac sarcoidosis patients with ventricular tachycardia
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Ventricular tachycardia (VT) in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis (CS) can lead to sudden cardiac death. The role of ventricular tachycardia ablation (VTA) in CS has been investigated in a few small, single-center, and some larger observational studies, but the evidence remains scarce.
Hypothesis: We hypothesize that patients with CS have worse cardiovascular outcomes.
Aims: This study aimed to investigate the clinical outcomes of VTA in patients with CS admitted with a diagnosis of VT.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted using TrinetX database: US collaborative network from 2010-2024. Patients undergoing ablation for VT with and without CS were identified. Two groups were created for propensity score analysis matching on history of hypertension, diabetes, obesity, peripheral vascular diseases, heart failure, ischemic heart diseases, atrial fibrillation, and chronic kidney disease. The primary outcome was incidence of death, cardiogenic shock, heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, hemorrhagic stroke, ischemic stroke, and ventricular tachycardia within one year from the date of the index procedure.
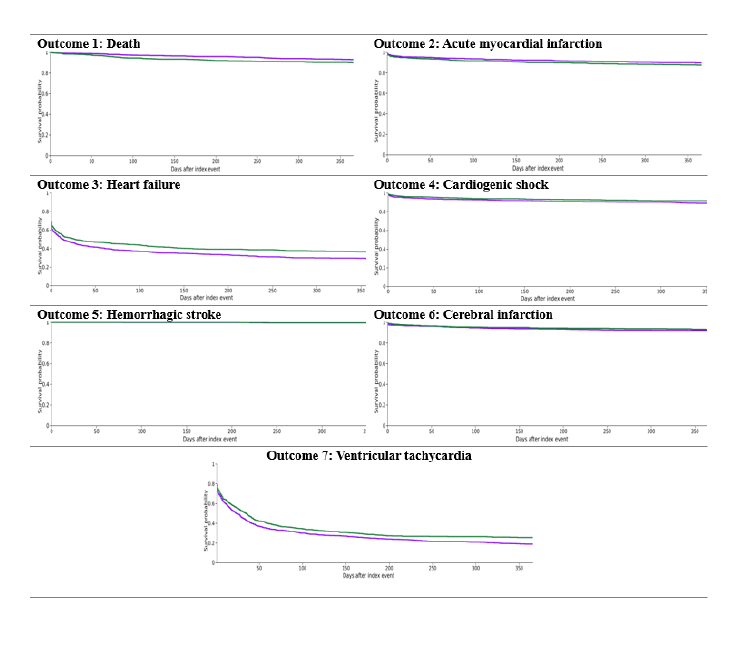
Results: Results: Out of 15,958 patients who underwent catheter ablation for VT, 776 patients had CS. The mean age of patients with VT and CS who underwent ablation was 58.6 (SD:11.3), compared to 61.1 (SD:15) in patients with VT without CS. In the propensity-matched analysis, there was no significant difference in one-year mortality (hazard ratio (HR) 0.65; 95% CI [0.45, 0.94], χ2 = 3.05, p = 0.08), heart failure (HR 1.18; 95% CI [1.04, 1.33], χ2 = 1.5, p = 0.2), cardiogenic shock (HR 1.33; 95% CI [0.95, 1.89], χ2 = 0.005, p = 0.94), acute myocardial infarction (HR 0.81; 95% CI [0.5, 1.11], p = 0.67), hemorrhagic stroke (HR 0.89; 95% CI [0.18, 4.41], p = 0.42), ischemic stroke (HR 1.18; 95% CI [0.80, 1.7], p = 0.79) or ventricular tachycardia (HR 1.17; 95% CI [1.04, 1.31], p = 0.19)
Conclusion: This analysis shows there is no significant difference in major complications in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis undergoing catheter ablation for ventricular tachycardia compared to patients without cardiac sarcoidosis.
Hypothesis: We hypothesize that patients with CS have worse cardiovascular outcomes.
Aims: This study aimed to investigate the clinical outcomes of VTA in patients with CS admitted with a diagnosis of VT.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted using TrinetX database: US collaborative network from 2010-2024. Patients undergoing ablation for VT with and without CS were identified. Two groups were created for propensity score analysis matching on history of hypertension, diabetes, obesity, peripheral vascular diseases, heart failure, ischemic heart diseases, atrial fibrillation, and chronic kidney disease. The primary outcome was incidence of death, cardiogenic shock, heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, hemorrhagic stroke, ischemic stroke, and ventricular tachycardia within one year from the date of the index procedure.
Results: Results: Out of 15,958 patients who underwent catheter ablation for VT, 776 patients had CS. The mean age of patients with VT and CS who underwent ablation was 58.6 (SD:11.3), compared to 61.1 (SD:15) in patients with VT without CS. In the propensity-matched analysis, there was no significant difference in one-year mortality (hazard ratio (HR) 0.65; 95% CI [0.45, 0.94], χ2 = 3.05, p = 0.08), heart failure (HR 1.18; 95% CI [1.04, 1.33], χ2 = 1.5, p = 0.2), cardiogenic shock (HR 1.33; 95% CI [0.95, 1.89], χ2 = 0.005, p = 0.94), acute myocardial infarction (HR 0.81; 95% CI [0.5, 1.11], p = 0.67), hemorrhagic stroke (HR 0.89; 95% CI [0.18, 4.41], p = 0.42), ischemic stroke (HR 1.18; 95% CI [0.80, 1.7], p = 0.79) or ventricular tachycardia (HR 1.17; 95% CI [1.04, 1.31], p = 0.19)
Conclusion: This analysis shows there is no significant difference in major complications in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis undergoing catheter ablation for ventricular tachycardia compared to patients without cardiac sarcoidosis.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Comparative Analysis of Esophageal Cooling for Preventing Esophageal Injury Post Atrial Fibrillation Catheter Ablation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Ibrahim Momen Mohamed, Al Hennawi Hussam, Tanas Yousef, Abourady Youmna, Sewedan Nourhan, Hashem Ahmed Magdy, Motawea Karam R.
Diagnosing An Uncommon Presentation of Cardiac Sarcoidosis with Isolated Bi-Atrial Involvement: A Case ReportNelson Favour, Rajkarnikar Ruja, Carry Brendan