Final ID: MP942
Proteomics analysis identifies sub-phenotypes amongst clinically similar patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH), a progressive pulmonary vasculopathy, may be clinically similar, yet have different responses to therapy and outcomes. Understanding proteomic profiles that distinguish amongst clinically similar patients could improve disease classification to better target treatment.
Research Question:
Can proteomic profiling identify molecular sub-phenotypes amongst otherwise clinically similar patients with IPAH?
Methods:
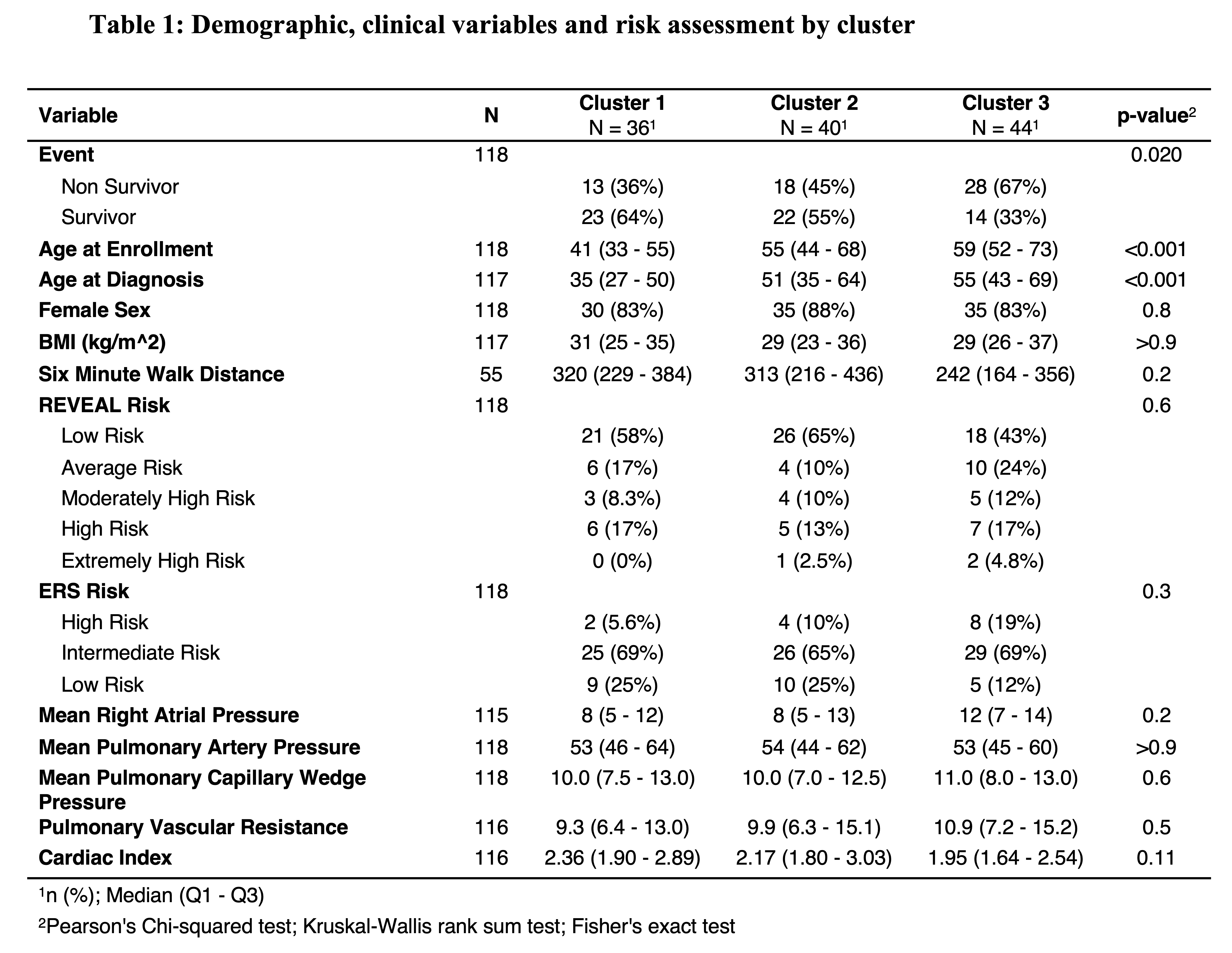
A cross-sectional, prevalent cohort of patients with IPAH (N=120, 60 survivors/60 non-survivors) was selected from the PAH Biobank to have similar clinical, genetic hemodynamic and risk profiles. Plasma protein levels of 11,000 proteins (SomaScan 11K Platform) were assayed. The top 10% of proteins with highest variance were used for spectral clustering. Survival by cluster was evaluated by Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox proportional hazards model, adjusted for enrollment age and sex. Clinical differences between clusters were assessed with Chi-squared, Kruskal-Wallis and Fisher’s exact tests. Pathway analysis identified major proteomic pathways differentiating each cluster.
Results:
Spectral clustering identified 3 clusters, with 36%, 45% and 68% events over 5-years in clusters 1, 2 and 3 respectively (Figure 1, p=0.0025). The adjusted hazard ratio for death was 1.40 and 2.78 in clusters 2, 3 comparing to cluster 1. Subjects in cluster 3 were older than cluster 1 and 2. Medications, six-minute walk test and hemodynamics were similar across clusters and most subjects were intermediate risk (ERS criteria) and low or average risk (REVEAL 2.0)(Table 1).Differentially expressed proteins showed enrichment of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) signaling (p=9.30E-04) between clusters 1 and 2, the Wnt signaling between clusters 1 and 3 (p=0.0014), and Neurotrophin signaling (p=4.82E-09) and VEGF signaling (p=5.93E-09) between clusters 2 and 3.
Conclusions:
This study identified differential expression of 3 pathways across clusters of similar IPAH patients with differences in outcomes not predicted by clinical risk assessment. All three of these pathways, Wnt, VEGF and Neurotrophin, have been implicated in pulmonary vascular and right ventricular dysfunction and may identify patients at higher risk or at different stages of the IPAH disease process. Understanding the proteome may identify molecular phenotypes of IPAH associated with outcomes but missed by clinical classification.
Patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH), a progressive pulmonary vasculopathy, may be clinically similar, yet have different responses to therapy and outcomes. Understanding proteomic profiles that distinguish amongst clinically similar patients could improve disease classification to better target treatment.
Research Question:
Can proteomic profiling identify molecular sub-phenotypes amongst otherwise clinically similar patients with IPAH?
Methods:
A cross-sectional, prevalent cohort of patients with IPAH (N=120, 60 survivors/60 non-survivors) was selected from the PAH Biobank to have similar clinical, genetic hemodynamic and risk profiles. Plasma protein levels of 11,000 proteins (SomaScan 11K Platform) were assayed. The top 10% of proteins with highest variance were used for spectral clustering. Survival by cluster was evaluated by Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox proportional hazards model, adjusted for enrollment age and sex. Clinical differences between clusters were assessed with Chi-squared, Kruskal-Wallis and Fisher’s exact tests. Pathway analysis identified major proteomic pathways differentiating each cluster.
Results:
Spectral clustering identified 3 clusters, with 36%, 45% and 68% events over 5-years in clusters 1, 2 and 3 respectively (Figure 1, p=0.0025). The adjusted hazard ratio for death was 1.40 and 2.78 in clusters 2, 3 comparing to cluster 1. Subjects in cluster 3 were older than cluster 1 and 2. Medications, six-minute walk test and hemodynamics were similar across clusters and most subjects were intermediate risk (ERS criteria) and low or average risk (REVEAL 2.0)(Table 1).Differentially expressed proteins showed enrichment of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) signaling (p=9.30E-04) between clusters 1 and 2, the Wnt signaling between clusters 1 and 3 (p=0.0014), and Neurotrophin signaling (p=4.82E-09) and VEGF signaling (p=5.93E-09) between clusters 2 and 3.
Conclusions:
This study identified differential expression of 3 pathways across clusters of similar IPAH patients with differences in outcomes not predicted by clinical risk assessment. All three of these pathways, Wnt, VEGF and Neurotrophin, have been implicated in pulmonary vascular and right ventricular dysfunction and may identify patients at higher risk or at different stages of the IPAH disease process. Understanding the proteome may identify molecular phenotypes of IPAH associated with outcomes but missed by clinical classification.
More abstracts on this topic:
Comprehensive Single-Cell Atlas of the Human Lung in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Hong Jason, Wong Brenda, Brownstein Adam, Graves Tammy, Aldred Micheala, Dai Zhiyu, Yang Xia, Eghbali Mansoureh
Dual Inhibition of Glutaminolysis and Pyruvate Carboxylase Attenuates Pulmonary Arterial HypertensionValuparampil Varghese Mathews, James Joel, Bharti Dinesh, Niihori Maki, Rafikova Olga, Rafikov Ruslan