Final ID: Sa4090
Inhibition of PKC Improves Cerebral Microvascular Endothelial Function in Streptozotocin-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is associated with cerebral microvascular dysfunction and metabolic alterations. We hypothesized that activation/overproduction of PKC contributes to AD related cerebral microvascular endothelial dysfunction. The objective of this study was to investigate whether inhibition of PKC protects against cerebral microvascular endothelial dysfunction in the setting of Streptozotocin (STZ)-Induced AD mice.
Methods: Mice (C57BL/6J, 10–12-month-old, male) received a single dose of STZ (3mg/kg, 3μl) intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection or citric buffer (control group). After one week of STZ-ICV injection (AD), some of the mice received the selective PKC inhibitor LY333531 (LY) treatment (10mg/kg, oral gavage). The control (n=6), STZ-AD (n =6) and the STZ-AD + LY (n =6) mice then underwent the Morris Water Maze test for assessing spatial learning and memory and in-vitro cerebral microvascular (pial arterioles) myography for examining microvascular reactivity. Mouse brain tissue samples were also harvested for protein analysis and mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells (MBMECs)were isolated/cultured for ion channel recording via whole cell patch clamp methods.
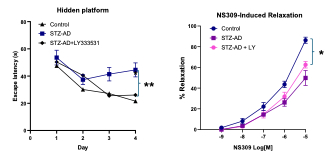
Results: Increased phospho-PKCβ and phospho-Tau (S202/T205), partially impaired spatially learning/memory and reduced cerebral microvascular relaxation were observed in mice with STZ-AD. Chronic treatment with LY partially reversed STZ-AD-impaired spatial learning and memory by showing a significant decrease in escape latency of STZ-AD mice over time compared with STZ-AD alone (P<0.05). Furthermore, treatment with LY significantly improved cerebral microvascular relaxation in response to the endothelium-dependent vasodilator NS309 as compared to STZ-AD alone (P<0.05). There were no significant differences in response to the endothelium-independent vasodilator SNP among the three groups, control, STZ-AD and STZ-AD +LY. Treatment with LY significantly improved MBMECs’ endothelial SK channel currents.
Conclusions: Our research presents novel findings which investigate the role of PKC inhibition in restoring cerebral microvascular function and in improving endothelial SK channel function in AD in the STZ-AD mice.
Methods: Mice (C57BL/6J, 10–12-month-old, male) received a single dose of STZ (3mg/kg, 3μl) intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection or citric buffer (control group). After one week of STZ-ICV injection (AD), some of the mice received the selective PKC inhibitor LY333531 (LY) treatment (10mg/kg, oral gavage). The control (n=6), STZ-AD (n =6) and the STZ-AD + LY (n =6) mice then underwent the Morris Water Maze test for assessing spatial learning and memory and in-vitro cerebral microvascular (pial arterioles) myography for examining microvascular reactivity. Mouse brain tissue samples were also harvested for protein analysis and mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells (MBMECs)were isolated/cultured for ion channel recording via whole cell patch clamp methods.
Results: Increased phospho-PKCβ and phospho-Tau (S202/T205), partially impaired spatially learning/memory and reduced cerebral microvascular relaxation were observed in mice with STZ-AD. Chronic treatment with LY partially reversed STZ-AD-impaired spatial learning and memory by showing a significant decrease in escape latency of STZ-AD mice over time compared with STZ-AD alone (P<0.05). Furthermore, treatment with LY significantly improved cerebral microvascular relaxation in response to the endothelium-dependent vasodilator NS309 as compared to STZ-AD alone (P<0.05). There were no significant differences in response to the endothelium-independent vasodilator SNP among the three groups, control, STZ-AD and STZ-AD +LY. Treatment with LY significantly improved MBMECs’ endothelial SK channel currents.
Conclusions: Our research presents novel findings which investigate the role of PKC inhibition in restoring cerebral microvascular function and in improving endothelial SK channel function in AD in the STZ-AD mice.
More abstracts on this topic:
ACLY Inhibition as a Novel Therapeutic Approach for Vascular Remodeling in Coronary Artery Disease.
Grobs Yann, Reem El-kabbout, Potus Francois, Provencher Steeve, Boucherat Olivier, Bonnet Sebastien, Romanet Charlotte, Lemay Sarah-eve, Bourgeois Alice, Voisine Pierre, Theberge Charlie, Sauvaget Melanie, Breuils Bonnet Sandra, Martineau Sandra
Association Between Meeting Physical Activity Time-Intensity Guidelines and Calf Muscle Oxygen Saturation in Patients with Symptomatic Peripheral Artery DiseaseGardner Andrew, Montgomery Polly, Wang Ming, Xu Xifei