Final ID: MP764
Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/ Kexin Type 9 Inhibitors Improve Lipid Profile and May Stabilize Vasculopathy in Heart Transplant Recipients with Chronic Allograft Vasculopathy: A Pooled Analysis of Existing Studies
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Dyslipidemia plays a critical role in the progression of chronic allograft vasculopathy (CAV), which is a major cause of long-term graft failure and mortality in heart transplant patients. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/ kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors have emerged as potent lipid-lowering agents, but their role in managing CAV in this high-risk population remains unclear.
Research Question:
Do PCSK9 inhibitors improve the lipid profile, stabilize maximal coronary intimal thickness, and affect serum biomarker levels compared to baseline in heart transplant patients with or at risk of chronic allograft vasculopathy?
Methods:
PubMed, Embase, Cochrane, ClinicalTrials.gov, and WHO ICTRP were searched. All analyses were conducted using RevMan Web, wherein pre- and post-PCSK9 inhibitor parameters were compared. A fixed- or random-effects model was used depending upon the observed heterogeneity.
Results:
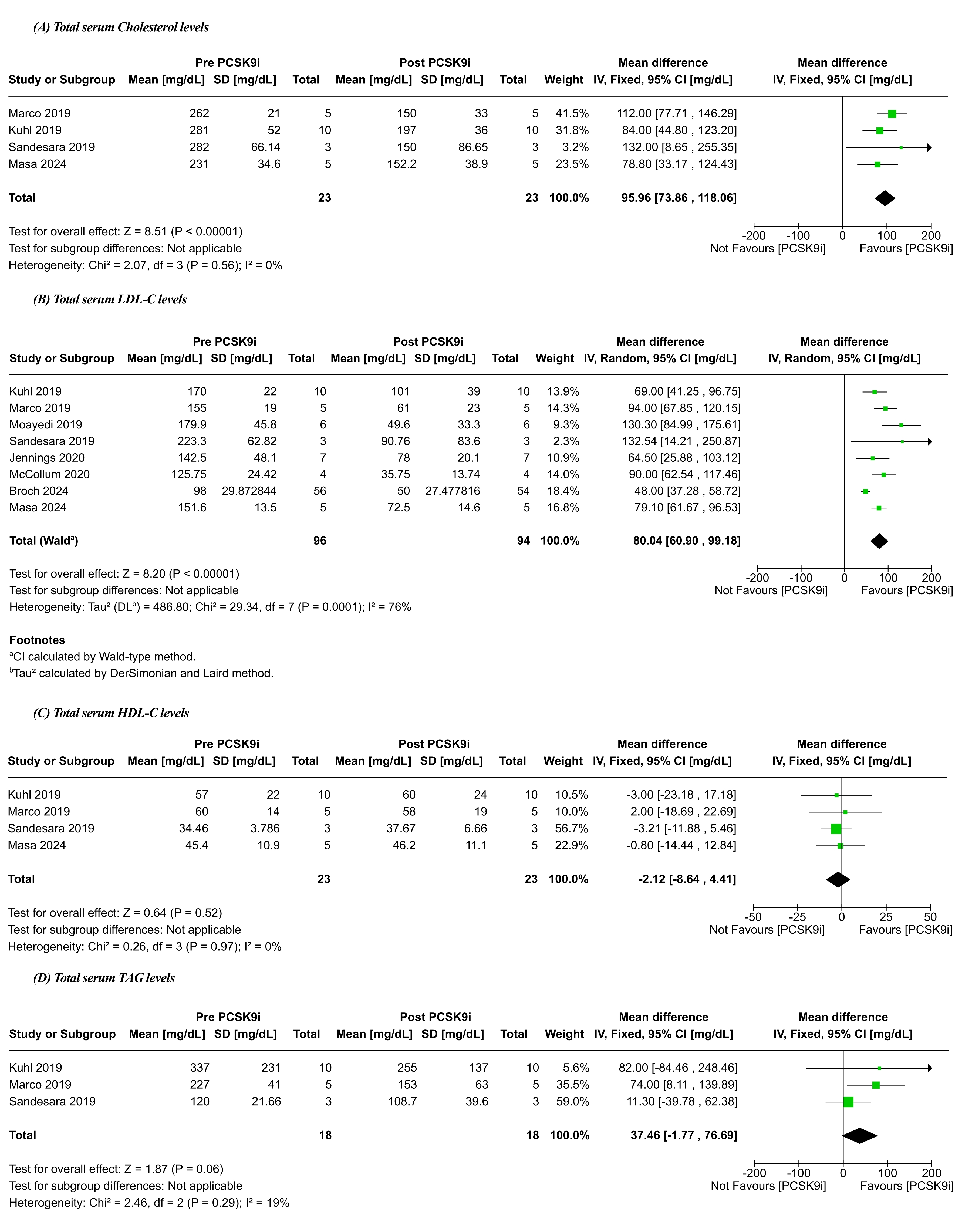
A total of nine studies comprising 240 patients were included. PCSK9 inhibitor therapy led to a statistically significant reduction in total cholesterol (MD=95.96 mg/dL; 95%CI: 73.86, 118.06; P<0.00001) and LDL-C (MD=80.04 mg/dL; 95%CI: 60.90, 99.18; P<0.00001). In contrast, no significant changes were observed in HDL-C (MD= -2.12 mg/dL; 95%CI: -8.64, 4.41; P=0.52) and triglycerides (MD=37.46 mg/dL; 95%CI: -1.77, 76.69; P=0.06). The maximal coronary intimal thickness pre- and post-PCSK9 inhibitor therapy was comparable (MD= -0.03 mm; 95%CI: -0.07, 0.02; P=0.23).
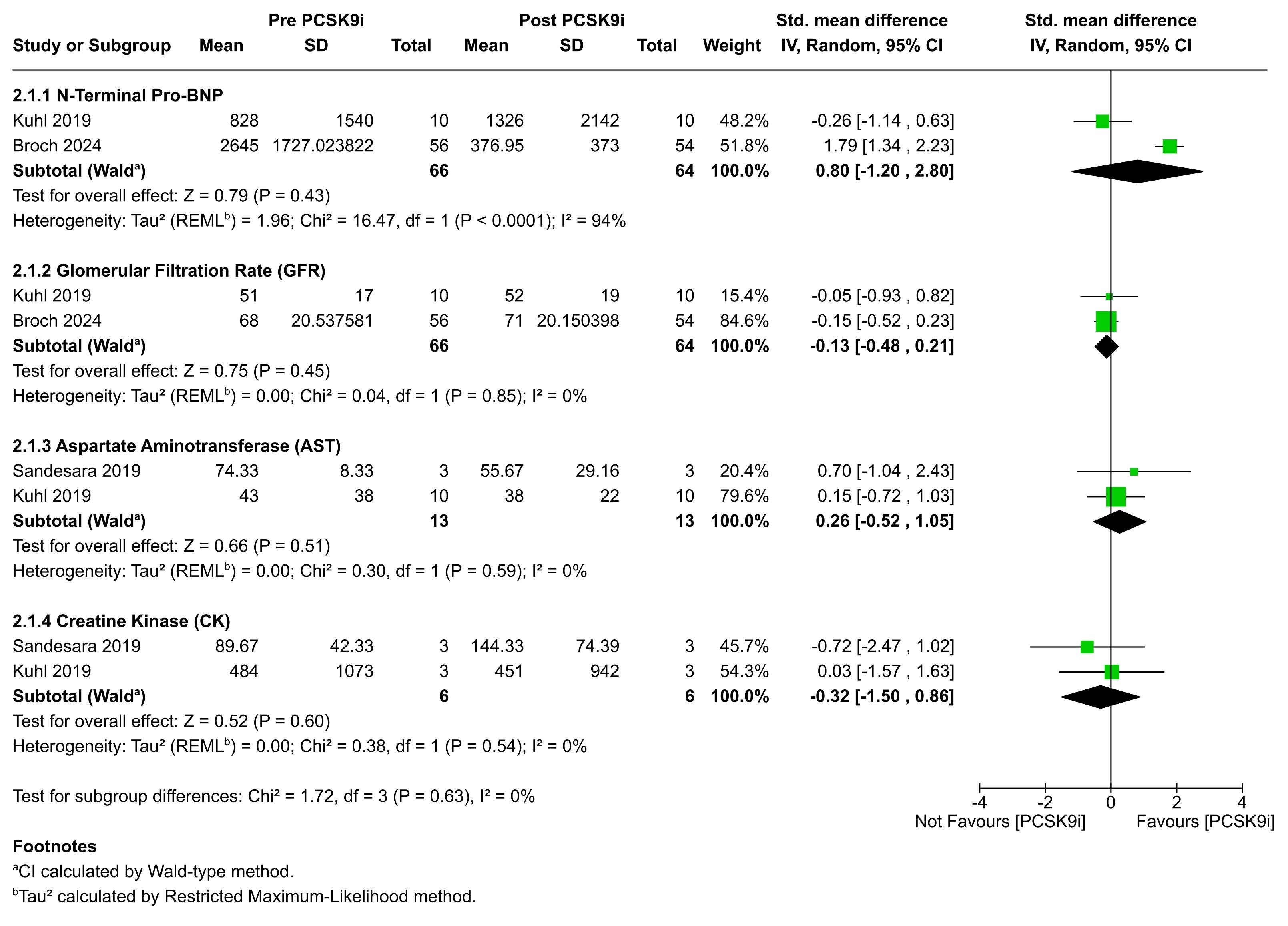
Additionally, there were no significant effects on key biomarkers, including N-terminal pro-BNP (SMD=0.80; 95%CI: -1.20, 2.80; P=0.43), glomerular filtration rate (SMD=-0.13; 95%CI: -0.48, 0.21; P=0.45), AST (SMD=0.26; 95%CI: -0.52, 1.05; P=0.51), or creatine kinase (SMD=-0.32; 95%CI: -1.50, 0.86; P=0.60) levels.
Conclusions:
PCSK9 inhibitors significantly improved lipid parameters, specifically total cholesterol and LDL-C levels, in heart transplant recipients, thereby supporting their role in dyslipidemia management within this high-risk cohort. The comparable pre- and post-therapy maximal coronary intimal thickness may indicate the slowing down of vasculopathy. The absence of significant effects on HDL-C, triglycerides, and non-lipid biomarkers suggests that the benefits are predominantly confined to reducing atherogenic lipoproteins. Further research is needed to evaluate the long-term impact of PCSK9 inhibition on cardiovascular outcomes in these patients.
Dyslipidemia plays a critical role in the progression of chronic allograft vasculopathy (CAV), which is a major cause of long-term graft failure and mortality in heart transplant patients. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/ kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors have emerged as potent lipid-lowering agents, but their role in managing CAV in this high-risk population remains unclear.
Research Question:
Do PCSK9 inhibitors improve the lipid profile, stabilize maximal coronary intimal thickness, and affect serum biomarker levels compared to baseline in heart transplant patients with or at risk of chronic allograft vasculopathy?
Methods:
PubMed, Embase, Cochrane, ClinicalTrials.gov, and WHO ICTRP were searched. All analyses were conducted using RevMan Web, wherein pre- and post-PCSK9 inhibitor parameters were compared. A fixed- or random-effects model was used depending upon the observed heterogeneity.
Results:
A total of nine studies comprising 240 patients were included. PCSK9 inhibitor therapy led to a statistically significant reduction in total cholesterol (MD=95.96 mg/dL; 95%CI: 73.86, 118.06; P<0.00001) and LDL-C (MD=80.04 mg/dL; 95%CI: 60.90, 99.18; P<0.00001). In contrast, no significant changes were observed in HDL-C (MD= -2.12 mg/dL; 95%CI: -8.64, 4.41; P=0.52) and triglycerides (MD=37.46 mg/dL; 95%CI: -1.77, 76.69; P=0.06). The maximal coronary intimal thickness pre- and post-PCSK9 inhibitor therapy was comparable (MD= -0.03 mm; 95%CI: -0.07, 0.02; P=0.23).
Additionally, there were no significant effects on key biomarkers, including N-terminal pro-BNP (SMD=0.80; 95%CI: -1.20, 2.80; P=0.43), glomerular filtration rate (SMD=-0.13; 95%CI: -0.48, 0.21; P=0.45), AST (SMD=0.26; 95%CI: -0.52, 1.05; P=0.51), or creatine kinase (SMD=-0.32; 95%CI: -1.50, 0.86; P=0.60) levels.
Conclusions:
PCSK9 inhibitors significantly improved lipid parameters, specifically total cholesterol and LDL-C levels, in heart transplant recipients, thereby supporting their role in dyslipidemia management within this high-risk cohort. The comparable pre- and post-therapy maximal coronary intimal thickness may indicate the slowing down of vasculopathy. The absence of significant effects on HDL-C, triglycerides, and non-lipid biomarkers suggests that the benefits are predominantly confined to reducing atherogenic lipoproteins. Further research is needed to evaluate the long-term impact of PCSK9 inhibition on cardiovascular outcomes in these patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Non-odorant Olfactory Receptor Ligand Depolymerizes the Platelet Actin Cytoskeleton to Prevent Thrombosis
Aggarwal Anu, Godwin Matthew, Ali Mariya, Jennings Courtney, Rajasekar Bhairavi, Scalise Alliefair, Stauffer Shaun, Mccrae Keith, Mcintyre Thomas, Cameron Scott, Wang Nancy, Josyula Vara Prasad, Yang Moua, Young Shim, Kennedy Quinn, Samuel Reina, Sangwan Naseer, Guntupalli Suman
Changes in Lipoprotein(a) and Oxidized Phospholipids Are Associated with Myocardial Inflammation but Not Systemic Inflammatory Markers Following an Acute Myocardial InfarctionAtallah Mark, Nasrallah Nadim, Harb Tarek, Valenta Ines, Schindler Thomas, Wallace Amelia, Tsimikas Sotirios, Gerstenblith Gary, Leucker Thorsten