Final ID: MP1664
Baseline Ejection Fraction and Concurrent Treatments Predict Risk of Cancer Therapy Related Cardiac Dysfunction Following Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have transformed cancer treatment but are associated with adverse effects. Incidence, predictors and timing of cancer therapy-related cardiac dysfunction (CTRCD) in ICI-treated patients remain poorly understood.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that among patients with solid tumors receiving ICI therapy, baseline cardiovascular and cancer-related risk factors would be associated with an increased risk of CTRCD or cardiovascular (CV) death following ICI initiation.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study of 5,991 cancer patients receiving ICIs at an academic medical center (2015-2024). We identified patients (n=974) with baseline and post-ICI initiation echocardiographic data, including 15 patients with myocarditis. We adjudicated patients with CTRCD after initiation of ICI therapy, defined as a ≥10% absolute decline in ejection fraction (EF) from baseline to <53%. We used Fine-Gray competing risks regression to identify predictors, with the composite outcome including CTRCD or CV-death and non-CV death as a competing event.
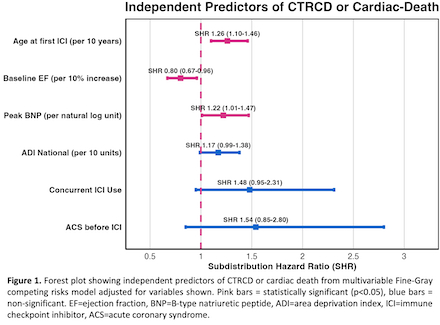
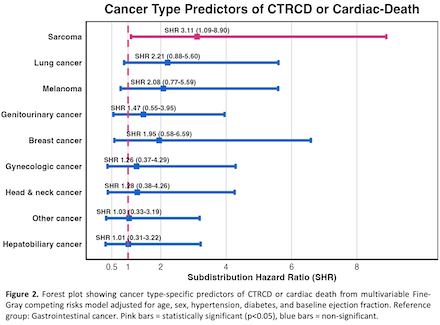
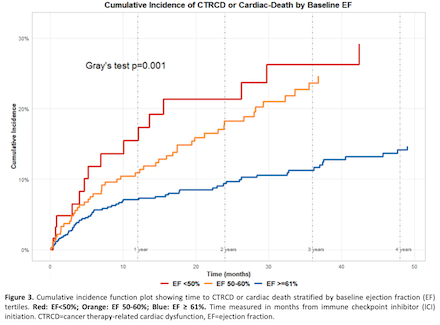
Results: Among 974 patients analyzed (mean age 66.2 ± 14.8 years, 56.2% male), 117 developed CTRCD and 16 experienced CV-death. The composite outcome occurred in 133 patients (13.7%). Patients with CTRCD or CV-death were significantly older (70.8 ± 13.0 vs 65.5 ± 15.0 years, p<0.001), had lower baseline ejection fraction (58.5 ± 8.6% vs 61.3 ± 7.3%, p<0.001), and higher rates of pre-existing cardiac conditions including heart failure (29.3% vs 15.3%, p<0.001) and arrhythmias (36.1% vs 25.6%, p=0.015). In multivariable Fine-Gray competing risks analysis, independent predictors of CTRCD or CV-death included: older age (subdistribution hazard ratio [SHR] 1.26 per 10 years, CI 1.1-1.46), lower baseline EF (SHR 0.8 per 10% EF increase, CI 0.67-0.96), higher peak BNP levels (SHR 1.22 per log-unit, CI 1.01-1.47), sarcoma cancer type (SHR 3.11, CI 1.09-8.90) and concurrent VEGF inhibitor use (SHR 2.35, CI 1.48-3.72). Among CTRCD survivors, only 24.8% received new guideline-directed medical therapy, with beta-blockers being the most prescribed (12.8%).
Conclusions: Advanced age, reduced baseline cardiac function, elevated peak BNP, sarcoma cancer type, and concurrent VEGF inhibitor therapy significantly amplified risk of CTRCD or CV-death. These findings support cardiac risk stratification before ICI therapy and suggest utility for improved surveillance protocols for high-risk patients.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that among patients with solid tumors receiving ICI therapy, baseline cardiovascular and cancer-related risk factors would be associated with an increased risk of CTRCD or cardiovascular (CV) death following ICI initiation.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study of 5,991 cancer patients receiving ICIs at an academic medical center (2015-2024). We identified patients (n=974) with baseline and post-ICI initiation echocardiographic data, including 15 patients with myocarditis. We adjudicated patients with CTRCD after initiation of ICI therapy, defined as a ≥10% absolute decline in ejection fraction (EF) from baseline to <53%. We used Fine-Gray competing risks regression to identify predictors, with the composite outcome including CTRCD or CV-death and non-CV death as a competing event.
Results: Among 974 patients analyzed (mean age 66.2 ± 14.8 years, 56.2% male), 117 developed CTRCD and 16 experienced CV-death. The composite outcome occurred in 133 patients (13.7%). Patients with CTRCD or CV-death were significantly older (70.8 ± 13.0 vs 65.5 ± 15.0 years, p<0.001), had lower baseline ejection fraction (58.5 ± 8.6% vs 61.3 ± 7.3%, p<0.001), and higher rates of pre-existing cardiac conditions including heart failure (29.3% vs 15.3%, p<0.001) and arrhythmias (36.1% vs 25.6%, p=0.015). In multivariable Fine-Gray competing risks analysis, independent predictors of CTRCD or CV-death included: older age (subdistribution hazard ratio [SHR] 1.26 per 10 years, CI 1.1-1.46), lower baseline EF (SHR 0.8 per 10% EF increase, CI 0.67-0.96), higher peak BNP levels (SHR 1.22 per log-unit, CI 1.01-1.47), sarcoma cancer type (SHR 3.11, CI 1.09-8.90) and concurrent VEGF inhibitor use (SHR 2.35, CI 1.48-3.72). Among CTRCD survivors, only 24.8% received new guideline-directed medical therapy, with beta-blockers being the most prescribed (12.8%).
Conclusions: Advanced age, reduced baseline cardiac function, elevated peak BNP, sarcoma cancer type, and concurrent VEGF inhibitor therapy significantly amplified risk of CTRCD or CV-death. These findings support cardiac risk stratification before ICI therapy and suggest utility for improved surveillance protocols for high-risk patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
A machine learning model for individualized risk prediction of ischemic heart disease in people with hypertension in Thailand
Sakboonyarat Boonsub, Poovieng Jaturon, Rangsin Ram
A Multimodal Artificial Intelligence Signature of Advanced Cardiac and Vascular Aging Defines Elevated Risk of Cardiovascular DiseasePerera Sudheesha, Biswas Dhruva, Dhingra Lovedeep, Aminorroaya Arya, Coppi Andreas, Khera Rohan