Final ID: Mo4032
Proteomic Signatures of Lipoprotein (a) Particles Reveal Novel Associations with Plasma Levels and KIV-2 Copy Number in an Elderly Multiethnic Cohort
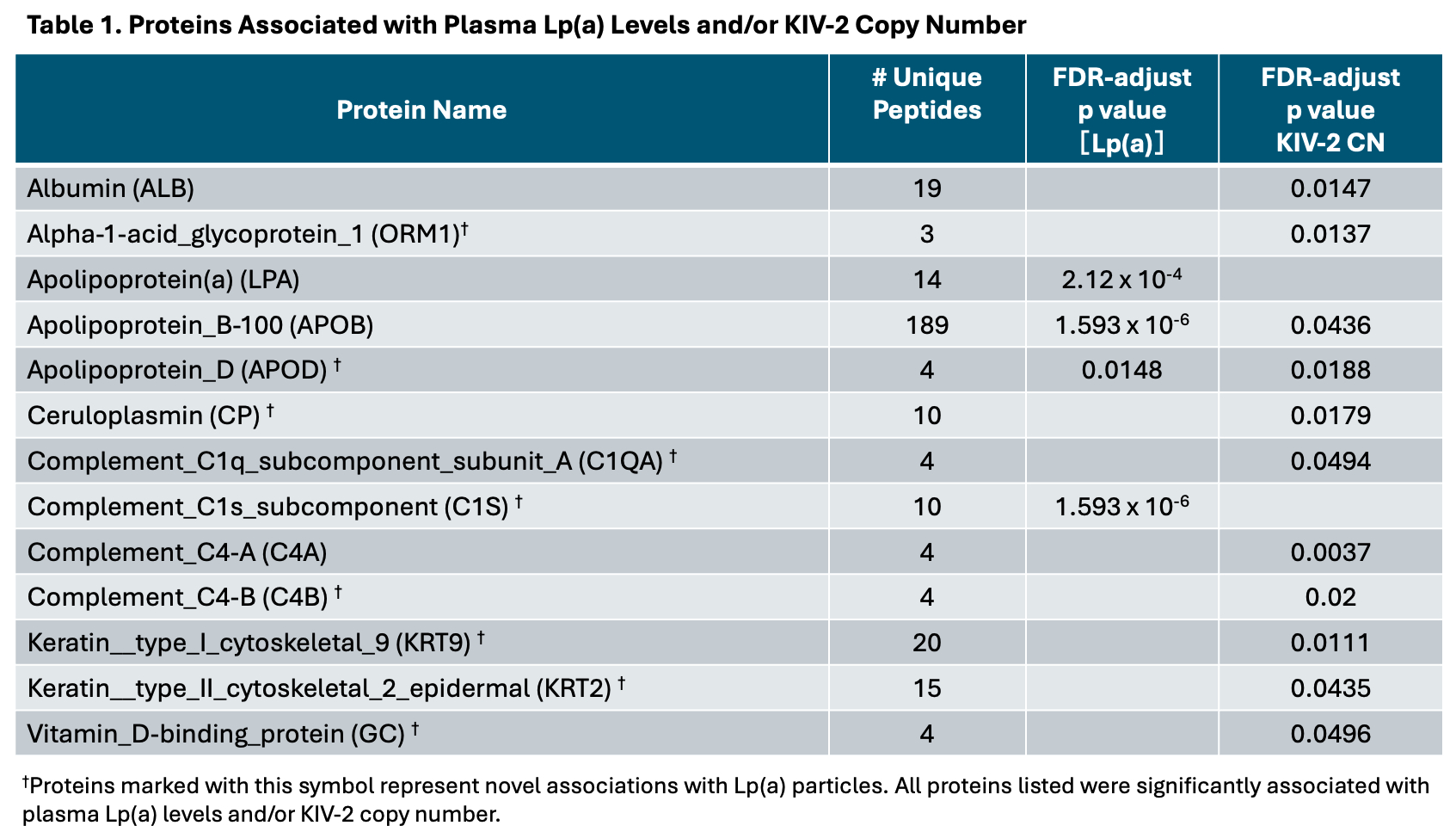
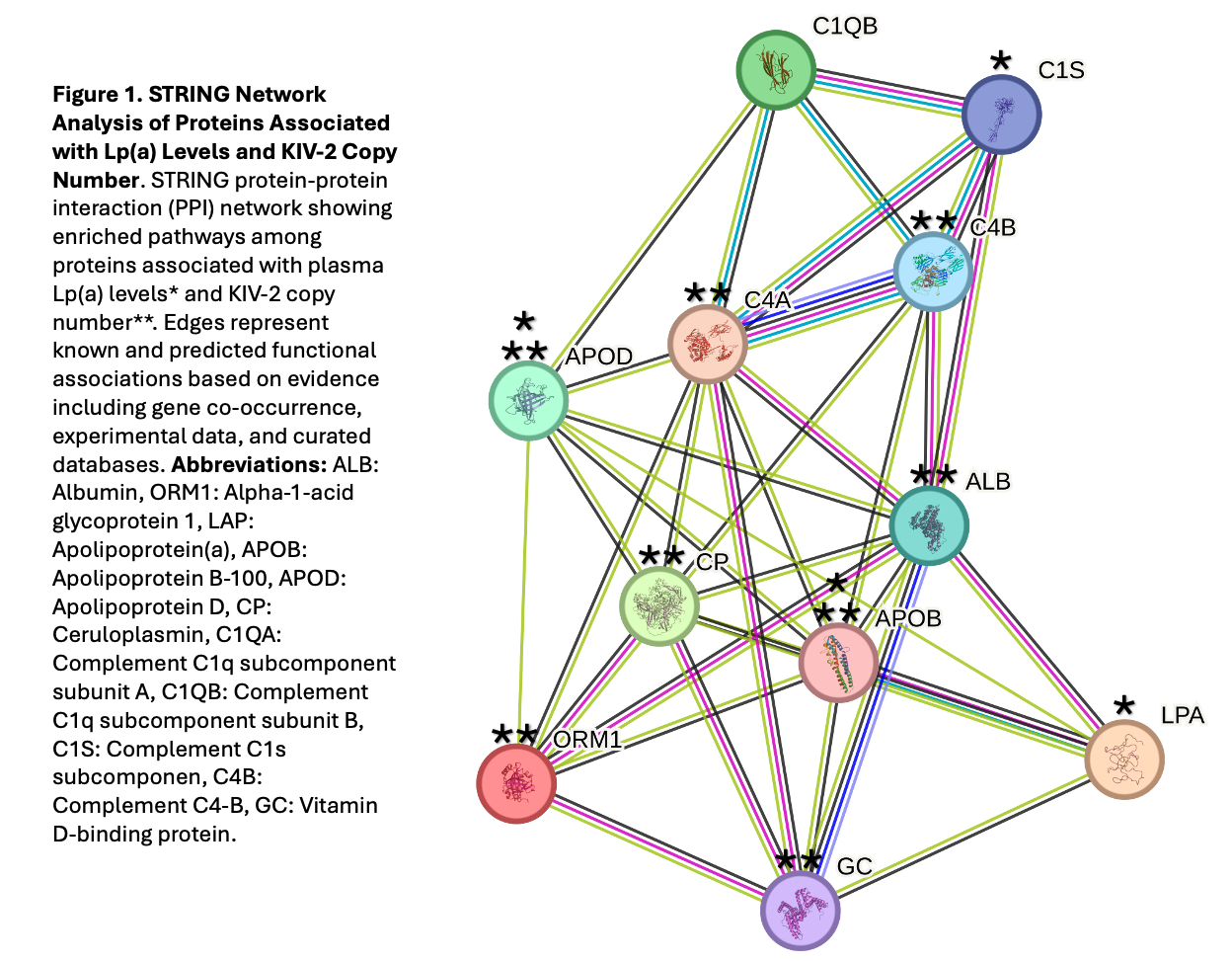
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: High lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] is a causal risk factor for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease, yet the mechanisms driving this risk remain unclear. Lp(a) levels are largely determined by variation in the LPAgene, but less is known about additional protein components and their relationship to genetic markers such as the kringle IV type 2 copy number (KIV-2 CN). Hypothesis: We hypothesized that the proteomic profile of Lp(a) particles would reveal novel proteins and pathways associated with Lp(a) levels providing mechanistic insight into Lp(a)-mediated risk. Methods: We conducted proteomic profiling of Lp(a) particles in 35 elderly participants (mean age 81 years; 71% female; 63% African American, 37% Caucasian) from the Washington Heights-Inwood Community Aging Project. Plasma Lp(a) was quantified using an isoform-independent ELISA, and KIV-2 CN was estimated using a published calling platform. Lp(a) particles were isolated by immunoprecipitation, and proteomic analysis was performed using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Protein associations with Lp(a) levels and KIV-2 CN were assessed using linear regression, adjusting for multiple testing with the Benjamini–Hochberg false discovery rate (FDR) method. Protein interaction networks were analyzed using the STRING database. Results: The median Lp(a) level was 37.1 nmol/L (interquartile range 13.1–86.2), and the mean KIV-2 CN was 20. In addition to 35 previously reported proteins, we identified two novel proteins: complement C1s (FDR-adjusted p= 2e-6) and apolipoprotein D (FDR-adjusted p=0.0148). Furthermore, several proteins, showed significant associations with KIV-2 CN, highlighting potential genotype-related effects, Table 1. STRING analysis revealed enrichment of immune and lipid metabolism pathways, including complement activation and apolipoprotein binding, Figure 1. Conclusion:The proteome of isolated Lp(a) particles reveals insights into pathways that link Lp(a) to cardiovascular and other disease processes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of thrombectomy with clinical outcomes in elderly patients presenting beyond 24 hours of last known well – A secondary analysis of SELECT LATE study
Pujara Deep, Sitton Clark, Wu Teddy, Blasco Jordi, Sangha Navi, Arenillas Juan, Opaskar Amanda, Mccullough-hicks Margy, Wallace Adam, Arthur Adam, Grotta James, Kleinig Timothy, Parsons Mark, Ribo Marc, Albers Gregory, Campbell Bruce, Sarraj Amrou, Hassan Ameer, Cardona Pedro, Ortega-gutierrez Santiago, Abraham Michael, Manning Nathan, Goyal Nitin, Blackburn Spiros
A Biomarker Based on Aneurysm Wall Enhancement and Blood Gene Expression to Identify Symptomatic Intracranial AneurysmsVeeturi Sricharan, Poppenberg Kerry, Jaikumar Vinay, Pinter Nandor, Levy Elad, Siddiqui Adnan, Tutino Vincent