Final ID: Sa2062
GLP-1 Eligibility and Use Among the Medicaid Population
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: The use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) has transformed the management of cardiovascular kidney metabolic syndrome, but the large number of individuals eligible for these high-cost therapies has raised concerns about affordability. In particular, there is sparse data on individuals insured by Medicaid.
Research Question: How many U.S. adults covered by Medicaid are eligible for GLP-1RA therapy, for which indications, and what would annual pharmaceutical spending on GLP-1RAs be if all eligible patients were to receive GLP-1RA therapy?
Methods: We analyzed cross sectional data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2017 - 2023. Eligibility criteria included diabetes, obesity or overweight with risk factors (diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia), and cardiovascular disease. We projected impact on pharmaceutical spending by multiplying the number of eligible individuals with an annual treatment cost of $8694 (diabetes) or $4476 (without diabetes) estimated by the 2024 U.S. net price of semaglutide.
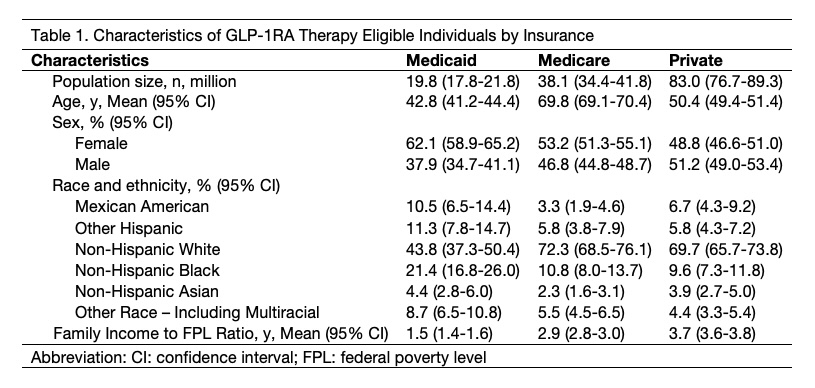
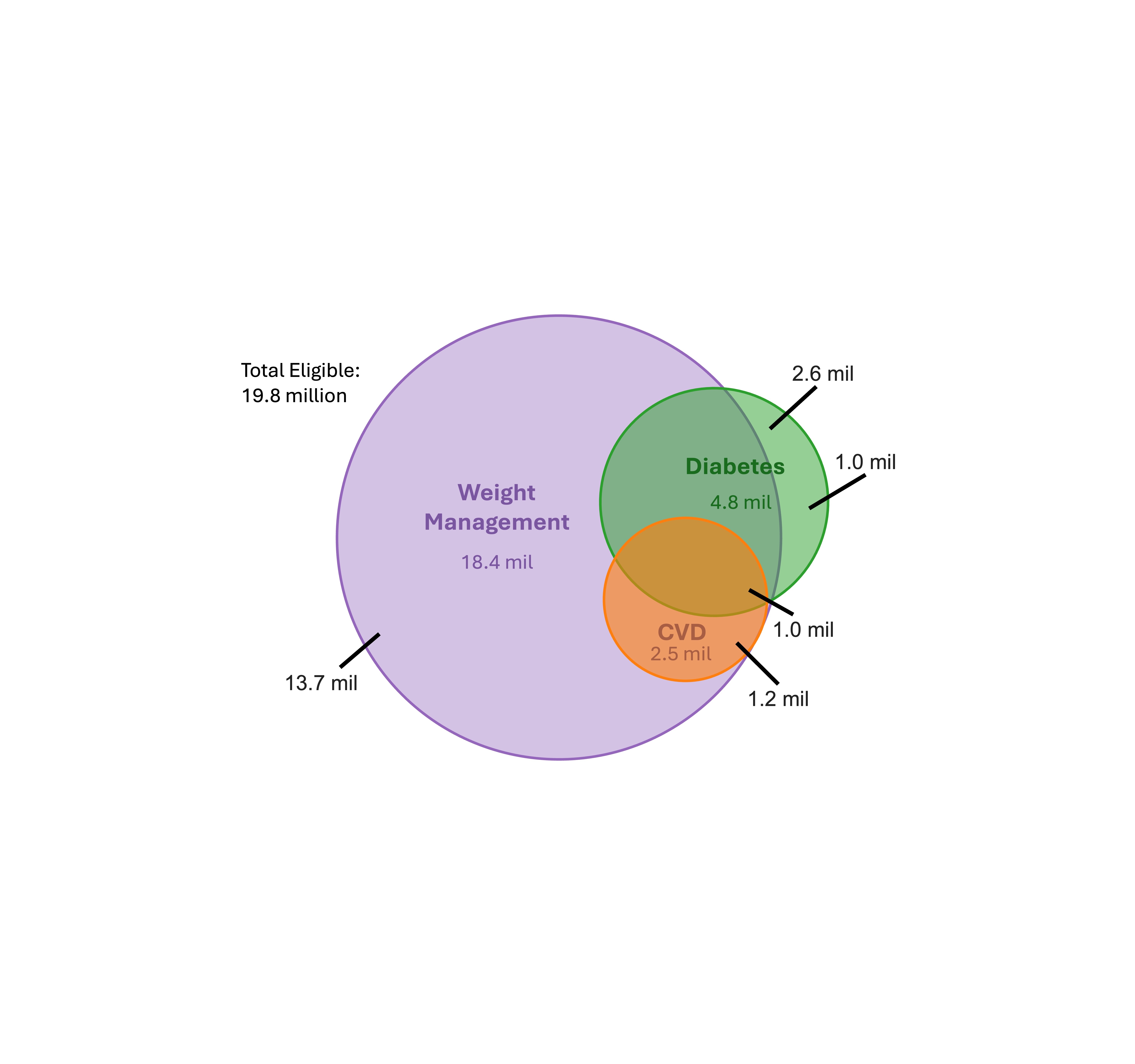
Results: A total of 19.8 million US adults on Medicaid are eligible for GLP-1RA therapy, representing 14% of the 145.3 million treatment-eligible US adults. The average age is 43 years, 62% are women, and 56% self-identify as a racial minority. They are on average younger, more likely to be female, more likely to be from a racial minority, and more likely to have lower income than eligible individuals covered by Medicare and private insurance (Image 1). Regardless of overlap, a total of 18.4 million individuals are eligible for weight loss, 4.8 million for DM, and 2.5 million for cardiovascular disease (Image 2). Of these, the majority are eligible solely for weight loss (n = 13.7 million, 69%), an indication not covered by most Medicaid plans. In contrast, 6.1 million adults (31%) have at least one indication other than weight loss and thus more likely to access GLP-1RAs through Medicaid. If all treatment-eligible patients were to receive therapy, annual pharmaceutical spending would be $166.3 billion, including $158.3 billion among individuals using therapy solely for weight loss and $8.0 billion among those with at least one other indication.
Conclusion: A total of 19.8 million Medicaid insurees are eligible for GLP-1RA therapy. Treating all eligible patients would increase pharmaceutical spending by $166.3 billion. Efforts to increase access among high-risk Medicaid patients are urgently needed.
Research Question: How many U.S. adults covered by Medicaid are eligible for GLP-1RA therapy, for which indications, and what would annual pharmaceutical spending on GLP-1RAs be if all eligible patients were to receive GLP-1RA therapy?
Methods: We analyzed cross sectional data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2017 - 2023. Eligibility criteria included diabetes, obesity or overweight with risk factors (diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia), and cardiovascular disease. We projected impact on pharmaceutical spending by multiplying the number of eligible individuals with an annual treatment cost of $8694 (diabetes) or $4476 (without diabetes) estimated by the 2024 U.S. net price of semaglutide.
Results: A total of 19.8 million US adults on Medicaid are eligible for GLP-1RA therapy, representing 14% of the 145.3 million treatment-eligible US adults. The average age is 43 years, 62% are women, and 56% self-identify as a racial minority. They are on average younger, more likely to be female, more likely to be from a racial minority, and more likely to have lower income than eligible individuals covered by Medicare and private insurance (Image 1). Regardless of overlap, a total of 18.4 million individuals are eligible for weight loss, 4.8 million for DM, and 2.5 million for cardiovascular disease (Image 2). Of these, the majority are eligible solely for weight loss (n = 13.7 million, 69%), an indication not covered by most Medicaid plans. In contrast, 6.1 million adults (31%) have at least one indication other than weight loss and thus more likely to access GLP-1RAs through Medicaid. If all treatment-eligible patients were to receive therapy, annual pharmaceutical spending would be $166.3 billion, including $158.3 billion among individuals using therapy solely for weight loss and $8.0 billion among those with at least one other indication.
Conclusion: A total of 19.8 million Medicaid insurees are eligible for GLP-1RA therapy. Treating all eligible patients would increase pharmaceutical spending by $166.3 billion. Efforts to increase access among high-risk Medicaid patients are urgently needed.
More abstracts on this topic:
Active Screening in Black, Hispanic/LatinX, Asian/Pacific Islander, and Native American Individuals Reduces Racial Disparities in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Diagnosis
Miner Grace, Govindarajulu Usha, Smolock Christopher, Faries Peter, Marin Michael
Adiponectin and Adiponectin/Leptin Ratio Associate with Cardiometabolic Risk in South Asian Americans: Updates from the MASALA StudyUttarwar Salil, Shah Nilay, Kanaya Alka, Gadgil Meghana