Final ID: 4365950
Renal Klotho Targeting Myocardial IQGAP1 Regulation of Mitochondrial Damage and PANoptosis in Heart Failure
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Heart failure following myocardial infarction (post-MI HF) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The presence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) often exacerbates post-MI HF severity. Investigation of heart-kidney interactions may yield novel approaches to post-MI HF treatment from a multi-organ perspective.
Research Questions
Is there a signaling mediator that mediates cardiorenal crosstalk, and what are its molecular targets and mechanisms in cardiomyocytes?
Methods
A post-myocardial infarction HF model was established in mice with or without CKD to investigate the interactions between cardiac and renal injury. Single-cell transcriptome data from renal tissue samples were retrieved to identify potential linking factors (Klotho, KL). A retrospective analysis was performed in post-MI HF patients (NYHA II: 74; NYHA III-IV: 108 ) to assess its clinical significance.Then, kidney-specific Klotho knockout or exogenous Klotho protein administration was employed to evaluate the role of renal-derived Klotho in protecting cardiac tissue.To further elucidate and confirm the underlying mechanisms, both in vitro experiments and computational analyses were performed.
Results & Conclusion
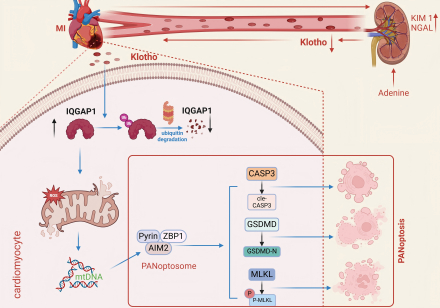
CKD exacerbated cardiac structural and functional impairments in mice with post-MI HF. Transcriptomic analysis suggested that renal Klotho might be a key regulatory factor in this process. Clinical data further indicated that Klotho is an independent risk factor for the development of heart failure following myocardial infarction.Further in vivo experiments involving kidney-specific Klotho knockout and Klotho supplementation demonstrated that renal-derived Klotho exerts significant protective effects on cardiomyocytes in mice with post-MI HF. Further results demonstrated that Klotho binds to cardiomyocyte IQGAP1 and increases its ubiquitination levels. Moreover, both Klotho protein intervention and IQGAP1 knockout significantly alleviated mitochondrial damage, mtDNA release, and PANoptosis induced by OGD injury in cardiomyocytes. This study identifies renal-derived Klotho as a critical mediator of cardiorenal crosstalk in post-MI HF. Renal Klotho exerts cardioprotective effects by targeting myocardial IQGAP1, promoting its ubiquitination, and thereby attenuating mitochondrial damage and PANoptosis in cardiomyocytes. These findings reveal a novel renal-Klotho-cardiac axis mediating cardiorenal communication in post-MI HF.
Heart failure following myocardial infarction (post-MI HF) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The presence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) often exacerbates post-MI HF severity. Investigation of heart-kidney interactions may yield novel approaches to post-MI HF treatment from a multi-organ perspective.
Research Questions
Is there a signaling mediator that mediates cardiorenal crosstalk, and what are its molecular targets and mechanisms in cardiomyocytes?
Methods
A post-myocardial infarction HF model was established in mice with or without CKD to investigate the interactions between cardiac and renal injury. Single-cell transcriptome data from renal tissue samples were retrieved to identify potential linking factors (Klotho, KL). A retrospective analysis was performed in post-MI HF patients (NYHA II: 74; NYHA III-IV: 108 ) to assess its clinical significance.Then, kidney-specific Klotho knockout or exogenous Klotho protein administration was employed to evaluate the role of renal-derived Klotho in protecting cardiac tissue.To further elucidate and confirm the underlying mechanisms, both in vitro experiments and computational analyses were performed.
Results & Conclusion
CKD exacerbated cardiac structural and functional impairments in mice with post-MI HF. Transcriptomic analysis suggested that renal Klotho might be a key regulatory factor in this process. Clinical data further indicated that Klotho is an independent risk factor for the development of heart failure following myocardial infarction.Further in vivo experiments involving kidney-specific Klotho knockout and Klotho supplementation demonstrated that renal-derived Klotho exerts significant protective effects on cardiomyocytes in mice with post-MI HF. Further results demonstrated that Klotho binds to cardiomyocyte IQGAP1 and increases its ubiquitination levels. Moreover, both Klotho protein intervention and IQGAP1 knockout significantly alleviated mitochondrial damage, mtDNA release, and PANoptosis induced by OGD injury in cardiomyocytes. This study identifies renal-derived Klotho as a critical mediator of cardiorenal crosstalk in post-MI HF. Renal Klotho exerts cardioprotective effects by targeting myocardial IQGAP1, promoting its ubiquitination, and thereby attenuating mitochondrial damage and PANoptosis in cardiomyocytes. These findings reveal a novel renal-Klotho-cardiac axis mediating cardiorenal communication in post-MI HF.
More abstracts on this topic:
β1-adrenergic autoantibodies (β1-AA) augment macropinocytosis in CD4+ T cells, leading to the expansion of CD4+CD28− T cell subsets in heart failure.
Sun Fei, Yao Junyan, Li Bingjie, Zhang Suli, Liu Huirong
A Case of Concomitant Wild-Type Transthyretin and Systemic Light Chain Amyloidosis Involving Separate OrgansChiu Leonard, Afrough Aimaz, Nadeem Urooba, Jebakumar Deborah, Grodin Justin