Final ID: Sa2031
Depression and anxiety increase risk of chronic kidney disease via gain of CVD risk factors with an accentuated effect among women and non-white individuals
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Anxiety and depression accelerate the development of both cardiovascular risk factors and renal disease. It has been previously shown that CVD, its risk factors, and mental health disorders differ by sex and race. However, the influence of sex and race differences on the association between anxiety and/or depression (anx/dep) and renal disease has not been explored. We hypothesized that: 1) anx/dep increase the risk of developing chronic kidney disease (CKD), 2) the association between anx/dep and the risk of CKD differs by sex and race, and 3) the development of hypertension (HTN) and/or diabetes (DM) mediate the link between anx/dep and CKD.
Methods:
Individuals (N=98,388; median age 57 years; 57.5% female) with data on CKD status, anxiety, and depression were identified in the Mass General Brigham Biobank. Diagnoses of CKD, anxiety, depression, HTN, and DM were collected using ICD-10 codes. Race was self-reported at the time of consent. Anx/dep were defined upon consent, and CKD was defined after consent. Those with CKD at baseline or incident anx/dep after consent were excluded. Mediation analyses accounted for temporal precedence of diagnoses.
Results:
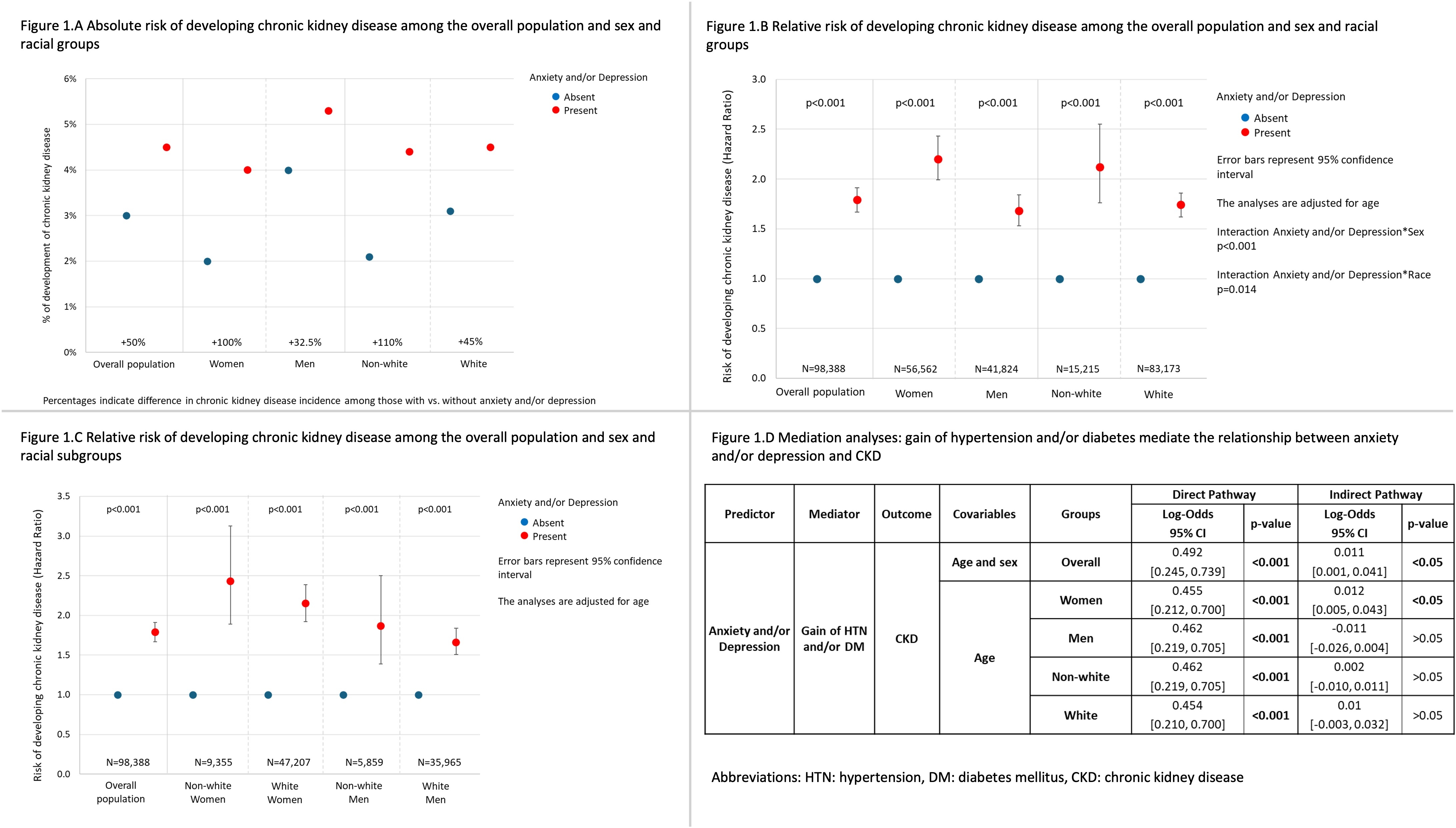
The absolute risk of CKD among those with and without anx/dep stratified by sex and race is shown (Figure 1A). Among the overall population, anx/dep associated with incident CKD (HR=1.79 [95% CI: 1.67, 1.91], p<0.001) after adjusting for age and sex. The interactions between anx/dep and CKD by sex and race were significant. The risk of CKD associated with anx/dep was numerically higher among women (2.20 [1.99, 2.43], p<0.001) than men (1.68 [1.53, 1.84], p<0.001, Figure 1B) in models adjusted for age. Also, the CKD risk was numerically higher among non-white (2.12 [1.76, 2.55], p<0.001) than white individuals (1.74 [1.62, 1.86], p<0.001, Figure 1B) in models adjusted for age. Further, significant differences in the risk of developing CKD related to anx/dep were observed across the subgroups of sex and race (Figure 1C). The development of HTN and/or DM mediated the link between anx/dep and CKD among the overall population and women (Figure 1D).
Conclusion:
These findings suggest that anx/dep contribute to sex and race related differences in the development of CKD with a greater effect in women and non-white individuals. These relationships are mediated in part by the accelerated development of HTN and/or DM.
Anxiety and depression accelerate the development of both cardiovascular risk factors and renal disease. It has been previously shown that CVD, its risk factors, and mental health disorders differ by sex and race. However, the influence of sex and race differences on the association between anxiety and/or depression (anx/dep) and renal disease has not been explored. We hypothesized that: 1) anx/dep increase the risk of developing chronic kidney disease (CKD), 2) the association between anx/dep and the risk of CKD differs by sex and race, and 3) the development of hypertension (HTN) and/or diabetes (DM) mediate the link between anx/dep and CKD.
Methods:
Individuals (N=98,388; median age 57 years; 57.5% female) with data on CKD status, anxiety, and depression were identified in the Mass General Brigham Biobank. Diagnoses of CKD, anxiety, depression, HTN, and DM were collected using ICD-10 codes. Race was self-reported at the time of consent. Anx/dep were defined upon consent, and CKD was defined after consent. Those with CKD at baseline or incident anx/dep after consent were excluded. Mediation analyses accounted for temporal precedence of diagnoses.
Results:
The absolute risk of CKD among those with and without anx/dep stratified by sex and race is shown (Figure 1A). Among the overall population, anx/dep associated with incident CKD (HR=1.79 [95% CI: 1.67, 1.91], p<0.001) after adjusting for age and sex. The interactions between anx/dep and CKD by sex and race were significant. The risk of CKD associated with anx/dep was numerically higher among women (2.20 [1.99, 2.43], p<0.001) than men (1.68 [1.53, 1.84], p<0.001, Figure 1B) in models adjusted for age. Also, the CKD risk was numerically higher among non-white (2.12 [1.76, 2.55], p<0.001) than white individuals (1.74 [1.62, 1.86], p<0.001, Figure 1B) in models adjusted for age. Further, significant differences in the risk of developing CKD related to anx/dep were observed across the subgroups of sex and race (Figure 1C). The development of HTN and/or DM mediated the link between anx/dep and CKD among the overall population and women (Figure 1D).
Conclusion:
These findings suggest that anx/dep contribute to sex and race related differences in the development of CKD with a greater effect in women and non-white individuals. These relationships are mediated in part by the accelerated development of HTN and/or DM.
More abstracts on this topic:
Ambulatory Atrial Fibrillation Ablation is Underutilized Among Women and Racial/Ethnic Minority Groups
Makmal Noam, Koplan Bruce
A Machine Learning Approach to Simplify Risk Stratification of Patients with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular DiseaseLi Hsin Fang, Gluckman Ty, Nute Andrew, Weerasinghe Roshanthi, Wendt Staci, Wilson Eleni, Sidelnikov Eduard, Kathe Niranjan, Swihart Charissa, Jones Laney