Final ID: Mo3147
Structural and Load-Dependent Arterial Stiffness Mechanisms and Sleep-Disordered Breathing: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is associated with increased arterial stiffness and adverse cardiovascular outcomes. Structural and load-dependent components reflect stiffening due to age-related changes in the blood vessel wall and from the pressure load on the arterial wall, respectively. The extent to which OSA severity, measured by Apnea Hypopnea Index (AHI) correlates with these distinct components of arterial stiffness remains unclear.
Hypothesis: In a multiethnic cohort, AHI exhibits distinct relationships with structural and load-dependent pulse wave velocity (PWV), contributing variably to total PWV independent of conventional cardiovascular risk factors.
Methods: Data from 2,033 participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) Exam 5 with corresponding MESA Sleep and Carotid Ultrasound Ancillary Studies were analyzed. AHI defined as all apneas & hypopneas with >=3% desaturation or arousals above 5 events/hour was logarithmically transformed for regression analysis. Total, structural, and load-dependent carotid PWV were calculated using participant-specific models. Multivariable linear regression was performed to assess the impact of AHI on Total, structural, and load-dependent PWV.
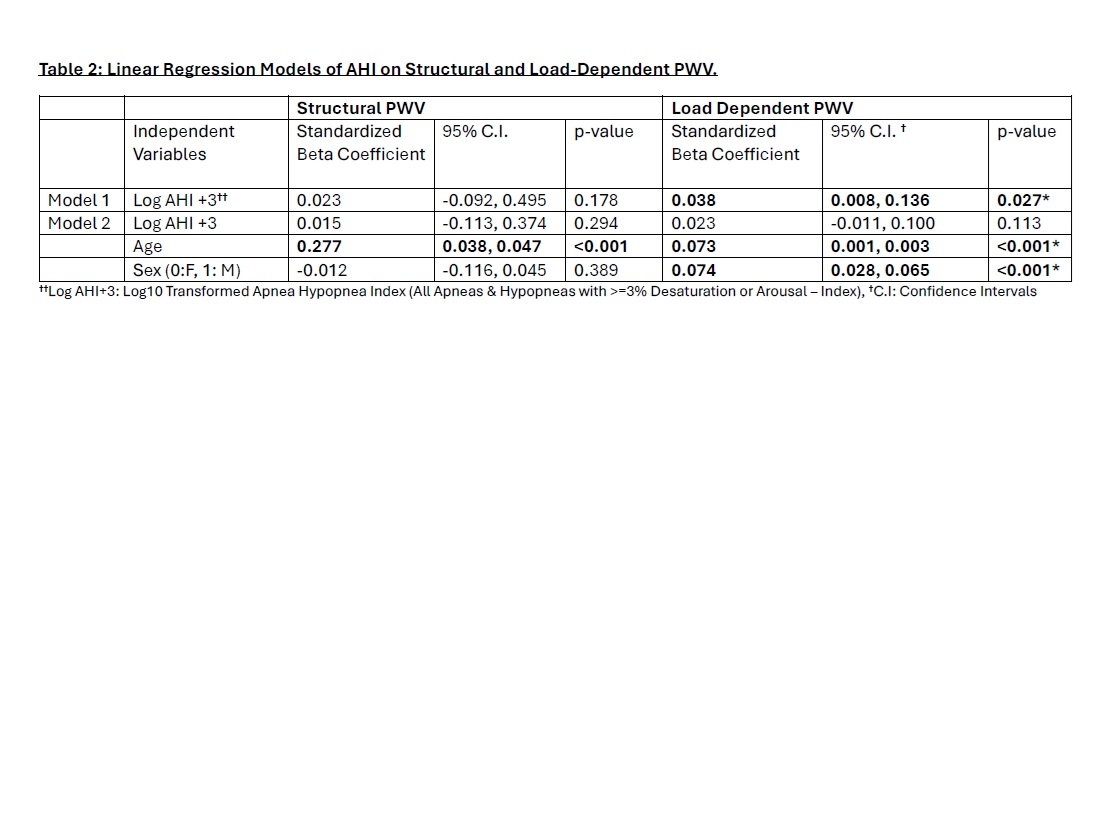
Results: Participants were 69.9 (±9.5) years old and 53.3% Female. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) was 129.6 (±18.9) mmHg. Total Carotid PWV was 7.41 (±2.0) m/s, while structural PWV was 7.37 (±1.9) m/s and load-dependent PWV was 0.04 (±0.42) m/s. Median AHI was 18.3 (IQR: 9.4, 18.3, 33.1) events/hour. In unadjusted models, AHI demonstrated a significant association with load-dependent PWV (β = 0.038, p = 0.027) but not with structural PWV (β = 0.023, p = 0.178). After adjustment for age and sex, AHI was no longer associated with any PWV component (Table 2). Age correlated significantly with both PWV components, while sex significantly affects only load-dependent PWV (β = 0.078, p < 0.001) with no interaction effects.
Conclusion: In this large, multiethnic cohort of older adults, AHI demonstrated a significant correlation with load-dependent PWV but was not meaningfully related to structural PWV. The association with load-dependent AHI was no longer present after adjustment for age and sex.
Hypothesis: In a multiethnic cohort, AHI exhibits distinct relationships with structural and load-dependent pulse wave velocity (PWV), contributing variably to total PWV independent of conventional cardiovascular risk factors.
Methods: Data from 2,033 participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) Exam 5 with corresponding MESA Sleep and Carotid Ultrasound Ancillary Studies were analyzed. AHI defined as all apneas & hypopneas with >=3% desaturation or arousals above 5 events/hour was logarithmically transformed for regression analysis. Total, structural, and load-dependent carotid PWV were calculated using participant-specific models. Multivariable linear regression was performed to assess the impact of AHI on Total, structural, and load-dependent PWV.
Results: Participants were 69.9 (±9.5) years old and 53.3% Female. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) was 129.6 (±18.9) mmHg. Total Carotid PWV was 7.41 (±2.0) m/s, while structural PWV was 7.37 (±1.9) m/s and load-dependent PWV was 0.04 (±0.42) m/s. Median AHI was 18.3 (IQR: 9.4, 18.3, 33.1) events/hour. In unadjusted models, AHI demonstrated a significant association with load-dependent PWV (β = 0.038, p = 0.027) but not with structural PWV (β = 0.023, p = 0.178). After adjustment for age and sex, AHI was no longer associated with any PWV component (Table 2). Age correlated significantly with both PWV components, while sex significantly affects only load-dependent PWV (β = 0.078, p < 0.001) with no interaction effects.
Conclusion: In this large, multiethnic cohort of older adults, AHI demonstrated a significant correlation with load-dependent PWV but was not meaningfully related to structural PWV. The association with load-dependent AHI was no longer present after adjustment for age and sex.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Loss of Function Polymorphism in the Propeptide of Lysyl Oxidase Exacerbates Atherosclerosis
Jung In-hyuk, Amrute Junedh, Luna Sophia, Wagoner Ryan, Lee Paul, Burks Kendall, Holloway Karyn, Alisio Arturo, Stitziel Nathan
Additive Prognostic Significance of Vascular Disease in Patients Referred for Exercise Stress EchocardiographyHart Hannah, Omar Alaa, Argulian Edgar