Final ID: MP445
Group Virtual Care for Women with Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome: Engagement and Lifestyle Change in a Scalable Model
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome is a growing public health challenge marked by rising morbidity, mortality, and healthcare costs. Traditional care models often struggle to engage patients, with no-show rates reaching 18–20%. Scalable strategies to engage at-risk patients are urgently needed.
Objective: To assess the impact of a group virtual care model on engagement, experience, and lifestyle behavior change in CKM.
Methods: Systole Health, a virtual group care organization, enrolled cohorts of 3–5 women into a six-week CKM optimization program across 16 U.S. states between April 2024 and March 2025. Eligible participants had documented or self-reported overweight/obesity, hypertension (HTN), dyslipidemia (DLD), and/or (pre)diabetes. Exclusion criteria included active pregnancy and unstable CKM. The intervention included weekly cardiologist-led shared medical appointments, lifestyle health coaching, medication optimization, and coach-led group and individual text support. Attendance was tracked, and satisfaction and self-reported behavior change were assessed via post-program surveys. Linear regression evaluated associations between attendance and changes in BMI, blood pressure, and LDL cholesterol.
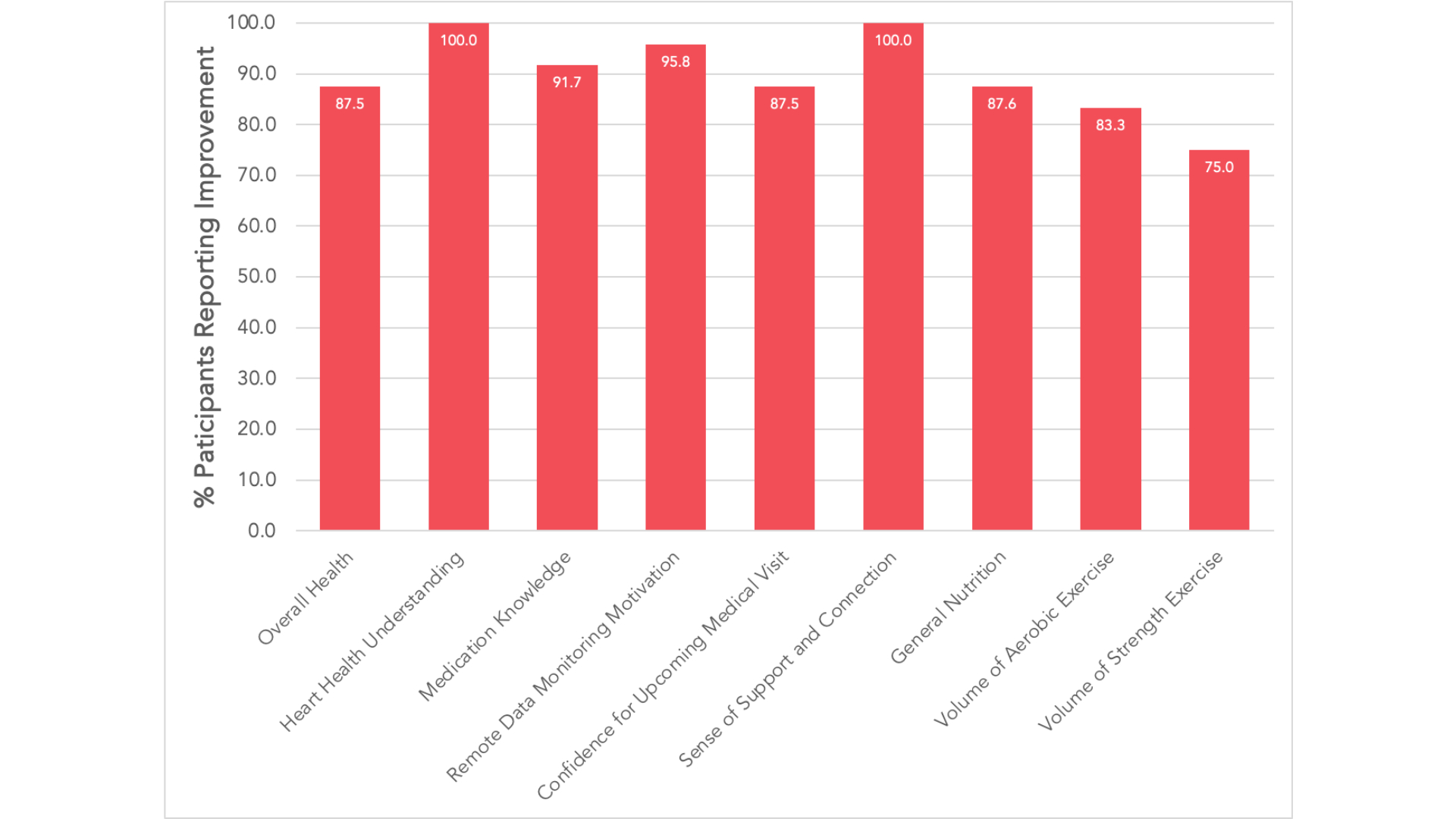
Results: A total of 45 women enrolled, contributing 247 patient visits. Mean age was 52.2 ± 11.5 years; 86.7% were White. Most participants (53.3%) had ≥3 CKM risk factors (BP ≥130/80, LDL-C above guideline-recommended thresholds, BMI ≥27, and/or A1c ≥5.7%); overall, 88.9% had overweight/obesity, 35.6% HTN, 44.4% DLD, and 24.4% (pre)diabetes. Median attendance was 6 of 6 sessions (interquartile range [IQR] 1), with a program completion rate (≥5 sessions) of 85.1%. Median satisfaction and likelihood to recommend were both 10/10 (IQRs 0.5 and 0.25, respectively). Participants reported improvements in heart health understanding (100.0%), medication knowledge (91.7%), motivation to monitor health data (95.8%), confidence preparing for medical visits (87.5), sense of support (100.0%), nutrition (87.6%), cardiovascular exercise (83.3%), and overall health (87.5) (Figure 1). Clinical outcomes trended favorably with higher attendance, though associations were not statistically significant.
Conclusion: A group virtual care model for women with CKM risk factors demonstrated high engagement, satisfaction, and self-reported behavior change, supporting its potential as a scalable, patient-centered strategy for CKM care.
Objective: To assess the impact of a group virtual care model on engagement, experience, and lifestyle behavior change in CKM.
Methods: Systole Health, a virtual group care organization, enrolled cohorts of 3–5 women into a six-week CKM optimization program across 16 U.S. states between April 2024 and March 2025. Eligible participants had documented or self-reported overweight/obesity, hypertension (HTN), dyslipidemia (DLD), and/or (pre)diabetes. Exclusion criteria included active pregnancy and unstable CKM. The intervention included weekly cardiologist-led shared medical appointments, lifestyle health coaching, medication optimization, and coach-led group and individual text support. Attendance was tracked, and satisfaction and self-reported behavior change were assessed via post-program surveys. Linear regression evaluated associations between attendance and changes in BMI, blood pressure, and LDL cholesterol.
Results: A total of 45 women enrolled, contributing 247 patient visits. Mean age was 52.2 ± 11.5 years; 86.7% were White. Most participants (53.3%) had ≥3 CKM risk factors (BP ≥130/80, LDL-C above guideline-recommended thresholds, BMI ≥27, and/or A1c ≥5.7%); overall, 88.9% had overweight/obesity, 35.6% HTN, 44.4% DLD, and 24.4% (pre)diabetes. Median attendance was 6 of 6 sessions (interquartile range [IQR] 1), with a program completion rate (≥5 sessions) of 85.1%. Median satisfaction and likelihood to recommend were both 10/10 (IQRs 0.5 and 0.25, respectively). Participants reported improvements in heart health understanding (100.0%), medication knowledge (91.7%), motivation to monitor health data (95.8%), confidence preparing for medical visits (87.5), sense of support (100.0%), nutrition (87.6%), cardiovascular exercise (83.3%), and overall health (87.5) (Figure 1). Clinical outcomes trended favorably with higher attendance, though associations were not statistically significant.
Conclusion: A group virtual care model for women with CKM risk factors demonstrated high engagement, satisfaction, and self-reported behavior change, supporting its potential as a scalable, patient-centered strategy for CKM care.
More abstracts on this topic:
A validated metabolite-based biomarker score for fruit and vegetable intake and associations with all-cause mortality and incident cardiometabolic diseases
Clinical Efficacy of Telemedicine vs Standard Outpatient Management for Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Oude Griep Linda, Li Chunxiao, Koulman Albert, Imamura Fumiaki, Wareham Nicholas, Forouhi Nita
Clinical Efficacy of Telemedicine vs Standard Outpatient Management for Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Syed Saif, Panjiyar Binay, Patel Sharvil, Vemulaghat Krishna Teja, Singla Ankur, Sharma Shivangi, Kc Anil, Gopu Sahithi, Kushagar Singla, Wagle Laxman, Tadigotla Chandana, Ochani Rohan Kumar, Mandava Snigdha, Shaik Deekshith Ameer, Hotwani Priya, Bashir Qasim, Almas Talal, Saha Shubhashis, Prasad Abishek, Arshad Sameed, Raj Rohan