Final ID: Mo4009
Exploring Stress-Related Myocardial Injury in Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Risk, Prevalence, and Outcomes.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a critical metabolic disorder that can trigger stress-related myocardial injury (SRMI), but national estimates of SRMI in DKA hospitalizations are limited.
Objective:
This study investigates the prevalence, risk factors, and associated outcomes of SRMI during DKA hospitalizations using a comprehensive and nationally representative dataset.
Methods:
We conducted a retrospective, cross-sectional study using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) data from 2016 to 2020, identifying 221,594 weighted adult hospitalizations for DKA. SRMI was defined using ICD-10-CM codes for myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, and Takotsubo syndrome. Predictors and outcomes were assessed using survey-weighted multivariable regression models, accounting for demographic, clinical, and hospital-level factors.
Results:
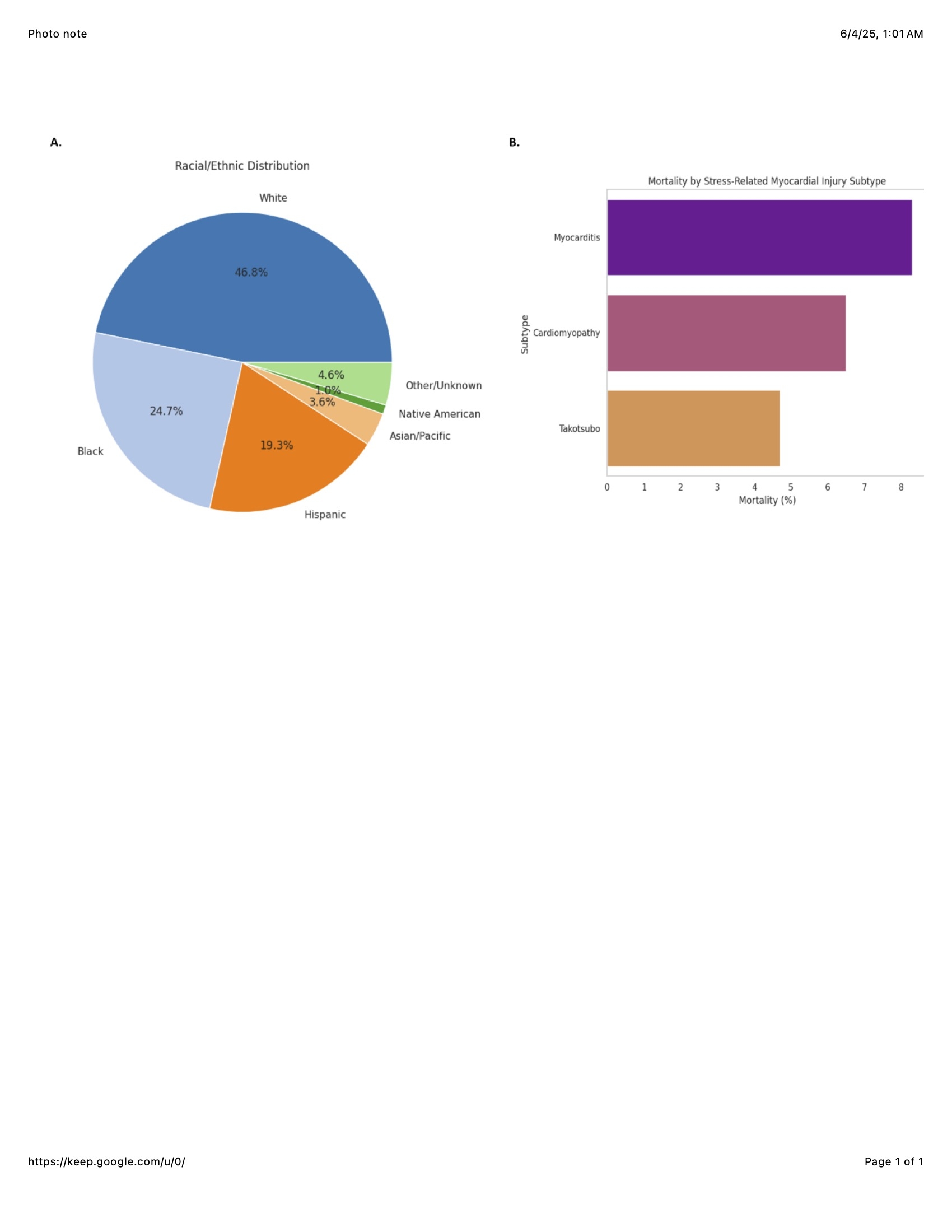
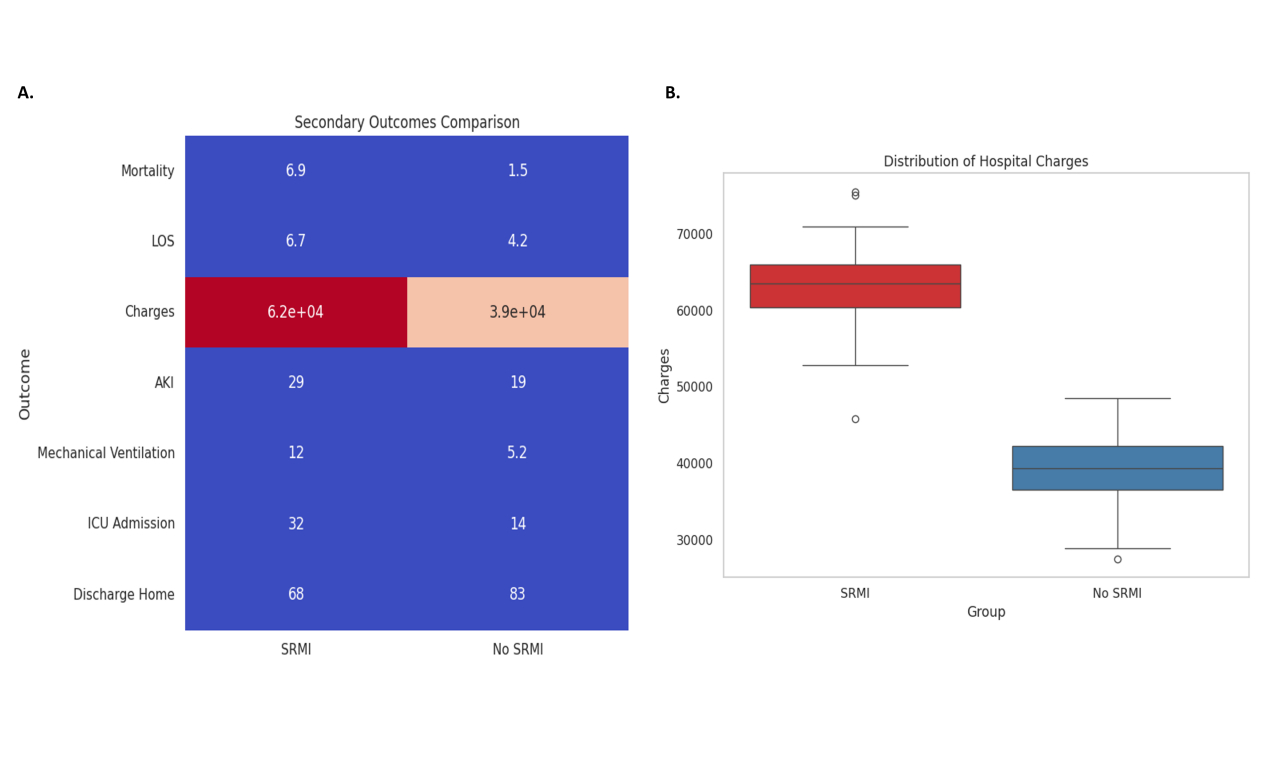
Among the identified DKA hospitalizations, 9,462 were diagnosed with SRMI, resulting in a weighted prevalence of 4.3% (95% CI: 4.1–4.5%). The most prevalent SRMI subtypes included myocarditis (1.5%), cardiomyopathy (2.3%), and Takotsubo syndrome (0.5%). Independent risk factors for SRMI included older age (≥65 years; OR: 1.82, 95% CI: 1.65–2.00), female sex (OR: 1.21, 95% CI: 1.12–1.31), sepsis (OR: 2.45, 95% CI: 2.29–2.62), and type 2 diabetes (OR: 1.16, 95% CI: 1.08–1.26). SRMI was associated with higher in-hospital mortality (6.9% vs. 1.5%; adjusted OR: 2.76, 95% CI: 2.50–3.05), increased length of stay (mean 6.7 vs. 4.2 days, p<0.001), and greater hospital costs (median $61,876 vs. $38,942, p<0.001).
Conclusions:
Stress-related myocardial injury is a significant and serious complication of diabetic ketoacidosis, associated with poor prognoses and high healthcare costs. Identifying SRMI early and implementing targeted interventions is crucial for improving patient outcomes and reducing the economic burden of DKA-related hospitalizations.
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a critical metabolic disorder that can trigger stress-related myocardial injury (SRMI), but national estimates of SRMI in DKA hospitalizations are limited.
Objective:
This study investigates the prevalence, risk factors, and associated outcomes of SRMI during DKA hospitalizations using a comprehensive and nationally representative dataset.
Methods:
We conducted a retrospective, cross-sectional study using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) data from 2016 to 2020, identifying 221,594 weighted adult hospitalizations for DKA. SRMI was defined using ICD-10-CM codes for myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, and Takotsubo syndrome. Predictors and outcomes were assessed using survey-weighted multivariable regression models, accounting for demographic, clinical, and hospital-level factors.
Results:
Among the identified DKA hospitalizations, 9,462 were diagnosed with SRMI, resulting in a weighted prevalence of 4.3% (95% CI: 4.1–4.5%). The most prevalent SRMI subtypes included myocarditis (1.5%), cardiomyopathy (2.3%), and Takotsubo syndrome (0.5%). Independent risk factors for SRMI included older age (≥65 years; OR: 1.82, 95% CI: 1.65–2.00), female sex (OR: 1.21, 95% CI: 1.12–1.31), sepsis (OR: 2.45, 95% CI: 2.29–2.62), and type 2 diabetes (OR: 1.16, 95% CI: 1.08–1.26). SRMI was associated with higher in-hospital mortality (6.9% vs. 1.5%; adjusted OR: 2.76, 95% CI: 2.50–3.05), increased length of stay (mean 6.7 vs. 4.2 days, p<0.001), and greater hospital costs (median $61,876 vs. $38,942, p<0.001).
Conclusions:
Stress-related myocardial injury is a significant and serious complication of diabetic ketoacidosis, associated with poor prognoses and high healthcare costs. Identifying SRMI early and implementing targeted interventions is crucial for improving patient outcomes and reducing the economic burden of DKA-related hospitalizations.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case Presentation of Severe Left Ventricular Dysfunction from Focal Myocarditis due to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor
Patel Romil, Hussain Kifah, Gordon Robert
Acculturation Class Influences Physical Activity Among African Immigrants Living with Diabetes and/or Hypertension: A Qualitative AnalysisOsokpo Onome, Bracy Danny, Adeniji Dolapo, Bankole Ayomide Okanlawon, Lewis Lisa, Riegel Barbara