Final ID: Su4032
Latest Insights in Drug-Induced Kounis Syndrome: A Systematic Review 2024
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Kounis syndrome (KS), also known as allergic myocardial infarction, is a rare but potentially life-threatening condition characterized by acute coronary syndrome in the setting of allergic reactions triggered by drugs, foods, vaccines, or environmental exposure. Our study provides an updated comprehensive insight into this patient cohort on a large scale.
Methods: We conducted a systemic literature search in PubMed, EMBASE, and Google Scholar between 2018 and 2024, using MeSH terms and keywords for “Kounis syndrome”, “drug”, and allergy to identify the cases of drug-induced KS. Initial search yielded 325 articles. After excluding duplicates, review articles and irrelevant studies, we included only 51 articles reporting drug-induced KS.
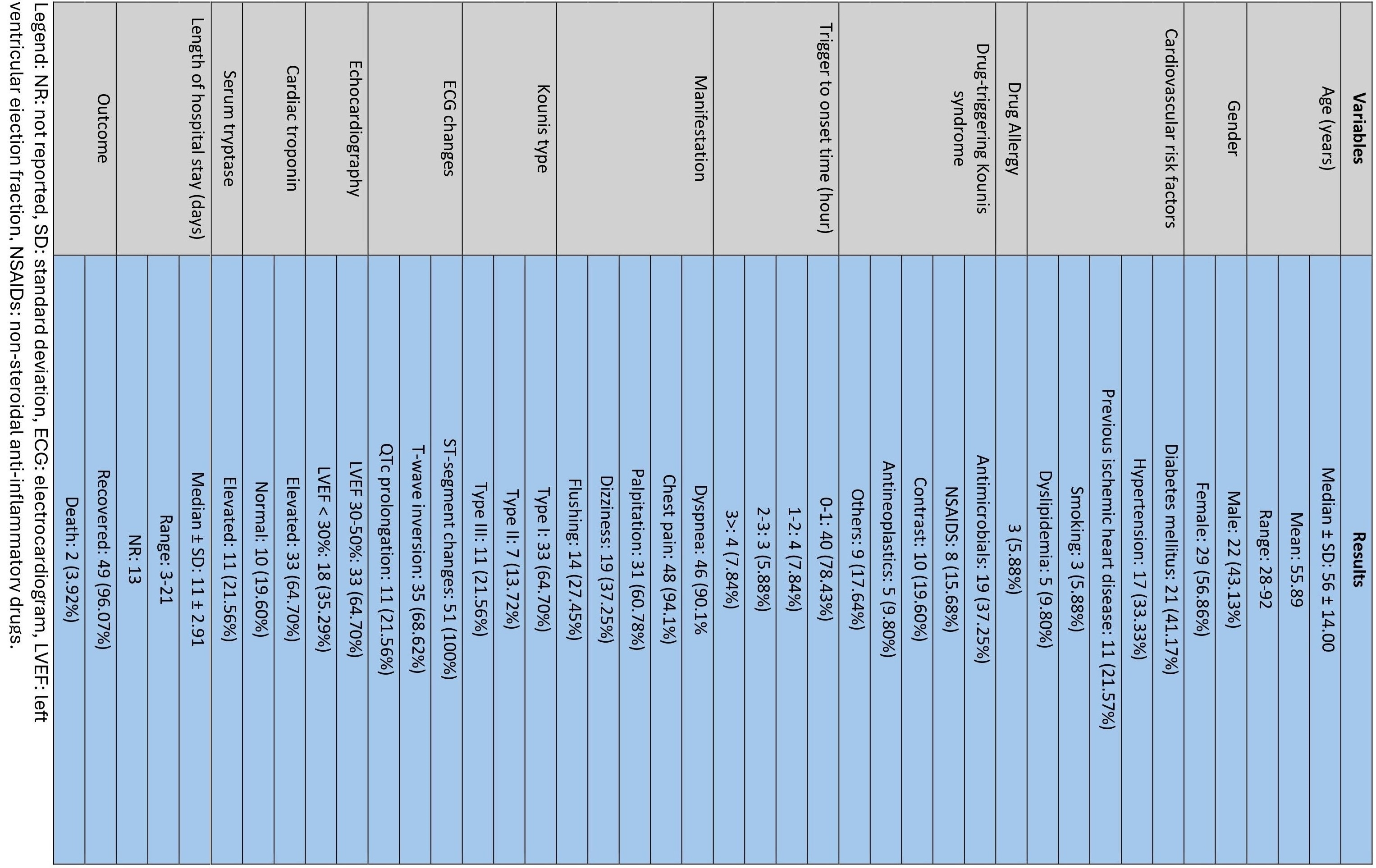
Results: Our study identified 51 patients of KS with a median age of 56 ± 14 years. Of those, 56.86% were female. The most frequently implicated drugs in KS were antimicrobials (37.25%), followed by iodinated contrast media (19.60%), NSAIDs (15.68%), and antineoplastics (9.80%). Of those, 64.70% of patients were diagnosed with KS-I, 13.72% with KS-II, and 21.56% with KS-III. Chest pain (94.1%), dyspnea (90.1%), and palpitations (60.78%) were predominant initial manifestations, and most cases (78.43%) were presented within 1st hour of drug ingestion. ST-segment changes (100%) were common ECG findings, and 64.70% of patients had elevated cardiac troponin. All patients had reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (<50%), with severe cardiomyopathy (EF< 30%) in 35.29%. 96.07% of patients were discharged after a median length of hospital stays (11 ± 2.91 days) (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Although rare, KS is a life-threatening adverse event of drug-induced allergic reactions. KS is challenging to diagnose due to mixed clinical presentations of acute coronary syndrome and allergic reactions. KS should be included in the differential diagnosis of patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome without typical risk factors after drug-induced allergic reactions, especially antimicrobials. Early recognition and appropriate management are crucial for optimum outcomes.
Methods: We conducted a systemic literature search in PubMed, EMBASE, and Google Scholar between 2018 and 2024, using MeSH terms and keywords for “Kounis syndrome”, “drug”, and allergy to identify the cases of drug-induced KS. Initial search yielded 325 articles. After excluding duplicates, review articles and irrelevant studies, we included only 51 articles reporting drug-induced KS.
Results: Our study identified 51 patients of KS with a median age of 56 ± 14 years. Of those, 56.86% were female. The most frequently implicated drugs in KS were antimicrobials (37.25%), followed by iodinated contrast media (19.60%), NSAIDs (15.68%), and antineoplastics (9.80%). Of those, 64.70% of patients were diagnosed with KS-I, 13.72% with KS-II, and 21.56% with KS-III. Chest pain (94.1%), dyspnea (90.1%), and palpitations (60.78%) were predominant initial manifestations, and most cases (78.43%) were presented within 1st hour of drug ingestion. ST-segment changes (100%) were common ECG findings, and 64.70% of patients had elevated cardiac troponin. All patients had reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (<50%), with severe cardiomyopathy (EF< 30%) in 35.29%. 96.07% of patients were discharged after a median length of hospital stays (11 ± 2.91 days) (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Although rare, KS is a life-threatening adverse event of drug-induced allergic reactions. KS is challenging to diagnose due to mixed clinical presentations of acute coronary syndrome and allergic reactions. KS should be included in the differential diagnosis of patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome without typical risk factors after drug-induced allergic reactions, especially antimicrobials. Early recognition and appropriate management are crucial for optimum outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Effectiveness of chest pain center accreditation on the hospital outcome of acute aortic dissection: a nationwide study in China
Liu Liwei, Sun Aijun, Ge Junbo
Feasibility of detecting CPR compression frequency using machine-learning software in video footage of CPRWetsch Wolfgang, Adams Niels-benjamin, Schmitz Michael, Ecker Hannes