Final ID: MP1998
HP-13CMRAnalyst: A MATLAB Application for Dynamic Cardiac Metabolic Imaging Analysis Using Hyperpolarized Carbon-13 MRI
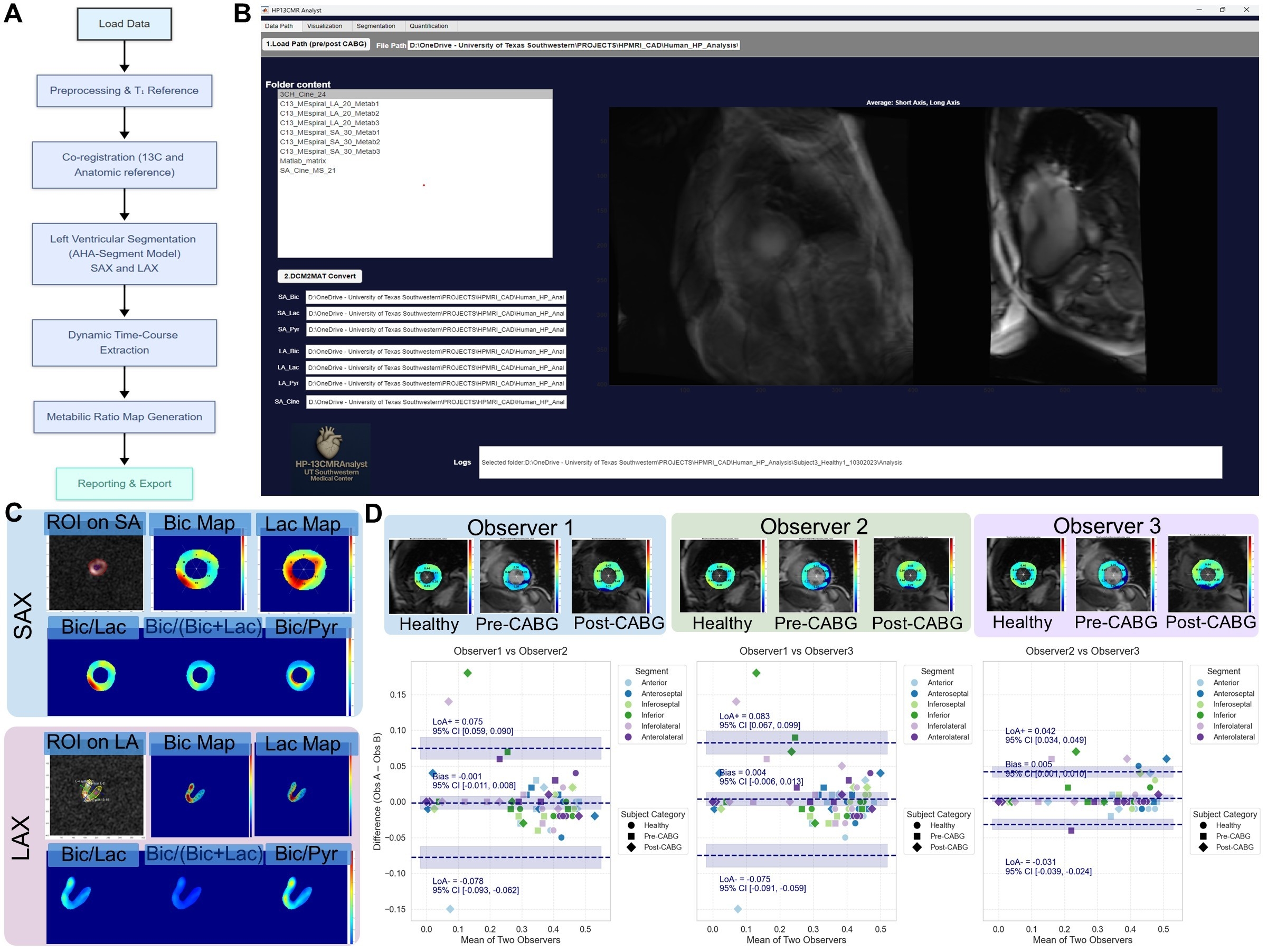
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Hyperpolarized [1-13C] pyruvate magnetic resonance imaging (HP-13C MRI) enables real-time, noninvasive assessment of myocardial metabolism. While the technique is increasingly applied in cardiac research, dedicated tools for standardized analysis remain limited. We developed HP-13CMRAnalyst, a MATLAB-based application that supports dynamic 13C data processing through semi-automated segmentation, time-course extraction, and metabolic ratio mapping (Figure 1A).
Hypothesis: An integrated platform combining multi-frame 13C data import, cine co-registration, multi-segment analysis, and voxel-level ratio mapping facilitates reproducible quantification of myocardial metabolism.
Methods: HP-13CMRAnalyst was implemented in MATLAB App Designer and distributed as an .mlappinstall package. It accepts DICOM or NIfTI dynamic pyruvate, lactate, and bicarbonate images (∼3 s resolution; ≤ 60 s)(Figure 1B). Cine-registered T1-weighted images guide AHA 17-segment LV segmentation on short axis (SAX) and long axis (LAX) views (Figure 1C). A time slider displays metabolite overlays. Peak intensities are extracted per segment to compute bicarbonate/lactate and bicarbonate/pyruvate ratios. Pixel-wise ratio maps are exported as CSV, MATLAB struct, and PDF summaries.
Results: Eight subjects (n = 4 healthy; n = 4 coronary artery disease [CAD]), each imaged pre- and post-CABG (total n = 12 datasets; age 55 ± 12 years), were processed in < 5 min per dataset on a standard desktop (MATLAB R2024b). Semi-automated versus manual segmentation agreement was high (Dice 0.89–0.93). Inter-observer variability for segmental bicarbonate/(bicarbonate + lactate) ratios were minimal biases < 0.005 and limits of agreement within ± 0.083 across all observer pairs (Figure 1D). Ratio maps qualitatively revealed regional metabolic heterogeneity. Automated reports accurately reflected metadata and segmental summaries. The GUI, logs, and summary files streamline standardized processing.
Conclusions: HP-13CMRAnalyst delivers a rapid (< 5 min), reproducible framework for dynamic HP-13C MRI analysis. By combining semi-automated segmentation and pixel-level ratio mapping with low inter-observer variability, this platform may accelerate adoption of 13C metabolic imaging in human cardiac research.
Hypothesis: An integrated platform combining multi-frame 13C data import, cine co-registration, multi-segment analysis, and voxel-level ratio mapping facilitates reproducible quantification of myocardial metabolism.
Methods: HP-13CMRAnalyst was implemented in MATLAB App Designer and distributed as an .mlappinstall package. It accepts DICOM or NIfTI dynamic pyruvate, lactate, and bicarbonate images (∼3 s resolution; ≤ 60 s)(Figure 1B). Cine-registered T1-weighted images guide AHA 17-segment LV segmentation on short axis (SAX) and long axis (LAX) views (Figure 1C). A time slider displays metabolite overlays. Peak intensities are extracted per segment to compute bicarbonate/lactate and bicarbonate/pyruvate ratios. Pixel-wise ratio maps are exported as CSV, MATLAB struct, and PDF summaries.
Results: Eight subjects (n = 4 healthy; n = 4 coronary artery disease [CAD]), each imaged pre- and post-CABG (total n = 12 datasets; age 55 ± 12 years), were processed in < 5 min per dataset on a standard desktop (MATLAB R2024b). Semi-automated versus manual segmentation agreement was high (Dice 0.89–0.93). Inter-observer variability for segmental bicarbonate/(bicarbonate + lactate) ratios were minimal biases < 0.005 and limits of agreement within ± 0.083 across all observer pairs (Figure 1D). Ratio maps qualitatively revealed regional metabolic heterogeneity. Automated reports accurately reflected metadata and segmental summaries. The GUI, logs, and summary files streamline standardized processing.
Conclusions: HP-13CMRAnalyst delivers a rapid (< 5 min), reproducible framework for dynamic HP-13C MRI analysis. By combining semi-automated segmentation and pixel-level ratio mapping with low inter-observer variability, this platform may accelerate adoption of 13C metabolic imaging in human cardiac research.
More abstracts on this topic:
A novel reproducible low-cost model of acute myocardial infarction in swine
Li Yichen, Zheng Zilong, Tang Weijie, Chen Wangping, Yang Jinfu, Fan Chengming
Cardiac Arginination Activates RIP3/CAMKII/MLKL Signaling RALBP1 Signal for ICIs-associated MyocarditisWang Xuejun