Final ID: MP1879
Identification and Functional Role of a Novel Macrophage Subset in Myocardial Infarction
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Myocardial infarction (MI) triggers complex inflammatory responses, during which myeloid cells, particularly macrophages, play pivotal roles in tissue healing and remodeling. Recent evidence suggests macrophages possess substantial heterogeneity and plasticity, contributing variably to cardiac repair processes. However, specific macrophage subsets and their functions during different phases of myocardial infarction remain inadequately defined.
Methods
In this study, we utilized two publicly available single-cell RNA sequencing datasets from murine (mmu) and human (hsa) myocardial infarction tissues to explore myeloid cell heterogeneity. We focused our analysis specifically on macrophage populations to identify distinct subsets with unique transcriptional profiles. Subsequently, dual-reporter mice models were employed to validate and visualize the identified macrophage subset in vivo during MI. Finally, targeted genetic knockout mice lacking this macrophage subset were generated and utilized to determine their functional role in cardiac recovery post-infarction.
Results
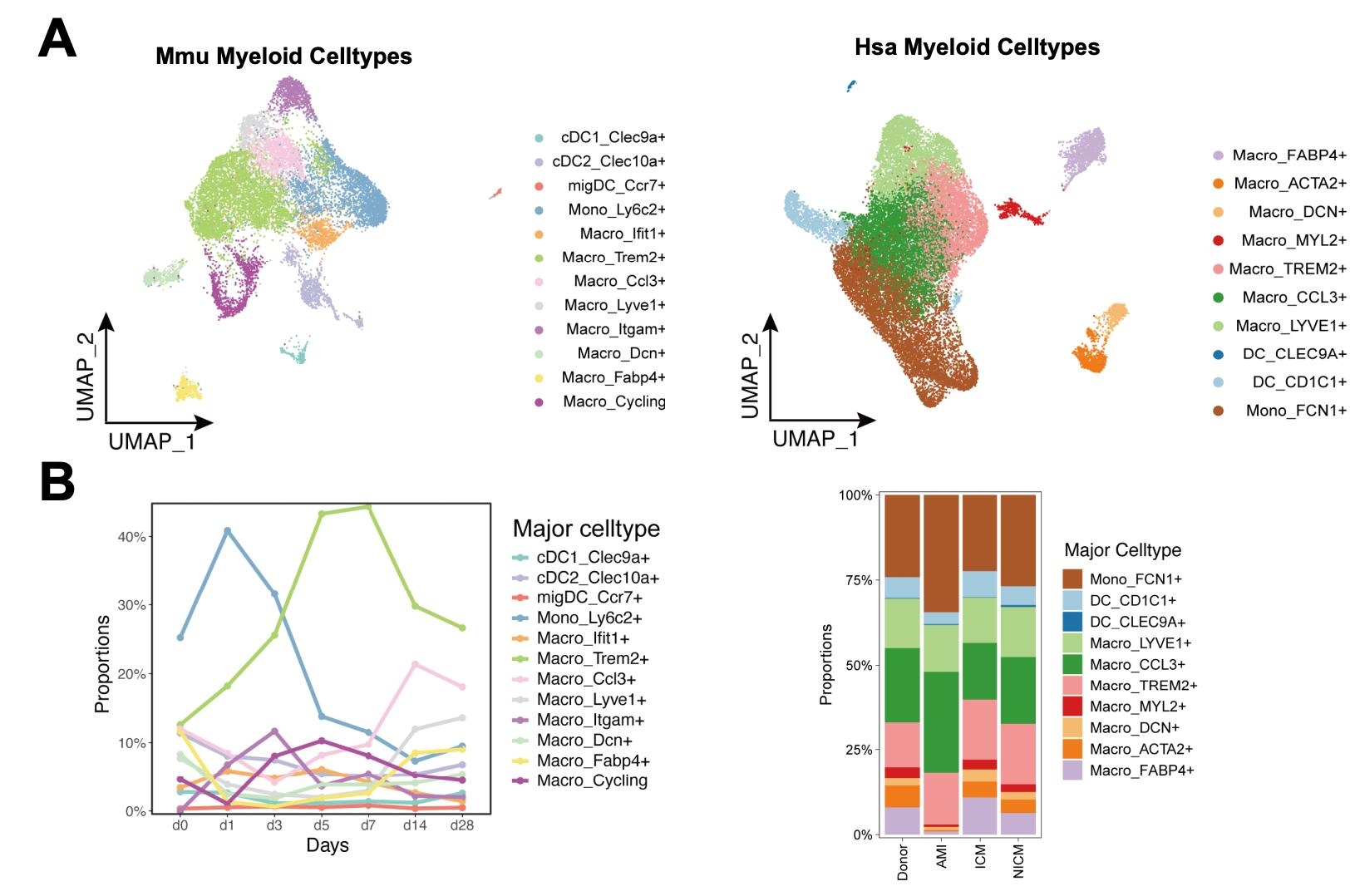
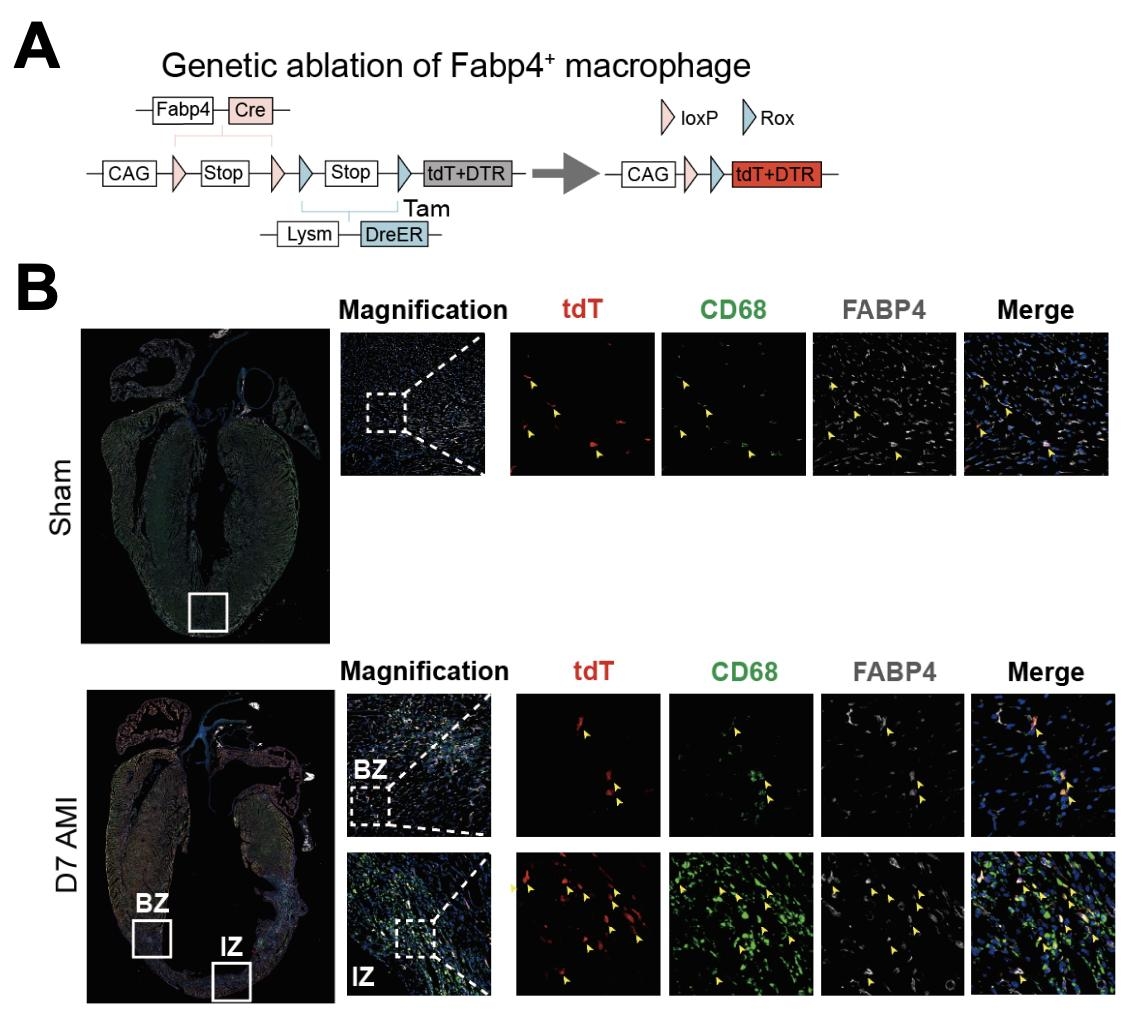
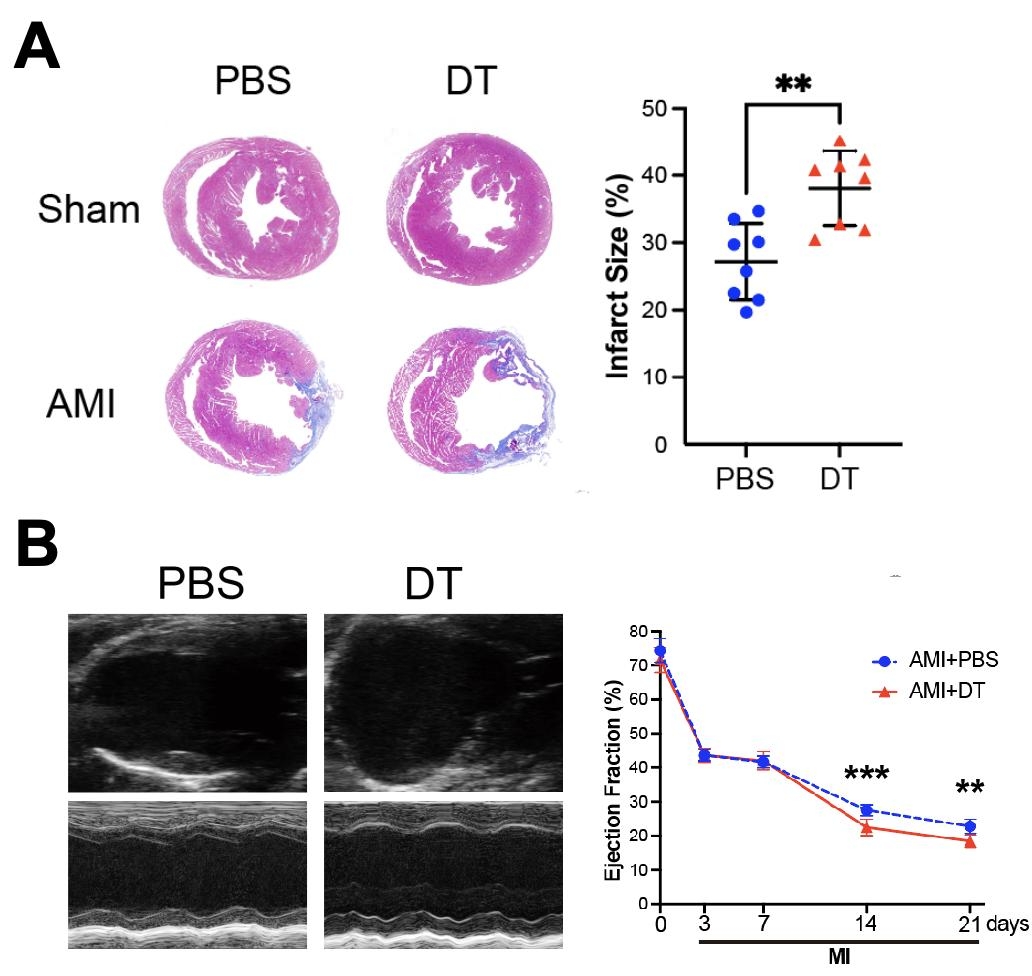
We identified a previously uncharacterized macrophage subset uniquely expressing endothelial cell markers in both human and mouse scRNA-seq datasets (Figure 1A). Importantly, this specific macrophage population progressively increased across distinct phases of myocardial infarction (control, inflammation, proliferation, and maturation) (Figure 1B), predominantly localizing within the myocardial border zone. Using dual-reporter mice (Figure 2A), we validated these findings in vivo, observing identical temporal and spatial distributions (Figure 2B). Notably, targeted knockout of this macrophage subset resulted in a significant enlargement of infarct areas (Figure 3A) and decline of cardiac function (Figure 3B), underscoring its protective role in myocardial healing.
Conclusion
Our study highlights a novel macrophage subset characterized by endothelial marker expression, crucially involved in the reparative response following myocardial infarction. The increased infarct zone following its knockout underscores the therapeutic potential of targeting this subset to enhance myocardial recovery and regeneration after cardiac injury.
Myocardial infarction (MI) triggers complex inflammatory responses, during which myeloid cells, particularly macrophages, play pivotal roles in tissue healing and remodeling. Recent evidence suggests macrophages possess substantial heterogeneity and plasticity, contributing variably to cardiac repair processes. However, specific macrophage subsets and their functions during different phases of myocardial infarction remain inadequately defined.
Methods
In this study, we utilized two publicly available single-cell RNA sequencing datasets from murine (mmu) and human (hsa) myocardial infarction tissues to explore myeloid cell heterogeneity. We focused our analysis specifically on macrophage populations to identify distinct subsets with unique transcriptional profiles. Subsequently, dual-reporter mice models were employed to validate and visualize the identified macrophage subset in vivo during MI. Finally, targeted genetic knockout mice lacking this macrophage subset were generated and utilized to determine their functional role in cardiac recovery post-infarction.
Results
We identified a previously uncharacterized macrophage subset uniquely expressing endothelial cell markers in both human and mouse scRNA-seq datasets (Figure 1A). Importantly, this specific macrophage population progressively increased across distinct phases of myocardial infarction (control, inflammation, proliferation, and maturation) (Figure 1B), predominantly localizing within the myocardial border zone. Using dual-reporter mice (Figure 2A), we validated these findings in vivo, observing identical temporal and spatial distributions (Figure 2B). Notably, targeted knockout of this macrophage subset resulted in a significant enlargement of infarct areas (Figure 3A) and decline of cardiac function (Figure 3B), underscoring its protective role in myocardial healing.
Conclusion
Our study highlights a novel macrophage subset characterized by endothelial marker expression, crucially involved in the reparative response following myocardial infarction. The increased infarct zone following its knockout underscores the therapeutic potential of targeting this subset to enhance myocardial recovery and regeneration after cardiac injury.
More abstracts on this topic:
Beyond Closure: A Case Report on Coronary Steal Syndrome by Previously Embolized Internal Mammary Artery Side Branch
Fuentes Jose, Garcia Almonte Karla, Suero Claudia, Urena Neme Ana Paula, Tarafa Jorge A., Urena V Pedro
Cardio-protective effect on myocardial mitochondrial damage with optimal dose leptin administration in the ischemic heart failure rat modelKang Ki-woon, Lee Hunghee, Ko Jae-hong, Lee Seongkyu