Final ID: MP1291
Spatial T1-Mapping of Cardiac Fibrosis Identifies Causal Protein Drivers through Deep Learning and Mendelian Randomization
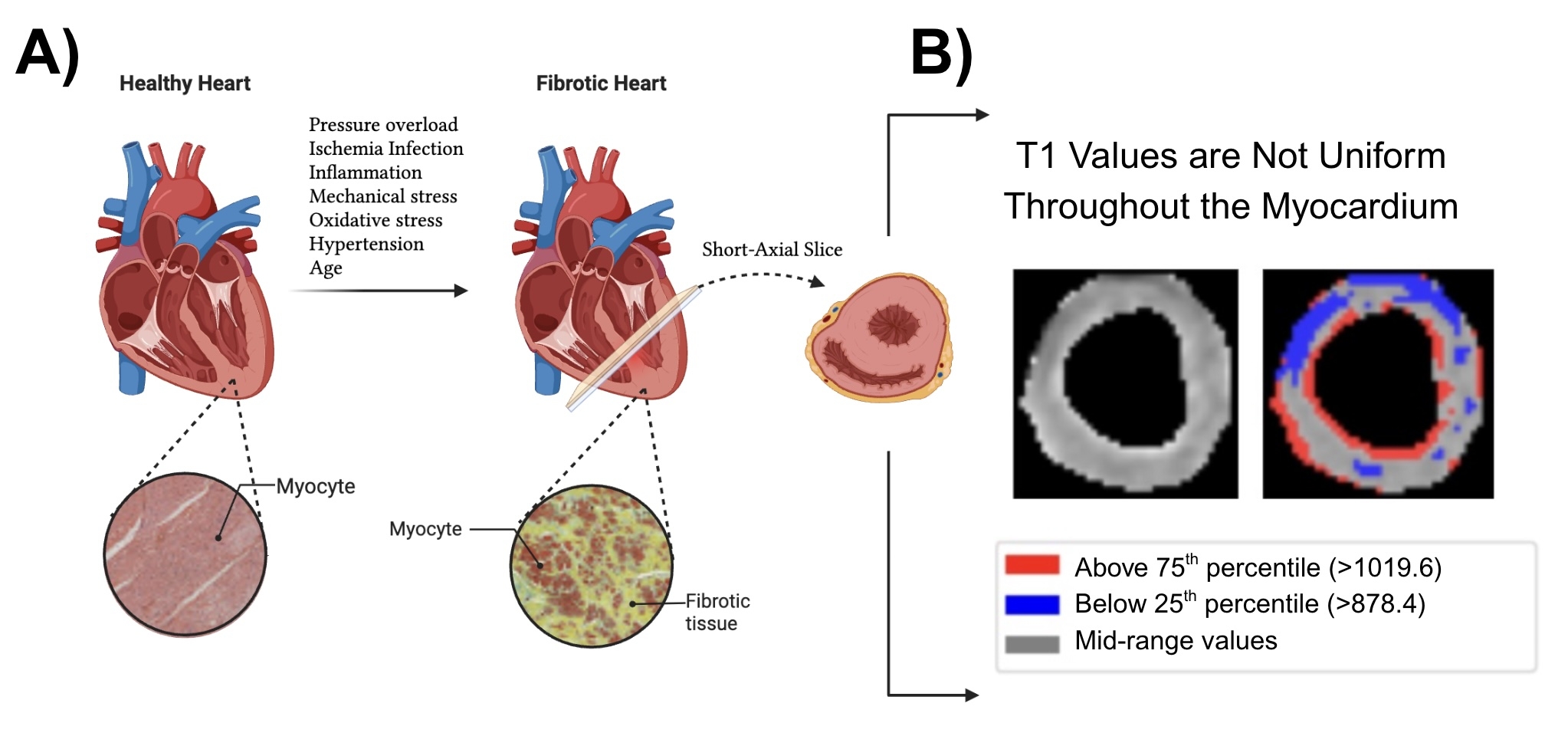
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background Diffuse myocardial fibrosis is a hallmark of heart failure progression. T1 mapping MRI quantifies fibrosis, but conventional mean-T1 metrics blur regional patterns characteristic of distinct biological pathways (Fig. 1).
Objective To retrieve regional fibrosis signatures at the population scale and identify molecular drivers with therapeutic potential.
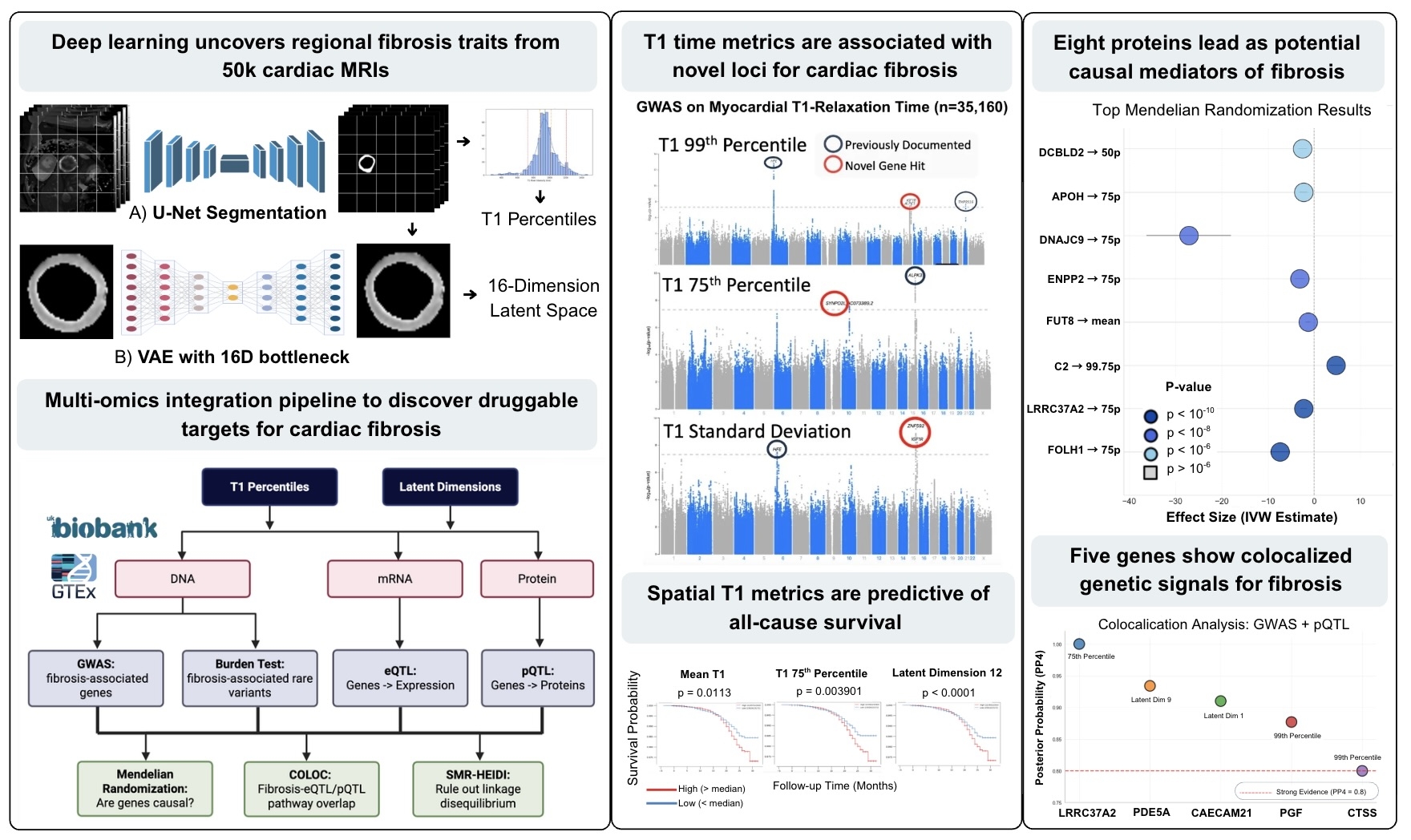
Methods Native-T1 maps from 50,239 CMRs were U-Net-segmented (Dice 0.85) and encoded by a 16-D variational autoencoder (VAE) (SSIM 0.92). We derived global T1 scalars—mean, SD, and 5th–95th percentiles—and latent features (LD1-LD16); gradient-based attention linked each factor to specific myocardial regions. Prognosis was tested with Kaplan–Meier curves and covariate-adjusted Cox models. Scalar and latent traits entered GWAS, rare-variant burden screens, and 3,000-plex Olink PWAS. Causal analysis combined cis-eQTL/pQTL COLOC, Mendelian randomisation, and SMR-HEIDI to flag druggable genes (Fig. 2).
Results Clinical impact T1 75th percentile showed highest heritability (10.3%) and mortality prediction (p=0.004). VAE dimension 12 had the strongest mortality association (p<0.0001), while dimension 8 predicted non-ischemic heart disease with superior discrimination to T1 scalar metrics.
Genomics Seven loci reached significance: iron-homeostasis (HFE p=2.6×10-13, TMPRSS6), growth-factor (IGF1R), sarcomere (ALPK3/SYNPO2L), and spatial-specific DLG2 (p=1.9×10-8). Rare-variant testing implicated 914 genes, enriching inflammatory/metabolic pathways.
Proteomics Leptin dominated (p=1.1×10-73) with FABP4/oxytocin. Dimension 8 identified stronger leptin association (p=1.13×10-73) plus inflammatory (TNFRSF1A), neuronal (RTN4R), and vascular (ADM) drivers.
Causal inference Cis-pQTL MR nominated eight proteins led by FOLH1 (β=0.17 SD, p=3.4×10-13), with HEIDI confirming pleiotropy. Colocalization confirmed LRRC37A2 (pp_h4>0.99), PDE5A (pp_h4=0.933), CTSS (pp_h4=0.80). eQTL SMR identified LMF1 (p=8.3×10-5), JMJD6 (p=1.7×10-4), RIT1 (p=3.96×10-4). Targets with existing inhibitors include CTSS (VBY-036, RO5459072), PDE5A (sildenafil, tadalafil), and ENPP2 (ONO-8430506, PF-8380, IOA-289).
Conclusions AI-derived spatial fibrosis phenotypes using VAE decomposition of T1 maps reveal hidden prognostic information and region-specific biological drivers invisible to conventional mean T1 analysis, identifying causal protein targets (FOLH1, ENPP2, CTSS, PDE5A) amenable to existing inhibitors for precision anti-fibrotic therapies.
Objective To retrieve regional fibrosis signatures at the population scale and identify molecular drivers with therapeutic potential.
Methods Native-T1 maps from 50,239 CMRs were U-Net-segmented (Dice 0.85) and encoded by a 16-D variational autoencoder (VAE) (SSIM 0.92). We derived global T1 scalars—mean, SD, and 5th–95th percentiles—and latent features (LD1-LD16); gradient-based attention linked each factor to specific myocardial regions. Prognosis was tested with Kaplan–Meier curves and covariate-adjusted Cox models. Scalar and latent traits entered GWAS, rare-variant burden screens, and 3,000-plex Olink PWAS. Causal analysis combined cis-eQTL/pQTL COLOC, Mendelian randomisation, and SMR-HEIDI to flag druggable genes (Fig. 2).
Results Clinical impact T1 75th percentile showed highest heritability (10.3%) and mortality prediction (p=0.004). VAE dimension 12 had the strongest mortality association (p<0.0001), while dimension 8 predicted non-ischemic heart disease with superior discrimination to T1 scalar metrics.
Genomics Seven loci reached significance: iron-homeostasis (HFE p=2.6×10-13, TMPRSS6), growth-factor (IGF1R), sarcomere (ALPK3/SYNPO2L), and spatial-specific DLG2 (p=1.9×10-8). Rare-variant testing implicated 914 genes, enriching inflammatory/metabolic pathways.
Proteomics Leptin dominated (p=1.1×10-73) with FABP4/oxytocin. Dimension 8 identified stronger leptin association (p=1.13×10-73) plus inflammatory (TNFRSF1A), neuronal (RTN4R), and vascular (ADM) drivers.
Causal inference Cis-pQTL MR nominated eight proteins led by FOLH1 (β=0.17 SD, p=3.4×10-13), with HEIDI confirming pleiotropy. Colocalization confirmed LRRC37A2 (pp_h4>0.99), PDE5A (pp_h4=0.933), CTSS (pp_h4=0.80). eQTL SMR identified LMF1 (p=8.3×10-5), JMJD6 (p=1.7×10-4), RIT1 (p=3.96×10-4). Targets with existing inhibitors include CTSS (VBY-036, RO5459072), PDE5A (sildenafil, tadalafil), and ENPP2 (ONO-8430506, PF-8380, IOA-289).
Conclusions AI-derived spatial fibrosis phenotypes using VAE decomposition of T1 maps reveal hidden prognostic information and region-specific biological drivers invisible to conventional mean T1 analysis, identifying causal protein targets (FOLH1, ENPP2, CTSS, PDE5A) amenable to existing inhibitors for precision anti-fibrotic therapies.
More abstracts on this topic:
Assessment of Adverse Left Ventricular Remodeling Following Ischemia Reperfusion Injury with SPECT Imaging Agent Targeting Fibroblast Activation Protein
Thorn Stephanie, Duncan James S, Spinale Francis, Luna Gutierrez Myrna, Ferro-flores Guillermina, Sinusas Albert, Porcaro Olivia, Burns Rachel, Zohora Fatema Tuj, Guerrera Nicole, Jang Sun-joo, Vermillion Billy, Lima Moroni, Liu Chi
Adipose tissue extracellular vesicles mediate pro-arrhythmic changes in atrial cardiomyocytesLimpitikul Worawan, Garcia Contreras Marta, Betti Michael, Sheng Quanhu, Xiao Ling, Chatterjee Emeli, Gamazon Eric, Shah Ravi, Das Saumya