Final ID: MP2383
Pharmacist Interventions Boosts Compliance and Cholesterol Medications Adherence
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Uncontrolled lipid levels significantly contribute to recurrent cardiovascular events and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) progression, resulting in increased morbidity and mortality. In the Veterans Affairs (VA) system, more than 65% of Veterans with ASCVD are poorly managed due to: clinical inertia, patient preferences, and outdated therapies. To improve lipid management and medication adherence, healthcare providers and pharmacists need to collaborate. The VA Caribbean Healthcare System (VACHS) is one of 50 VA sites participating in a national quality improvement initiative called the VA Lipid Optimization Reimagined Quality Improvement Program (VALOR-QI). This is a collaborative project between the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and the American Heart Association (AHA) and aims to impact Veterans’ cardiovascular health positively. VA sites work with an AHA QI consultant to develop and implement local quality improvement plans that address specific barriers preventing Veterans from achieving optimal cholesterol levels.
Methodology: At VACHS, a comprehensive care model was adopted, focusing on guideline-directed therapy using high-intensity statins and combination treatment for Veterans aged ≥18 years with ASCVD and LDL-C ≥70 mg/dL or non-HDL-C ≥100 mg/dL. Veterans identified as non-adherent to cholesterol-lowering medications were referred to a cardiology pharmacist for targeted education, refill assistance, adherence support, and follow-up laboratory testing 12 weeks after therapeutic optimization. A healthcare coach reinforced this approach by coordinating medication refills, clinical reminders, appointments, and continuous patient engagement.
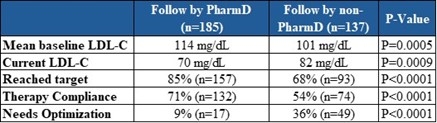
Results: This analysis includes 322 Veterans stratified by pharmacist involvement. Veterans followed by the PharmD (n=185) had a mean baseline LDL-C of 114 mg/dL, compared to 101 mg/dL in those not followed (n=137). The PharmD group had 85% of Veterans that reached the target versus 68% in the not followed group (P<0.0001). Veterans followed by the PharmD are 71% compliant versus 54% (P<0.0001).
Conclusions: These findings underscore the critical importance of multidisciplinary clinical engagement, particularly the pharmacist’s role in achieving and maintaining lipid goals, improving long-term adherence, reducing the overall burden of ASCVD and supporting the role of pharmacist integration in chronic disease management programs to optimize ASCVD outcomes.
Methodology: At VACHS, a comprehensive care model was adopted, focusing on guideline-directed therapy using high-intensity statins and combination treatment for Veterans aged ≥18 years with ASCVD and LDL-C ≥70 mg/dL or non-HDL-C ≥100 mg/dL. Veterans identified as non-adherent to cholesterol-lowering medications were referred to a cardiology pharmacist for targeted education, refill assistance, adherence support, and follow-up laboratory testing 12 weeks after therapeutic optimization. A healthcare coach reinforced this approach by coordinating medication refills, clinical reminders, appointments, and continuous patient engagement.
Results: This analysis includes 322 Veterans stratified by pharmacist involvement. Veterans followed by the PharmD (n=185) had a mean baseline LDL-C of 114 mg/dL, compared to 101 mg/dL in those not followed (n=137). The PharmD group had 85% of Veterans that reached the target versus 68% in the not followed group (P<0.0001). Veterans followed by the PharmD are 71% compliant versus 54% (P<0.0001).
Conclusions: These findings underscore the critical importance of multidisciplinary clinical engagement, particularly the pharmacist’s role in achieving and maintaining lipid goals, improving long-term adherence, reducing the overall burden of ASCVD and supporting the role of pharmacist integration in chronic disease management programs to optimize ASCVD outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Health Coach-Based Multi-Level Personalized Strategy Lowers LDL-Cholesterol and Enhances Lipid Control in Veterans with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease – The VA Lipid Optimization Reimagined Quality Improvement Project at VA New York Harbor Healthcare System
Chen Tina, Ingerman Diana, Haley Leah, Salovaara Priscilla, Nicholson Andrew, Illenberger Nicholas, Natarajan Sundar
An Economic Evaluation of Non-HDL-Cholesterol and Apolipoprotein B as Treatment Targets for Lipid-Lowering Therapy in Primary PreventionLuebbe Samuel, Wilkins John, Moran Andrew, Sniderman Allan, Kohli-lynch Ciaran