Final ID: 4363716
The efficacy and safety of hydroxychloroquine in patients with chronic inflammatory cardiomyopathy: A multicenter randomized study (HYPIC trial)
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Chronic inflammatory cardiomyopathy (infl-CMP) is a persistent cardiac disorder that often arises from the progression of acute myocarditis. This condition is marked by chronic heart failure, arrhythmias, and reduced quality of life. Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), known for its immunomodulatory properties, has been suggested as a potential treatment option for reducing chronic inflammation in these individuals.
Research Questions
Can HCQ combined with prednisolone (PDN) improve cardiovascular outcomes in patients with chronic infl-CMP compared to PDN alone? What are the effects of this combination on heart function and inflammatory markers? Furthermore, is HCQ safe for long-term use in this setting?
Methods
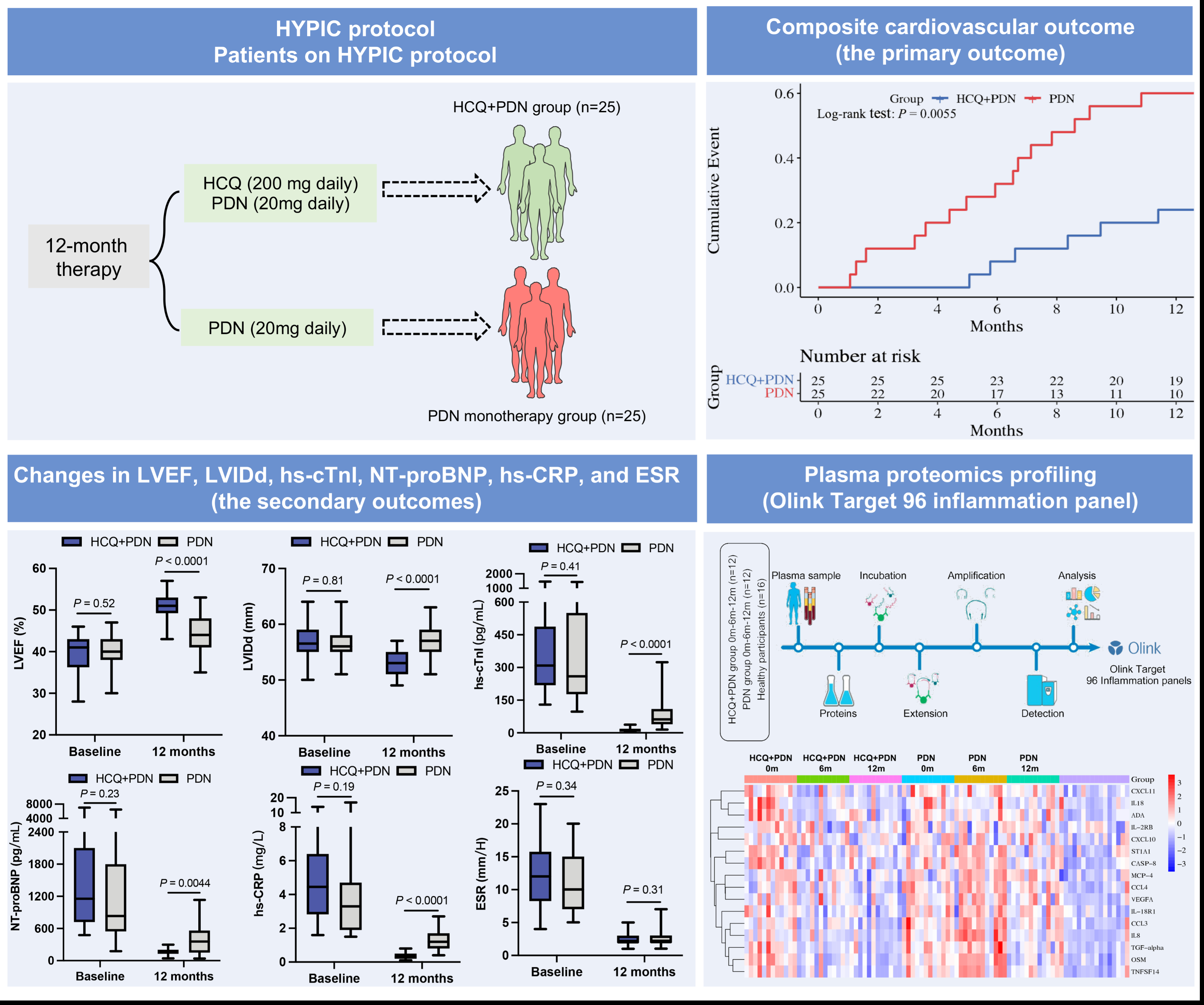
We conducted a multicenter, randomized controlled trial involving 50 patients diagnosed with chronic infl-CMP post-fuminant myocarditis (FM). Participants were randomly assigned to receive either a combination of HCQ and PDN or PDN alone over 12 months. The primary outcome measured was a composite of cardiovascular events, including time to cardiovascular death or heart transplant, hospitalization for heart failure, recurrence of myocarditis, and the requirement for a permanent pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). Secondary outcomes included changes in LVEF, LVIDd, hs-cTnI, NT-proBNP, hs-CRP, and ESR from baseline to 12 months.
Results
The trial demonstrated that HCQ combined with PDN significantly improved primary cardiovascular outcomes compared to PDN monotherapy, with a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.28 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.11–0.71). There were notable improvements in LVEF and reductions in LVIDd, hs-cTnI, NT-proBNP, and hs-CRP levels in the combination treatment group. Specifically, the estimated between-group differences in changes were as follows: LVEF improved by 8.01 (95% CI: 5.27 to 10.76), LVIDd decreased by -4.02 (95% CI: -6.20 to -1.85), hs-cTnI reduced by -98.40 (95% CI: -174.80 to -5.90), NT-proBNP by -399.30 (95% CI: -877.00 to -14.00), hs-CRP by -1.65 (95% CI: -3.10 to -0.40), and ESR by -1.70 (95% CI: -4.58 to 1.19). Importantly, no serious drug-related adverse events were reported, and HCQ treatment normalized the levels of 16 plasma cytokines.
Conclusion
The combination of HCQ and PDN significantly enhances cardiovascular outcomes, heart function, and inflammatory inhibition in patients with chronic infl-CMP without serious adverse events.
Chronic inflammatory cardiomyopathy (infl-CMP) is a persistent cardiac disorder that often arises from the progression of acute myocarditis. This condition is marked by chronic heart failure, arrhythmias, and reduced quality of life. Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), known for its immunomodulatory properties, has been suggested as a potential treatment option for reducing chronic inflammation in these individuals.
Research Questions
Can HCQ combined with prednisolone (PDN) improve cardiovascular outcomes in patients with chronic infl-CMP compared to PDN alone? What are the effects of this combination on heart function and inflammatory markers? Furthermore, is HCQ safe for long-term use in this setting?
Methods
We conducted a multicenter, randomized controlled trial involving 50 patients diagnosed with chronic infl-CMP post-fuminant myocarditis (FM). Participants were randomly assigned to receive either a combination of HCQ and PDN or PDN alone over 12 months. The primary outcome measured was a composite of cardiovascular events, including time to cardiovascular death or heart transplant, hospitalization for heart failure, recurrence of myocarditis, and the requirement for a permanent pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). Secondary outcomes included changes in LVEF, LVIDd, hs-cTnI, NT-proBNP, hs-CRP, and ESR from baseline to 12 months.
Results
The trial demonstrated that HCQ combined with PDN significantly improved primary cardiovascular outcomes compared to PDN monotherapy, with a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.28 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.11–0.71). There were notable improvements in LVEF and reductions in LVIDd, hs-cTnI, NT-proBNP, and hs-CRP levels in the combination treatment group. Specifically, the estimated between-group differences in changes were as follows: LVEF improved by 8.01 (95% CI: 5.27 to 10.76), LVIDd decreased by -4.02 (95% CI: -6.20 to -1.85), hs-cTnI reduced by -98.40 (95% CI: -174.80 to -5.90), NT-proBNP by -399.30 (95% CI: -877.00 to -14.00), hs-CRP by -1.65 (95% CI: -3.10 to -0.40), and ESR by -1.70 (95% CI: -4.58 to 1.19). Importantly, no serious drug-related adverse events were reported, and HCQ treatment normalized the levels of 16 plasma cytokines.
Conclusion
The combination of HCQ and PDN significantly enhances cardiovascular outcomes, heart function, and inflammatory inhibition in patients with chronic infl-CMP without serious adverse events.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Rare Cause of a Classic Presentation of NSTEMI: Case of 39-Year-Old Female with Hypothyroidism Induced Myocarditis
Quadri Fayz, Qazi Mariam, Teague Taylor
A Heart Transplant Patient’s Mysterious Illness: A Diagnostic OdysseyAlkalbani Mutaz, Nayer Hassan, Cochrane Adam, Saeed Ibrahim, Psotka Mitchell, Rollins Allman, Kennedy Jamie, Blumer Vanessa