Final ID: MP94
Higher Blood Pressure Time-in-Target Range May Improve Primary Cardiovascular Outcome in Patients with Hypertension and Coronary Artery Disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Higher blood pressure Time-in-Target Range (BP-TTR) has been associated with lower risk of cardiovascular outcomes. However, the prognostic value of BP-TTR among patients with hypertension (HTN) and coronary artery disease (CAD) remains unclear.
Research Question: Is higher BP-TTR over a 6-month period associated with a reduced risk of primary cardiovascular outcome (composite all-cause mortality, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke) among patients with HTN+CAD?
Methods: In this post-hoc analysis of the randomized INternational VErapamil-trandolapril STudy (INVEST), we pooled patients (aged ≥50 years with HTN+CAD) randomized to a calcium antagonist or non-calcium antagonist strategy, which had equivalent outcomes in INVEST. Of 22,576 INVEST participants, we identified those with ≥4 BP readings, and without the primary outcome or loss to follow-up within the first 6 months post-randomization (including randomization date). We performed linear interpolation with constant extrapolation using eligible participants’ BP readings during this 6-month period (168 days) to estimate BP-TTR, defined as the proportion of days with BP readings below the target (140/90 mmHg) over the 168-day window. Cox proportional hazards regression was used to examine the association between BP-TTR in the first 6 months post-randomization and the primary outcome thereafter.
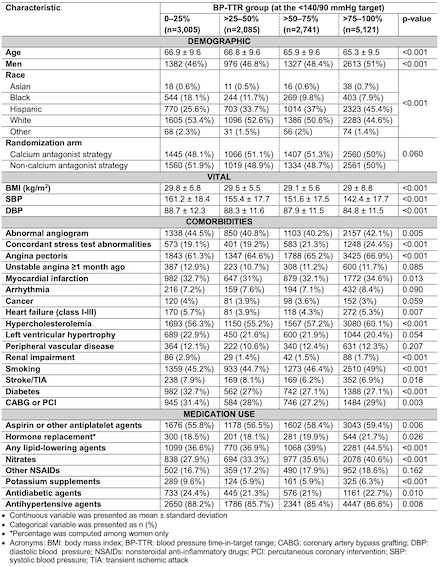
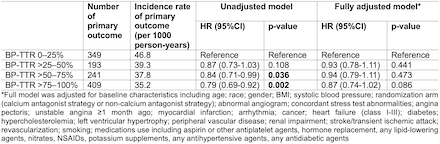
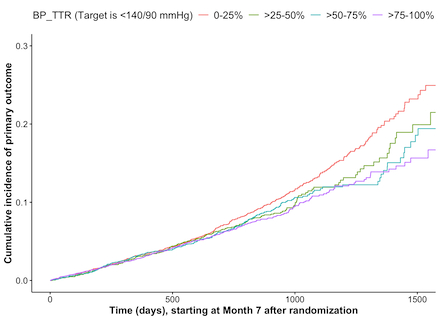
Results: A total of 12,952 eligible participants were included (mean±SD age, 66.1±9.6 years; 48.6% men). Among four BP-TTR groups (0–25%, >25–50%, >50–75%, and >75–100%), individuals with a BP-TTR of >75–100% had the lowest incidence rate of the primary outcome (35.2 per 1,000 person-years). Compared to individuals in the lowest BP-TTR group, those in higher BP-TTR groups had a reduced risk of the primary outcome in both unadjusted and adjusted models. However, statistically significant reductions were observed only in the unadjusted model for the BP-TTR >50–75% group (hazard ratio [95% CI], 0.84 [0.71-0.99]; p=0.036), and the BP-TTR >75–100% group (0.79 [0.69-0.92]; p=0.002).
Conclusions: In patients with HTN+CAD, higher BP-TTR at the target of <140/90 mmHg may be associated with a reduced risk of the composite outcome of all-cause mortality, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and nonfatal stroke, though statistical significance was not reached after adjustment. As a next step, we plan to conduct additional analyses applying alternative BP targets and assessing other outcomes in the INVEST.
Research Question: Is higher BP-TTR over a 6-month period associated with a reduced risk of primary cardiovascular outcome (composite all-cause mortality, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke) among patients with HTN+CAD?
Methods: In this post-hoc analysis of the randomized INternational VErapamil-trandolapril STudy (INVEST), we pooled patients (aged ≥50 years with HTN+CAD) randomized to a calcium antagonist or non-calcium antagonist strategy, which had equivalent outcomes in INVEST. Of 22,576 INVEST participants, we identified those with ≥4 BP readings, and without the primary outcome or loss to follow-up within the first 6 months post-randomization (including randomization date). We performed linear interpolation with constant extrapolation using eligible participants’ BP readings during this 6-month period (168 days) to estimate BP-TTR, defined as the proportion of days with BP readings below the target (140/90 mmHg) over the 168-day window. Cox proportional hazards regression was used to examine the association between BP-TTR in the first 6 months post-randomization and the primary outcome thereafter.
Results: A total of 12,952 eligible participants were included (mean±SD age, 66.1±9.6 years; 48.6% men). Among four BP-TTR groups (0–25%, >25–50%, >50–75%, and >75–100%), individuals with a BP-TTR of >75–100% had the lowest incidence rate of the primary outcome (35.2 per 1,000 person-years). Compared to individuals in the lowest BP-TTR group, those in higher BP-TTR groups had a reduced risk of the primary outcome in both unadjusted and adjusted models. However, statistically significant reductions were observed only in the unadjusted model for the BP-TTR >50–75% group (hazard ratio [95% CI], 0.84 [0.71-0.99]; p=0.036), and the BP-TTR >75–100% group (0.79 [0.69-0.92]; p=0.002).
Conclusions: In patients with HTN+CAD, higher BP-TTR at the target of <140/90 mmHg may be associated with a reduced risk of the composite outcome of all-cause mortality, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and nonfatal stroke, though statistical significance was not reached after adjustment. As a next step, we plan to conduct additional analyses applying alternative BP targets and assessing other outcomes in the INVEST.
More abstracts on this topic:
25-Year Decline in Aortic Aneurysm and Dissection Mortality in the U.S.: Impact of Endovascular Repair and Forecast to 2030
Ali Manzer, Umar Haddaya, Nazir Tahira, Nizam Muhammad, Steafo Lark, Sharif Ayesha, Jehangir Hanzala, Arham Muhammad, Hamza Anfal, Hassan Arbaz, Amjad Ans, Ali Iman, Zuha Zuha
A pilot study of an intervention for self-management of blood pressure among refugees fleeing war and resettled in the United StatesBehnam Rawnaq, Godino Job, Celis Deisy, Anderson Cheryl, Al-rousan Tala