Final ID: MDP1071
Dual Trajectories of Allopurinol and Colchicine Use and Cardiovascular Outcomes among Older Adults
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Several anti-inflammatory and urate-lowering drugs commonly used in gout have shown promise in reducing cardiovascular risk. However, there remains controversy regarding the benefits of concomitant allopurinol and colchicine in cardiovascular risk prevention, and many previous studies have failed to account for time-varying dose and duration of use for both medications. Thus, we aimed to 1) examine dual trajectories of allopurinol-colchicine use and 2) evaluate risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) according to trajectories.
Methods: Using 2011-2020 Medicare claims, we identified new users of allopurinol. We defined the date of first allopurinol fill as the index date and required continuous enrollment in Medicare Parts A. B, and D for 12 months before and after index date Then, we used group-based multi-trajectory modeling to identify allopurinol and colchicine use patterns by calculating average daily dose for each medication separately during each 2-week period during the first 12 months of allopurinol use. We then constructed inverse probability of treatment weighted Cox survival models to compare time-to-incident MACE across trajectories.
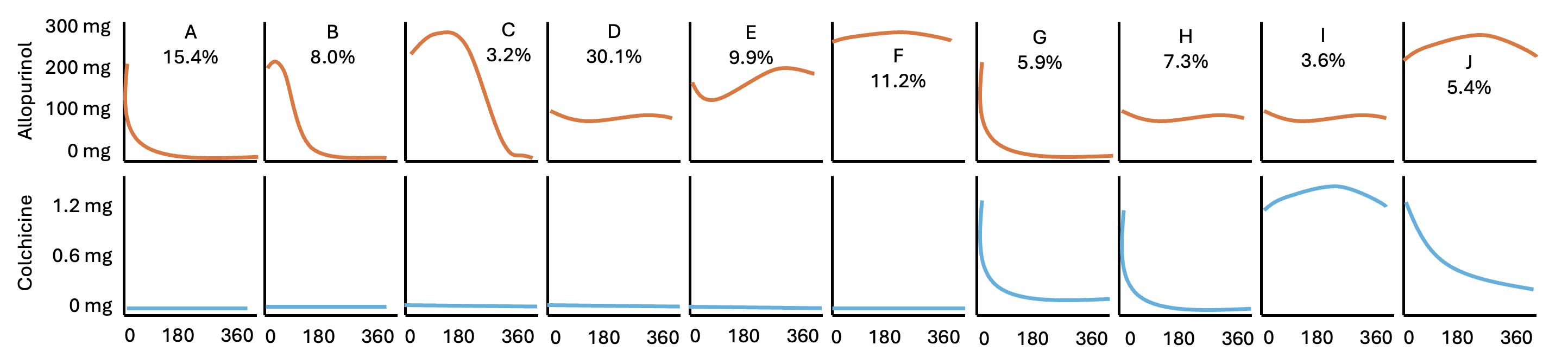
Results: We identified 59,429 beneficiaries (mean age: 73.9; 82.6% non-Hispanic white) and ten unique trajectories including: six trajectories with no colchicine use (Trajectory A-F) and four trajectories with colchicine use (Trajectory G-J). Compared to Trajectory A (rapidly decreasing allopurinol - no colchicine), we observed a lower risk for MACE among Trajectories E (~200 mg allopurinol - no colchicine; aHR: 0.89 [95% CI: 0.87-0.92), F (~300 mg allopurinol - no colchicine; aHR: 0.91 [95% CI: 0.89-0.94]), I (~100 mg allopurinol - ~1.2 mg colchine [stable]; aHR: 0.96 [95% CI: 0.93-0.99]), and J (~300 mg allopurinol - gradually decreasing colchicine; aHR: 0.88 [95% CI: 0.85-0.91]).
Conclusions: These findings suggest that older adults may benefit from interventions aimed at optimizing dose and duration of allopurinol and colchcine when initiating allopurinol among older adults and further support the need for additional research on the role of concomitant allopurinol and colchicine in cardiovascular risk prevention.
Methods: Using 2011-2020 Medicare claims, we identified new users of allopurinol. We defined the date of first allopurinol fill as the index date and required continuous enrollment in Medicare Parts A. B, and D for 12 months before and after index date Then, we used group-based multi-trajectory modeling to identify allopurinol and colchicine use patterns by calculating average daily dose for each medication separately during each 2-week period during the first 12 months of allopurinol use. We then constructed inverse probability of treatment weighted Cox survival models to compare time-to-incident MACE across trajectories.
Results: We identified 59,429 beneficiaries (mean age: 73.9; 82.6% non-Hispanic white) and ten unique trajectories including: six trajectories with no colchicine use (Trajectory A-F) and four trajectories with colchicine use (Trajectory G-J). Compared to Trajectory A (rapidly decreasing allopurinol - no colchicine), we observed a lower risk for MACE among Trajectories E (~200 mg allopurinol - no colchicine; aHR: 0.89 [95% CI: 0.87-0.92), F (~300 mg allopurinol - no colchicine; aHR: 0.91 [95% CI: 0.89-0.94]), I (~100 mg allopurinol - ~1.2 mg colchine [stable]; aHR: 0.96 [95% CI: 0.93-0.99]), and J (~300 mg allopurinol - gradually decreasing colchicine; aHR: 0.88 [95% CI: 0.85-0.91]).
Conclusions: These findings suggest that older adults may benefit from interventions aimed at optimizing dose and duration of allopurinol and colchcine when initiating allopurinol among older adults and further support the need for additional research on the role of concomitant allopurinol and colchicine in cardiovascular risk prevention.
More abstracts on this topic:
Activated CD8+HLA-DR+ T Cells as Immune Biomarkers of Metabolic Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Risk in Prediabetes
Alrashed Fatema, Alsaeed Halemah, Alturaiki Wael, Akhter Nadeem, Alosaimi Bandar, Almutairi Saeedah, Mubarak Ayman, Al-mulla Fahd, Ahmad Rasheed
Accelerometer-derived physical activity, long-term exposure to ambient PM2.5 and risk of cardiovascular disease mortalityYuan Sheng, Lin Zhangyu, Song Yanjun, Dou Kefei