Final ID: MP2150
Correlates of Nocturnal Hypertension in a Real-World Cohort
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Nocturnal hypertension (NH) is associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes beyond and independent of daytime hypertension (DH). Although cohort studies have evaluated demographic and clinical correlates of NH, there is comparably less data available from real-world clinical practice and for population subsets that tend to be underrepresented in cohort studies.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included all patients who underwent ABPM testing at a large academic medical center from 2013-2023. We extracted electronic health record data on demographic characteristics and comorbidities documented via ICD-10 coding at the time of testing. We classified DH as a mean daytime systolic BP ≥130 mmHg or diastolic BP ≥80 mmHg, and NH as a mean evening systolic BP ≥110 mmHg or diastolic BP ≥65 mmHg. Isolated NH was defined as presence of NH with normal daytime BP. We used multivariable-adjusted logistic regression to assess DH as a correlate of NH, covariates related to the co-occurrence of DH and NH, and correlates of isolated NH.
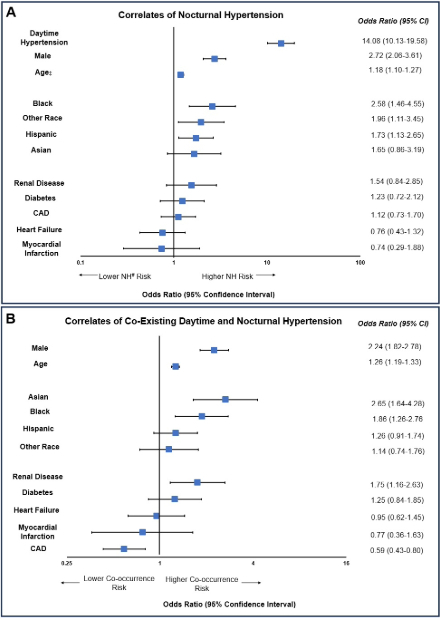
Results: A total of 1566 patients were included. In non-mutually exclusive groups, there were 812 (51.9%) patients with DH, 1125 (71.8%) with NH, and 363 (23.2%) with isolated NH; seventy-one (80.7%) Asian patients, 104 (83.2%) Black patients, and 148 (75.9%) Hispanic patients had NH. A total of 762 (48.7%) patients had co-occurrent DH and NH, and 93.8% of patients with DH also had NH. In multivariable analysis, significant correlates of NH included DH, male sex, age, Black race, and Hispanic race. By comparison, significant correlates of co-occurrent DH and NH included male sex, age, Asian race, Black race, and renal disease; coronary artery disease was inversely associated with this co-occurrence. Among all covariates, only coronary artery disease was associated with isolated NH.
Conclusion: In a real-world cohort of patients who underwent ABPM, over 90% of patients with DH had co-occurrence of DH with NH, and DH was the strongest predictor of NH. Nearly a quarter of patients also had isolated NH. Our study results highlight the generally underrecognized prominence of isolated NH, as well as the presence of NH among Hispanic and Asian-American populations, which has been underrecognized in less representative cohort analyses. Further prospective investigations are needed to evaluate whether broader screening for NH is needed for populations at risk, including but not limited to those with more easily identified DH.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included all patients who underwent ABPM testing at a large academic medical center from 2013-2023. We extracted electronic health record data on demographic characteristics and comorbidities documented via ICD-10 coding at the time of testing. We classified DH as a mean daytime systolic BP ≥130 mmHg or diastolic BP ≥80 mmHg, and NH as a mean evening systolic BP ≥110 mmHg or diastolic BP ≥65 mmHg. Isolated NH was defined as presence of NH with normal daytime BP. We used multivariable-adjusted logistic regression to assess DH as a correlate of NH, covariates related to the co-occurrence of DH and NH, and correlates of isolated NH.
Results: A total of 1566 patients were included. In non-mutually exclusive groups, there were 812 (51.9%) patients with DH, 1125 (71.8%) with NH, and 363 (23.2%) with isolated NH; seventy-one (80.7%) Asian patients, 104 (83.2%) Black patients, and 148 (75.9%) Hispanic patients had NH. A total of 762 (48.7%) patients had co-occurrent DH and NH, and 93.8% of patients with DH also had NH. In multivariable analysis, significant correlates of NH included DH, male sex, age, Black race, and Hispanic race. By comparison, significant correlates of co-occurrent DH and NH included male sex, age, Asian race, Black race, and renal disease; coronary artery disease was inversely associated with this co-occurrence. Among all covariates, only coronary artery disease was associated with isolated NH.
Conclusion: In a real-world cohort of patients who underwent ABPM, over 90% of patients with DH had co-occurrence of DH with NH, and DH was the strongest predictor of NH. Nearly a quarter of patients also had isolated NH. Our study results highlight the generally underrecognized prominence of isolated NH, as well as the presence of NH among Hispanic and Asian-American populations, which has been underrecognized in less representative cohort analyses. Further prospective investigations are needed to evaluate whether broader screening for NH is needed for populations at risk, including but not limited to those with more easily identified DH.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adaptive Cardiac Arrest Training Curriculum for Capacity Building in Northern Ghana: Addressing Contextual Challenges for Sustainability
Ahadzi Dzifa, Boateng Laud, Hernandez Odalys Rivera, Akanbong Prosper, Leung Claudia, Al-hassan Rahma, Baba Yabasin Iddrisu, Yakubu Abdul-subulr, Cournooh Annette, Ikeda Scott, Alomatu Samuel, Sakeah Patience
Active Screening in Black, Hispanic/LatinX, Asian/Pacific Islander, and Native American Individuals Reduces Racial Disparities in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm DiagnosisMiner Grace, Govindarajulu Usha, Smolock Christopher, Faries Peter, Marin Michael