Final ID: MP1957
Targeted IL-1 Inhibition in Coxsackievirus-Induced Incessant Pericarditis: An Immunotherapy Approach
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Case Presentation: A previously healthy 33-year-old woman developed acute pericarditis with early tamponade physiology following a Coxsackievirus B infection contracted from her child. Despite urgent pericardiocentesis (550 mL) and standard anti-inflammatory therapy with NSAIDs and colchicine, she progressed to incessant pericarditis necessitating corticosteroids.
Clinical Course and Timeline:
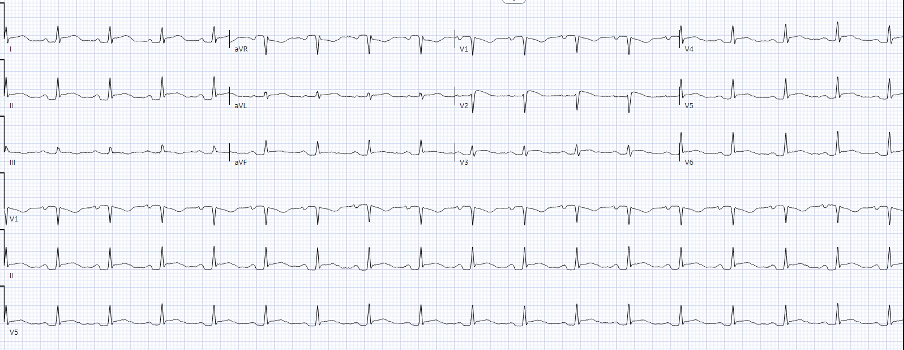
Day 1: Initial presentation with tamponade physiology; Coxsackie B serology positive
Days 9–10: Escalating NSAID therapy failed to control symptoms
Week 2: Prednisone (30 mg/day) initiated with temporary symptom relief
Week 3: Relapse during taper, resulting in rehospitalization
Week 7: Recurrence despite slow taper to prednisone 5 mg
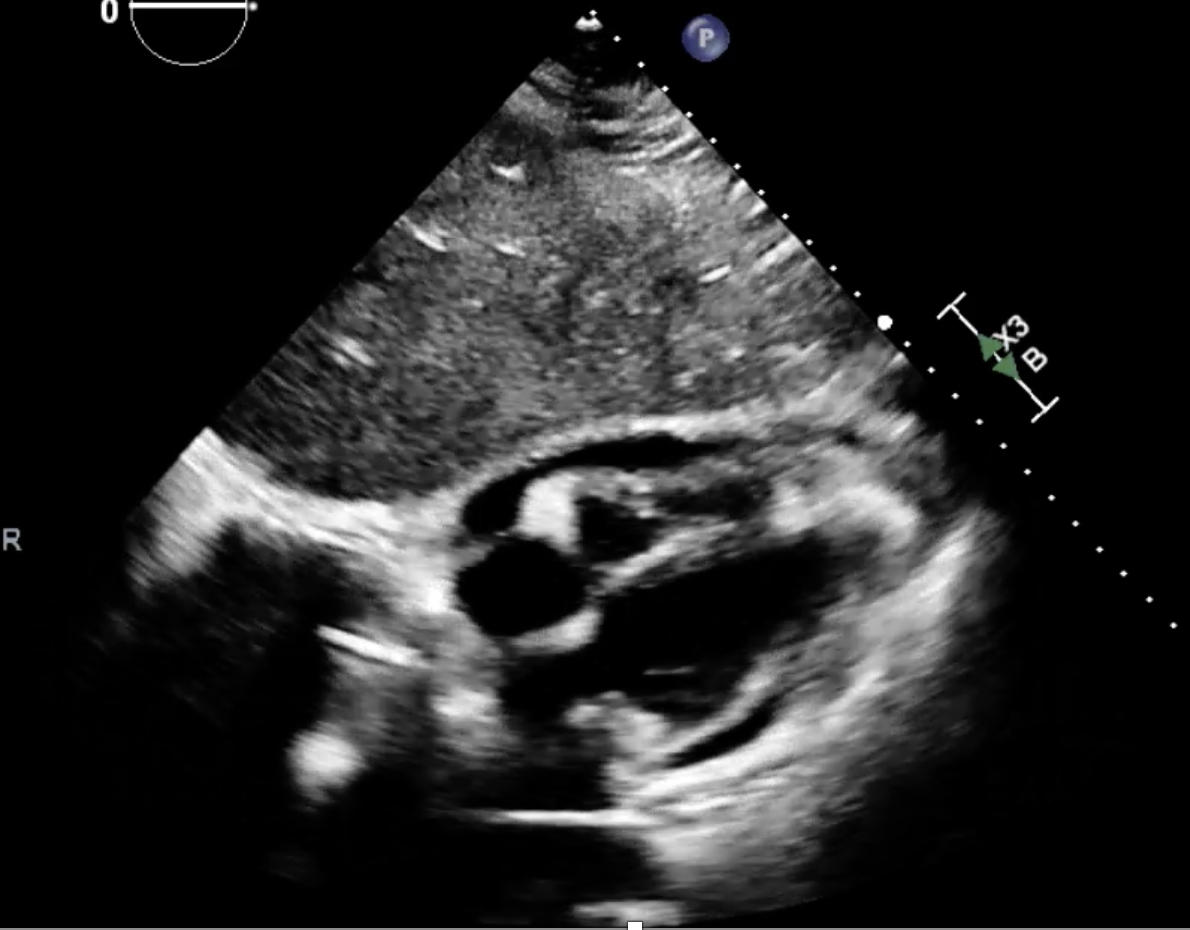
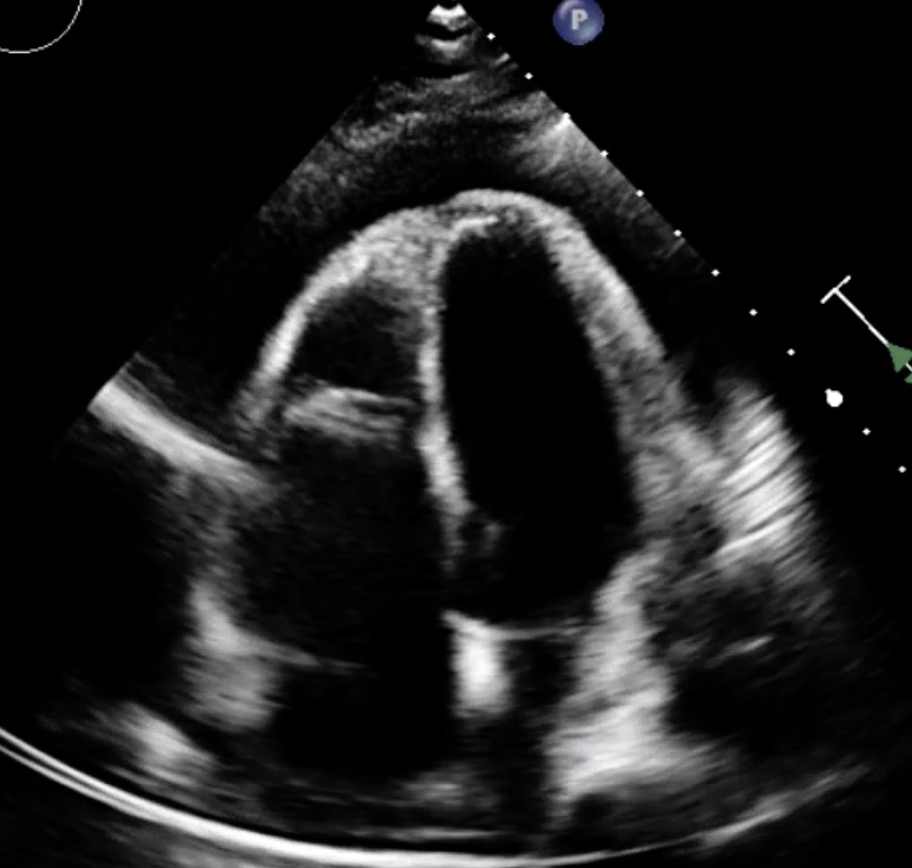
Rilonacept was initiated at week 7 due to persistent steroid dependence. Within 4–6 weeks, the patient achieved complete clinical remission, normalization of inflammatory markers, and resolution of echocardiographic abnormalities. Corticosteroids were successfully discontinued over a 3-month taper while maintaining remission on rilonacept at 21-week follow-up.
Discussion: This case underscores the pathophysiological relevance of IL-1β in viral pericarditis. Coxsackievirus infection induces myocardial inflammation via IL-1–mediated cytokine cascades. Traditional steroid dependence—affecting 15-30% of pericarditis patients—represents a major therapeutic challenge with significant morbidity. By acting as a soluble decoy receptor, rilonacept interrupts this pathway, offering a targeted therapeutic strategy beyond traditional broad-spectrum immunosuppression.
Key Insights:
1. IL-1–mediated inflammation was a critical driver in disease persistence
2. Steroid dependence emerged despite optimal guideline-directed therapy
3. Rilonacept enabled sustained steroid-free remission
Clinical Significance: IL-1 inhibition with rilonacept represents a paradigm shift in managing steroid-refractory pericarditis, especially in virally mediated cases. This case supports the growing role of biologics in cardiac inflammation and raises important questions about earlier IL-1 blockade to preempt steroid dependence.
Conclusion: This case illustrates the efficacy of IL-1–targeted therapy in a complex, steroid-dependent pericarditis case and advocates for broader clinical consideration of rilonacept in viral pericarditis. Further investigation is warranted to define optimal timing and patient selection for IL-1 blockade in this setting.
Clinical Course and Timeline:
Day 1: Initial presentation with tamponade physiology; Coxsackie B serology positive
Days 9–10: Escalating NSAID therapy failed to control symptoms
Week 2: Prednisone (30 mg/day) initiated with temporary symptom relief
Week 3: Relapse during taper, resulting in rehospitalization
Week 7: Recurrence despite slow taper to prednisone 5 mg
Rilonacept was initiated at week 7 due to persistent steroid dependence. Within 4–6 weeks, the patient achieved complete clinical remission, normalization of inflammatory markers, and resolution of echocardiographic abnormalities. Corticosteroids were successfully discontinued over a 3-month taper while maintaining remission on rilonacept at 21-week follow-up.
Discussion: This case underscores the pathophysiological relevance of IL-1β in viral pericarditis. Coxsackievirus infection induces myocardial inflammation via IL-1–mediated cytokine cascades. Traditional steroid dependence—affecting 15-30% of pericarditis patients—represents a major therapeutic challenge with significant morbidity. By acting as a soluble decoy receptor, rilonacept interrupts this pathway, offering a targeted therapeutic strategy beyond traditional broad-spectrum immunosuppression.
Key Insights:
1. IL-1–mediated inflammation was a critical driver in disease persistence
2. Steroid dependence emerged despite optimal guideline-directed therapy
3. Rilonacept enabled sustained steroid-free remission
Clinical Significance: IL-1 inhibition with rilonacept represents a paradigm shift in managing steroid-refractory pericarditis, especially in virally mediated cases. This case supports the growing role of biologics in cardiac inflammation and raises important questions about earlier IL-1 blockade to preempt steroid dependence.
Conclusion: This case illustrates the efficacy of IL-1–targeted therapy in a complex, steroid-dependent pericarditis case and advocates for broader clinical consideration of rilonacept in viral pericarditis. Further investigation is warranted to define optimal timing and patient selection for IL-1 blockade in this setting.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Multicenter Study of Detection of Pulmonary Hypertension Based on Point-of-Care 12- Lead ECG Data
Dubrock Hilary, Wieczorek Mikolaj, Hackett Sarah, Alger Heather, Carlson Katherine, Klugherz Paul, Carter Rickey, Wagner Tyler, Johnson Patrick, Frantz Robert, Strom Jordan, Waks Jonathan, Agarwal Richa, Hemnes Anna, Steinberg Benjamin, Pandey Ambarish
A Case Report of Cardiac Tamponade due to Mycoplasma Pneumoniae-induced Pericarditis - A Rare Complication of a Commonly seen Bacterial InfectionPatel Vidhi, Maharjan Reeju, Okan Tetyana, Singh Bhupinder, Colasacco Joseph